-
Review
-
Research trends on water-related natural disasters and vulnerability of people with disabilities: A bibliometric analysis
서지자료 분석을 통한 수재해와 장애인 취약성 관련 국제 연구동향
-
Woo, HyoseopㆍWoo, SeokkyunㆍKim, Sang Yong
우효섭, 우석균, 김상용
- People with disabilities (PWD) are often at greater risk during natural disasters compared to the general population. Nevertheless, domestic research examining the …
자연재해 발생 시 장애인은 비장애인에 비해 더 큰 위험에 처할 수 있다. 그러나 국내에서 자연재해 발생시 장애인 취약성을 상호 연관하여 연구한 사례는 …
- People with disabilities (PWD) are often at greater risk during natural disasters compared to the general population. Nevertheless, domestic research examining the relationship between disaster occurrence and the vulnerability of PWD remains scarce. To address this gap, this study conducted a scoping review using bibliometric analysis based on literature retrieved from the Web of Science platform, focusing on the relations between natural disasters—particularly water-related disasters—and the vulnerability of PWD. The analysis identified only 184 relevant scientific journal articles published between the 1990s and 2025 worldwide. Research output has increased rapidly since the mid-2000s and is expected to continue growing into the 2020s and beyond. Approximately 30% of recent studies originate from Asian countries, notably Japan and China. Floods are the most prevalent disaster type examined, followed by hurricanes, droughts, cyclones, and tsunamis. However, studies explicitly addressing disaster impacts by disability type remain very limited. Japan exhibits a relatively advanced level of research in disability-inclusive disaster risk reduction, whereas China tends to address disability indirectly, often through indicators such as ageing or chronic illness. In contrast, research in Korea remains extremely limited. Finally, climate change emerges as one of the most frequent author keywords, indicating growing concern over its dual effect: exacerbating vulnerability among socially disadvantaged groups, including PWD, and intensifying water-related hazards such as floods.
- COLLAPSE
자연재해 발생 시 장애인은 비장애인에 비해 더 큰 위험에 처할 수 있다. 그러나 국내에서 자연재해 발생시 장애인 취약성을 상호 연관하여 연구한 사례는 드물다. 본 연구는 이러한 점에 착안하여 Web of Science 플랫폼 자료를 기반으로 주제범위 문헌고찰 방식(scoping review)으로 컴퓨터에 의한 서지분석(bibliometric analysis) 기법을 이용하여 자연재해 중 특히 수재해와 장애인 취약성 간 관계 연구동향을 고찰하였다. 1990년대 이후 2025년까지 과학기술 분야 논문 중 이 분야는 세계적으로 단 184편 수준이다. 이 중 최근 들어 일본, 중국 등 아시아지역에서 전체 연구의 30% 내외를 차지하였다. 이 분야 연구는 2000년대 중반 이후 급속히 증가하고 있으며, 이러한 추세는 2020년대 이후에도 계속될 전망이다. 수재해 유형 별 이 분야 연구자들의 최대 관심은 예상대로 홍수이며, 그다음 허리케인, 가뭄, 사이클론, 쓰나미 순이다. 그러나, 장애 유형별 수재해 관련 연구는 매우 미흡하다. 일본은 장애포괄적 재해위험 경감 분야에서 상당한 연구수준을 보여주는 반면, 중국은 장애를 노령 또는 만성질환 지표를 통한 간접적 형태로 다루는 경향이 있다. 한국의 관련 연구는 매우 제한적이다. 마지막으로, 저자들의 핵심용어만을 대상으로 빈번하게 출현하는 용어 중 하나는 기후변화이며, 이는 기후변화가 단지 기온의 상승, 저하 등에 의해 사회적 약자인 장애인에 부정적 영향을 주는 동시에 홍수 등 수재해에 직접적 영향을 준다는 점을 시사한다.
-
Research trends on water-related natural disasters and vulnerability of people with disabilities: A bibliometric analysis
-
Research Article
-
Development of a decision support framework for enhancing the design performance of urban underground infrastructure
도시 지하인프라의 설계 성능 향상을 위한 시나리오기반 의사결정 지원 프레임워크 개발
-
Choi, Young HwanㆍSung, Seung MinㆍKwon, Hui GeunㆍKim, Teagyun
최영환, 성승민, 권희근, 김태균
- With the increased frequency and intensity of extreme rainfall due to climate change, the limitations of conventional urban drainage systems have become …
기후변화로 인해 도시에서 극한 강우 발생 빈도가 증가함에 따라, 기존 배수체계의 한계를 보완하기 위한 대심도 지하 인프라 구축 필요성이 부각되고 있다. 본 …
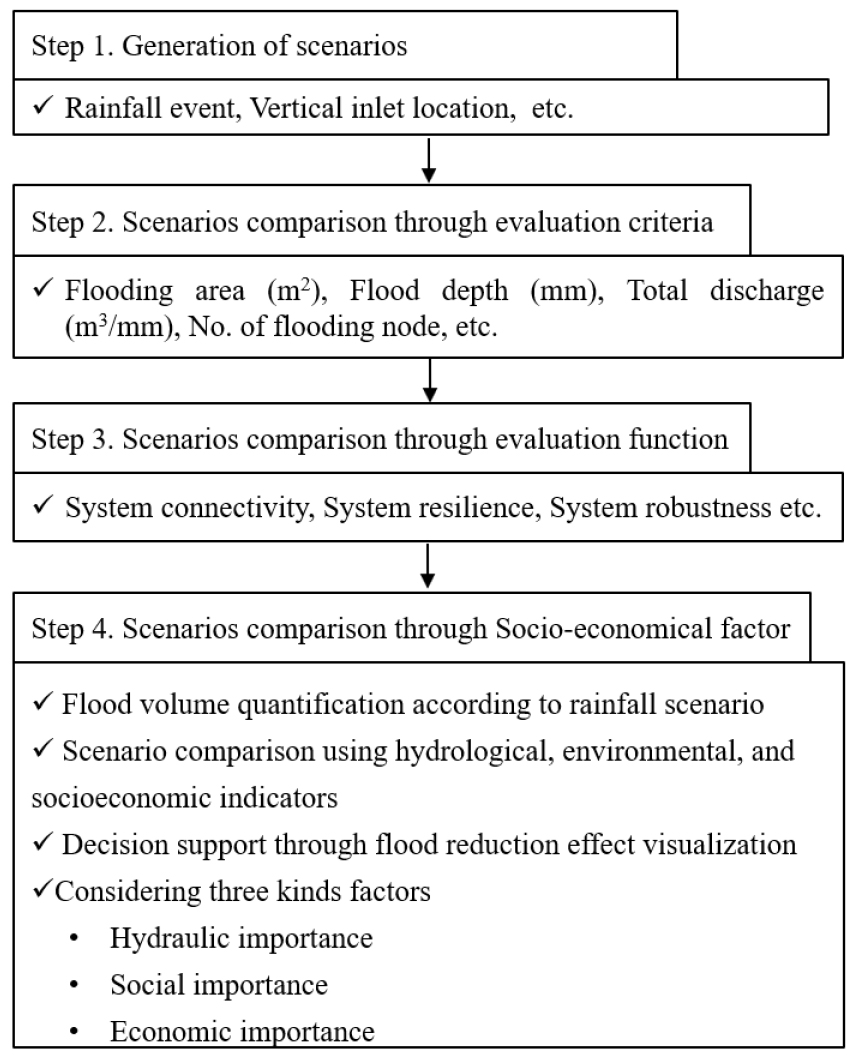
- With the increased frequency and intensity of extreme rainfall due to climate change, the limitations of conventional urban drainage systems have become evident. In response, this study proposes a decision support framework for the optimal design of deep underground drainage infrastructure, including stormwater storage systems. Various scenarios were developed considering vertical inlet positions, storage capacity, and rainfall patterns. Quantitative performance indicators were derived through hydrologic-hydraulic simulations, and two evaluation functions (System Connectivity and System Resilience) were applied along with socio-economic considerations (e.g., proximity to critical infrastructure and land use) to assess each scenario. Applied to a flood-prone district in S-catchment, the analysis showed that among the combinations with four vertical inlets, Scenario S3076 emerged as the optimal solution when socio-economic indicators were taken into account. This confirms that scenarios with similar hydraulic performance can be prioritized differently depending on social vulnerability and protection of critical infrastructure. This study presents a practical decision-making framework that integrates quantitative and qualitative evaluation for deep underground infrastructure planning in urban flood management. The proposed approach can be further generalized through inclusion of additional components and expansion to diverse urban networks.
- COLLAPSE
기후변화로 인해 도시에서 극한 강우 발생 빈도가 증가함에 따라, 기존 배수체계의 한계를 보완하기 위한 대심도 지하 인프라 구축 필요성이 부각되고 있다. 본 연구에서는 대심도 저류시설 설계를 위한 의사결정 지원 프레임워크를 제안하고, 수직 유입구 조합, 저장 용량, 강우 패턴 등을 고려한 다양한 시나리오를 구성한 후 수리·수문학적 해석을 통해 정량적 성능 지표를 산출하였다. 이후 평가함수(System Connectivity, Resilience)와 사회·경제적 요소(중요 시설 위치, 토지 이용 등)를 종합적으로 반영하여 시나리오 간 상대적 가치 평가를 수행하였다. S-catchment 지역을 사례로 적용한 결과, 수직 유입구가 4개인 조합 중 사회·경제적 지표가 우수한 시나리오가 최적 설계안으로 선정되었다. 특히 동일한 수리 성능을 가지는 시나리오 간에도 사회적 피해 가능성과 중요 시설 보호 여부에 따라 평가 순위가 달라질 수 있음을 확인하였다. 본 연구는 극한 강우 대응을 위한 도시 지하 인프라 설계에서 정량적·정성적 요소를 통합한 실질적 의사결정 프레임워크를 제시하였다. 향후 다양한 시설 요소와 네트워크를 대상으로 한 확장적 적용과 평가지표의 다원화를 통해 본 기법의 일반화 가능성을 제시할 수 있을 것으로 판단된다.
-
Development of a decision support framework for enhancing the design performance of urban underground infrastructure
-
Research Article
-
A study on the prediction of comprehensive performance grade using a bayesian model based on key variables of estuary barrage
하구둑 주요 변수 기반 베이지안 모델을 활용한 종합성능등급 예측에 관한 연구
-
Oh, Won-JoonㆍCho, Choong-YeunㆍLee, Young-Jun
오원준, 조중연, 이용준
- Estuary barrages are critical water infrastructure facilities exposed to complex external loads such as upstream flooding and tidal backflow. Given that failures …
하구둑은 홍수 유입과 조석 역류 등 복합적인 외력에 노출되는 핵심 수자원시설로, 사고 발생 시 광범위한 침수·기능 마비로 이어질 수 있어 정량적 성능 …
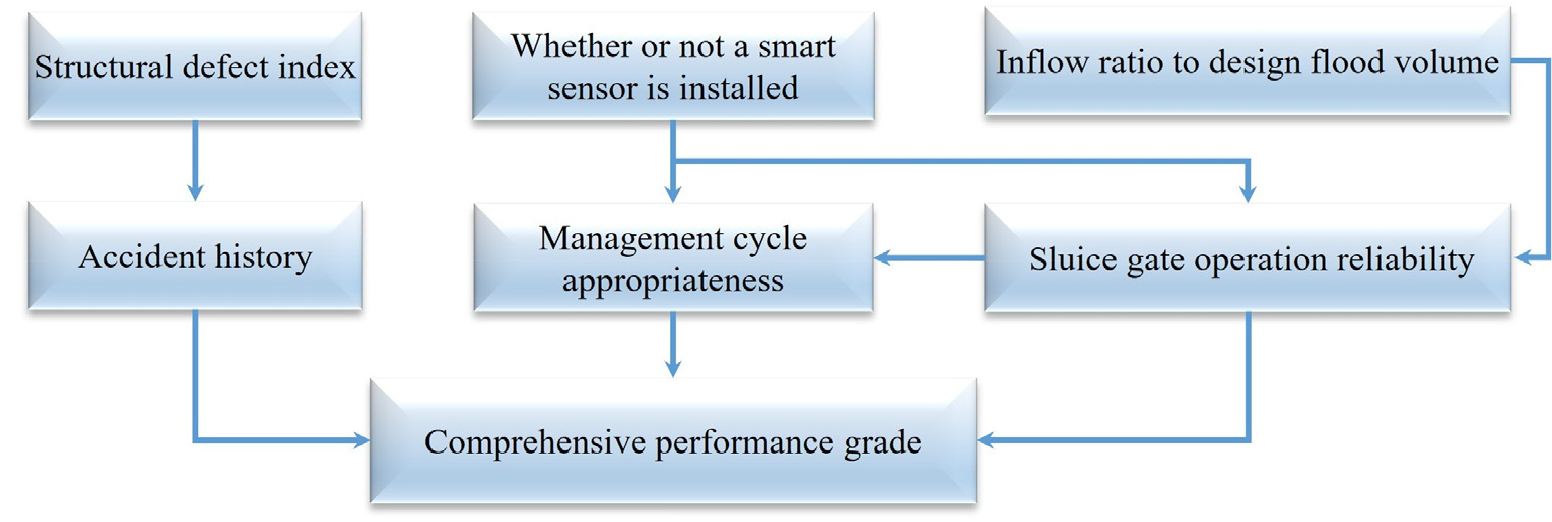
- Estuary barrages are critical water infrastructure facilities exposed to complex external loads such as upstream flooding and tidal backflow. Given that failures may result in large-scale inundation and the disruption of essential functions, the development of a quantitative performance prediction model is essential. This study proposes a Bayesian Network–based performance assessment model to quantitatively predict the comprehensive performance grade of estuary barrages. Six key variables representing structural, operational, and environmental factors were selected, and their causal relationships were represented in a DAG. A total of 148 performance assessment cases were collected and divided into a training set (118 cases) and a validation set (30 cases) to derive CPT based on empirical data. The validation results indicated that the proposed model shows satisfactory predictive performance, with an accuracy of 0.867 and a macro F1-score of 0.883. In particular, the model achieved a balanced and stable prediction for grades B and C, and misclassifications were limited mainly to adjacent grades in the confusion matrix analysis. Nevertheless, the proposed Bayesian model can serve as a practical decision-support tool for predicting performance degradation in estuary barrages, and its predictive capability could be further improved by incorporating time-series data and additional performance grade cases in future studies.
- COLLAPSE
하구둑은 홍수 유입과 조석 역류 등 복합적인 외력에 노출되는 핵심 수자원시설로, 사고 발생 시 광범위한 침수·기능 마비로 이어질 수 있어 정량적 성능 예측을 지원할 수 있는 모델 개발이 필수적이다. 본 연구는 하구둑의 종합성능등급을 정량적으로 예측하기 위하여 베이지안 네트워크 기반 성능평가 모델을 제안하였다. 기존 점수 단순 합산 방식의 한계를 극복하기 위해, 구조, 운영, 환경 요소를 고려한 6개의 핵심 변수를 선정하고 각 변수 간 인과 관계를 기반으로 한 DAG 구조를 구성하였다. 148건의 성능평가 데이터를 수집하고, 학습(118건)과 검증(30건)으로 구분하여 조건부 확률 기반 CPT를 도출하였다. 검증 결과, 제안된 모델은 accuracy 0.867, macro F1 0.883 등의 우수한 성능을 나타냈으며 특히 B 및 C 등급에 대해 균형 있고 안정적인 예측 능력을 보였다. 혼동행렬 분석에서도 오 분류는 대부분 인접 등급 간에서 제한적으로 발생하였다. 종합적으로 본 모델은 하구둑의 성능 저하 위험을 사전에 예측할 수 있는 실무적 의사결정 도구로 활용될 수 있으며, 향후 시계열 데이터 및 다양한 평가등급을 반영할 경우 성능향상이 가능할 것으로 기대된다.
-
A study on the prediction of comprehensive performance grade using a bayesian model based on key variables of estuary barrage
-
Research Article
-
Evaluating the continuity of a MODIS-Based NDVI with VIIRS data
VIIRS를 활용한 MODIS 기반 NDVI의 연속 가능성 검토
-
Jang, WonjinㆍKim, JinukㆍChung, JeehunㆍLee, YonggwanㆍJang, CheolheeㆍKim, Seongjoon
장원진, 김진욱, 정지훈, 이용관, 장철희, 김성준
- Drought is a widespread hazard whose severity is increasing under climate change, making precise and continuous assessment indispensable. This study aims to …
가뭄은 기후 변화에 따라 심각도가 증대되고 있는 광범위한 재해로, 이에 대한 정밀하고 연속적인 현황 진단이 필수적이다. 본 연구는 수명 만료로 자료 중단이 …
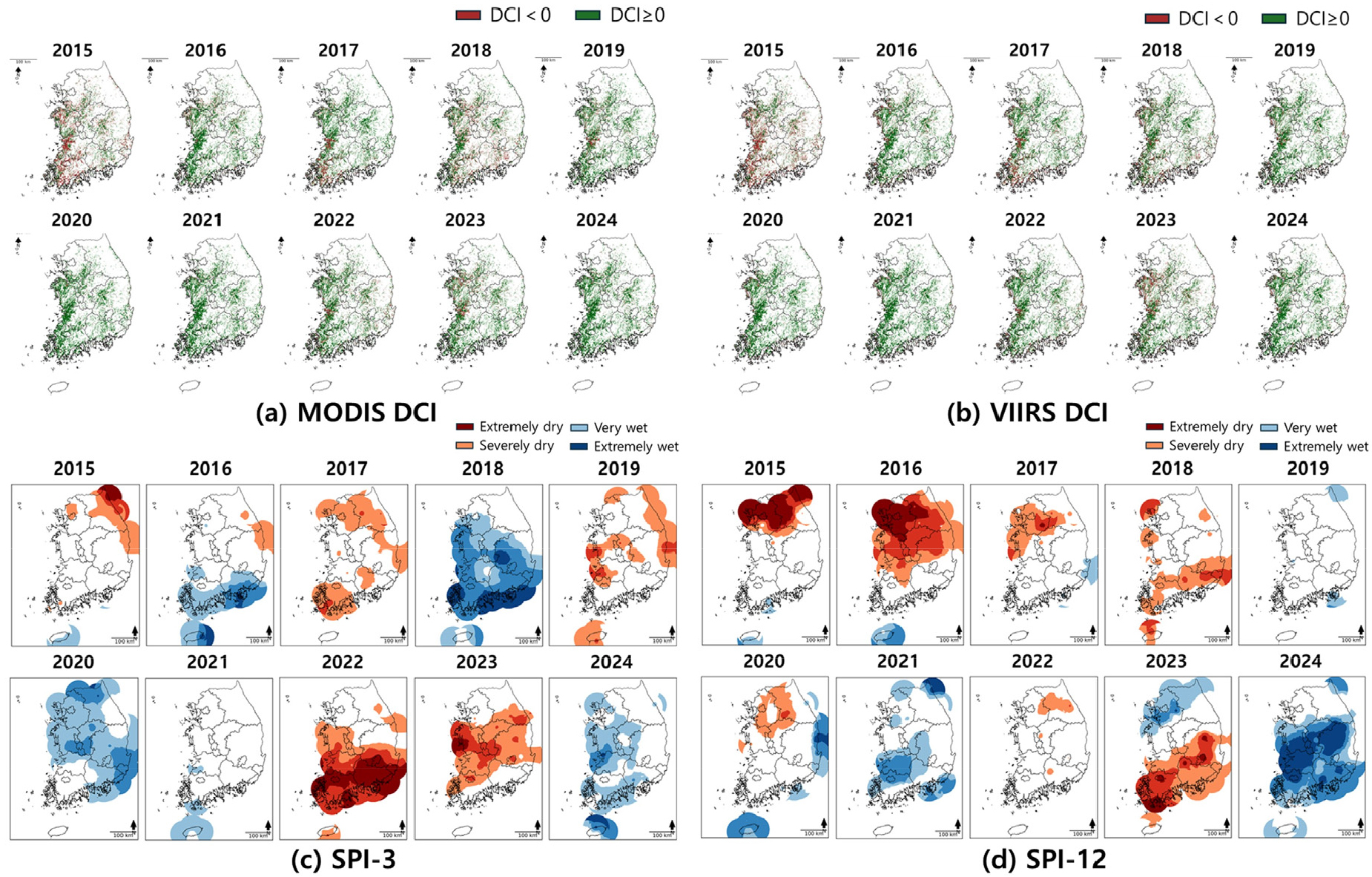
- Drought is a widespread hazard whose severity is increasing under climate change, making precise and continuous assessment indispensable. This study aims to verify the continuity of long-term records by employing the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (SNPP) Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) the successor to the MODerate resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS), whose data production is expected to cease as it reaches end-of-life and to evaluate the capability of the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) based Dry Condition Index (DCI) for assessing agricultural drought in Korean paddy areas. Using Google Earth Engine, we compiled and analyzed MODIS and VIIRS NDVI datasets for 2015-2024. VIIRS NDVI showed high consistency with MODIS, demonstrating strong each sensor compatibility; in particular, during the key agricultural drought season (February-May), the each sensor deviation was 0.008. Time series analysis of DCI confirmed that VIIRS can sustain continuous agricultural drought detection based on MODIS derived drought metrics and effectively capture the timing and progression of drought events. These findings provide an objective basis for the continued use of VIIRS as a replacement for MODIS in drought research and are expected to contribute policy-relevant information for effective drought response.
- COLLAPSE
가뭄은 기후 변화에 따라 심각도가 증대되고 있는 광범위한 재해로, 이에 대한 정밀하고 연속적인 현황 진단이 필수적이다. 본 연구는 수명 만료로 자료 중단이 예정된 MODerate resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS)의 후속 센서인 Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (SNPP)와 Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS)를 활용하여 장기 시계열 자료의 연속성을 검증하고, Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) 기반으로 산정되는 Dry Condition Index (DCI)를 활용하여 국내 논 지역에 대한 농업가뭄 평가 능력을 분석하는 것을 목표로 하였다. 연구를 위해 2015년부터 2024년까지 Google Earth Engine (GEE)을 활용하여 MODIS 및 VIIRS NDVI를 구축하고 분석을 수행하였다. 그 결과 VIIRS NDVI 자료는 MODIS 자료와 높은 상관성을 보였으며, 특히 농업가뭄 주요시기인 2월 ~ 5월에 두 센서 간 편차가 0.008로 높은 자료 호환성을 입증하였다. DCI 시계열 분석을 통해 VIIRS는 MODIS 기반 가뭄 인자를 활용한 연속적인 농업가뭄 탐지 능력을 성공적으로 검증하였으며, 가뭄 발생 시기에 가뭄의 천이 양상을 효과적으로 포착하였다. 본 연구의 결과는 MODIS를 대체하여 VIIRS 자료를 가뭄 연구에 연속적으로 활용할 수 있는 객관적인 근거를 제시하였으며, 가뭄 대응 차원에서 실효적인 정책 자료로 기여할 것으로 기대된다.
-
Evaluating the continuity of a MODIS-Based NDVI with VIIRS data
-
Research Article
-
Comparative analysis of ENSO and AO periodic influences on Korean snowfall using Wavelet coherence
웨이블릿 일치성 분석을 통한 ENSO 및 AO의 주기적 영향 비교와 한국 적설량 응답 특성
-
Lee, HyeongjooㆍChung, Gunhui
이형주, 정건희
- This study investigates the spatiotemporal coherence between snowfall in South Korea and two major climate oscillation indices—El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO, Niño 3.4 …
본 연구는 2005년부터 2024년까지의 기간 동안, 대한민국 전역의 적설량과 주요 기후 요동 지수인 엘니뇨-남방진동(ENSO, Niño 3.4 지수) 및 북극진동(AO) 간의 시공간적 파동 …
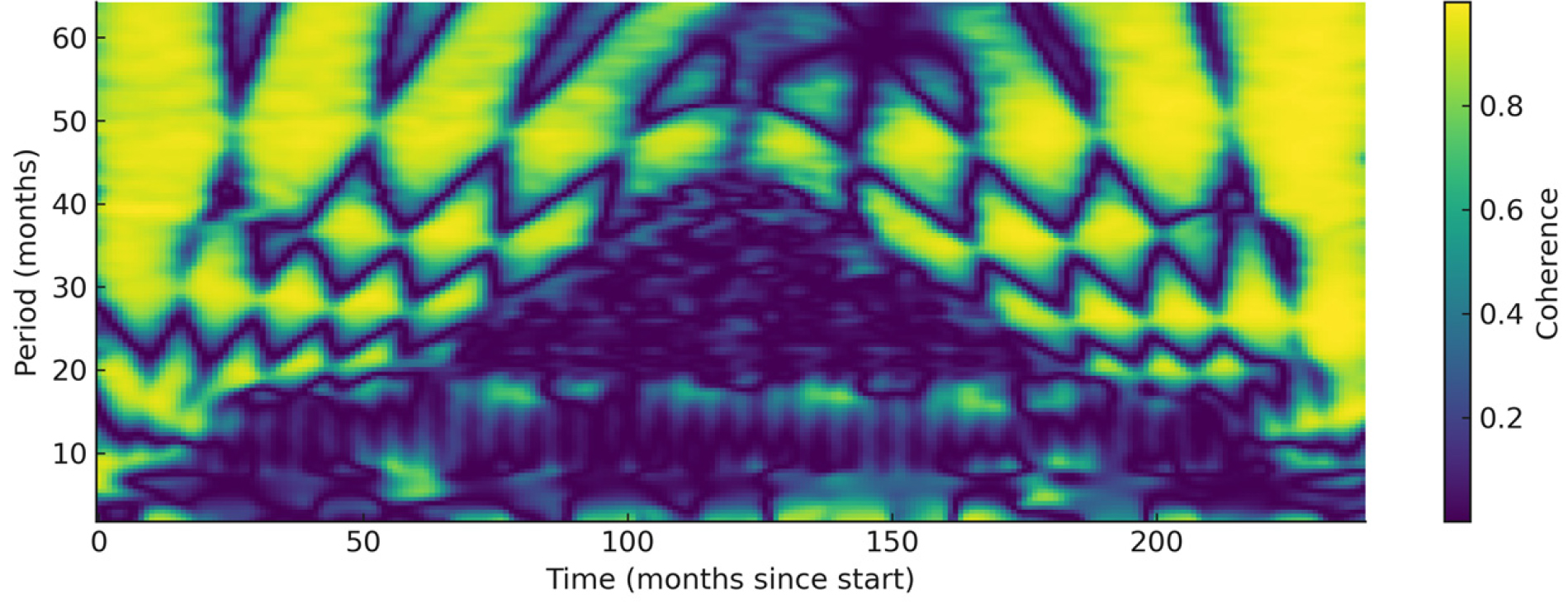
- This study investigates the spatiotemporal coherence between snowfall in South Korea and two major climate oscillation indices—El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO, Niño 3.4 index) and Arctic Oscillation (AO)—over the period from 2005 to 2024. Using daily snowfall data from nationwide ASOS stations and monthly ENSO/AO indices, wavelet transform coherence (WTC) analysis was employed to capture the frequency- and time-specific relationships between the indices and snowfall. The results indicate that ENSO exerts a persistent and long-term influence on Korean snowfall, with a peak coherence of 0.837 at a 48-month periodicity. ENSO-related episodes such as El Niño and La Niña coincide with elevated coherence and a lagging phase response from snowfall, suggesting its predictive utility. In contrast, AO demonstrated intermittent and short-term coherence patterns, peaking at a 28-month period (coherence = 0.688) but showing greater temporal variability and regional disparity. These findings highlight the contrasting dynamical roles of oceanic and atmospheric oscillations in modulating winter snowfall patterns over Korea and offer insights for improved seasonal forecasting and climate risk management strategies.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 2005년부터 2024년까지의 기간 동안, 대한민국 전역의 적설량과 주요 기후 요동 지수인 엘니뇨-남방진동(ENSO, Niño 3.4 지수) 및 북극진동(AO) 간의 시공간적 파동 일치성을 분석하였다. 전국 ASOS 관측소의 일별 적설 자료와 ENSO/AO 월별 지수를 활용하여, 시간-주파수 영역에서의 상관 구조를 파악하기 위해 연속 웨이블릿 일치성(WTC) 분석을 적용하였다. 분석 결과, ENSO는 48개월 주기에서 최대 coherence (0.837)를 기록하며, 장기적이고 구조적인 영향력을 갖는 것으로 나타났다. 특히 El Niño 및 La Niña 발생 시기에 coherence가 상승하며, 적설량의 위상 반응이 후행하는 양상이 관측되어 예측 지표로서의 가능성을 보인다. 반면 AO는 28개월 주기에서 coherence 0.688을 기록하였으나, 시간적 변동성이 크고 지역별 편차가 뚜렷한 단기적 영향 특성을 보였다. 이러한 결과는 해양성과 대기성 기후 요동이 한국 겨울철 적설 패턴에 상이한 방식으로 작용함을 보여주며, 계절 예보 정밀도 향상 및 기후 리스크 대응 전략 수립에 실질적 기여를 할 수 있다.
-
Comparative analysis of ENSO and AO periodic influences on Korean snowfall using Wavelet coherence
-
Research Article
-
Development of a water quality assessment framework using multistandard load duration curves
다수질기준 부하지속곡선을 활용한 수질평가 프레임워크 개발
-
Kim, JaehyeongㆍKim, KyungminㆍLee, JuseongㆍKim, MinahㆍKim, JinsunㆍPark, MinjiㆍJeong, Hanseok
김재형, 김경민, 이주성, 김민아, 김진선, 박민지, 정한석
- A load duration curve (LDC) illustrates the relationship between streamflow and both observed and target pollutant loads. LDCs are widely used to …
부하지속곡선은 유량에 따른 관측부하량과 목표부하량의 관계를 나타내는 곡선으로, 수질오염상태의 진단뿐만 아니라 수질관리 대책에 따른 효과 분석 및 목표 달성여부 평가에 널리 사용되고 …
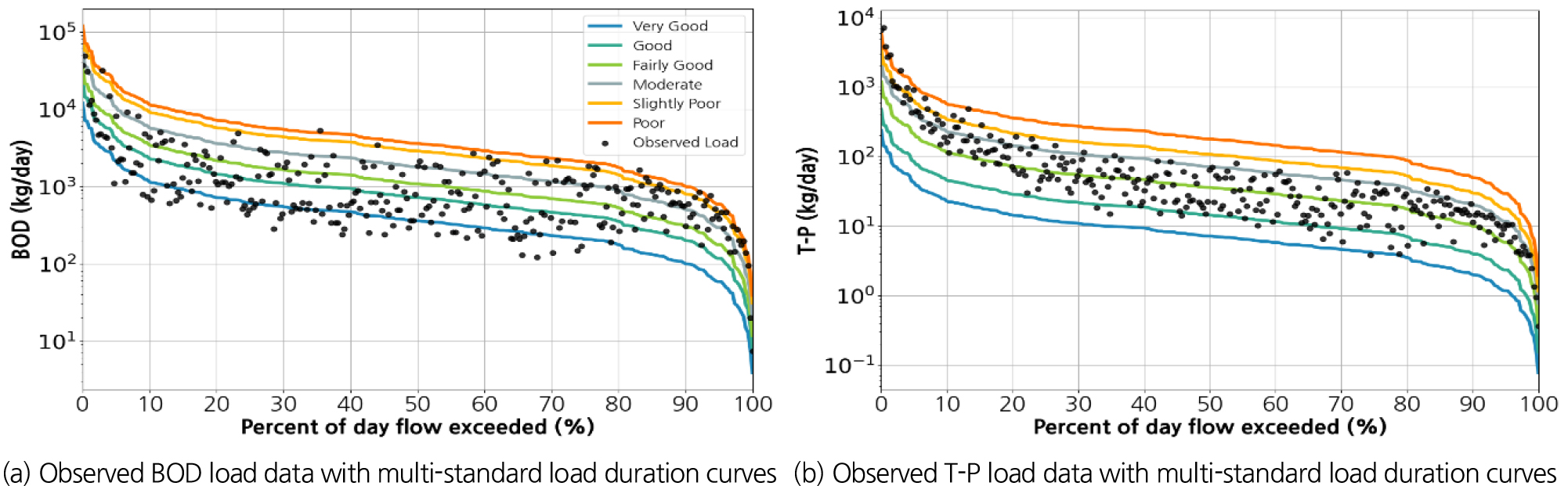
- A load duration curve (LDC) illustrates the relationship between streamflow and both observed and target pollutant loads. LDCs are widely used to diagnose water quality conditions, evaluate the effectiveness of water quality management strategies, and assess the achievement of water quality goals. In the current Total Maximum Daily Load management plan, water quality assessments are based on LDCs and exceedance rates of target water quality standards across flow regimes. However, these assessments only consider whether the standards are exceeded, without reflecting the extent of exceedance, which may lead to misinterpretations. To address this limitation, this study proposes an enhanced water quality assessment framework that incorporates multi-standard LDCs, the proportional distribution of water quality grades, and the rate of change in the proportion of “Good quality” water. We applied the framework to the Cheongmicheon in the Hangang basin to evaluate its practical applicability. The results demonstrate that multi-standard LDCs enable intuitive assessment of the distribution of observed loads across water quality grades and the degree of pollution. Additionally, analyzing the proportional distribution of water quality grades makes it possible to identify persistent occurrences of lower water quality grades, detect temporal trends in stream water quality, and characterize water quality conditions while accounting for differences across monitoring stations. Furthermore, when evaluating stream water quality across different flow regime divisions, the differences in the proportion of “Good quality” water were minimal. This study confirms that multi-standard LDCs can provide richer information than conventional LDCs and serve as a useful tool for stream water quality assessment and policy decision-making.
- COLLAPSE
부하지속곡선은 유량에 따른 관측부하량과 목표부하량의 관계를 나타내는 곡선으로, 수질오염상태의 진단뿐만 아니라 수질관리 대책에 따른 효과 분석 및 목표 달성여부 평가에 널리 사용되고 있다. 현재 오염총량관리시행계획 이행평가에 적용되는 하천 수질평가는 부하지속곡선과 유량구간별 목표수질 초과율에 기반하나 이는 수질기준 초과 여부만을 판단하며 초과 수준을 반영하지 못해 수질평가결과에 왜곡을 초래할 수 있다. 따라서 본 연구에서는 기존 수질평가 방법의 한계를 보완하기 위해, 다수질기준 부하지속곡선, 수질등급비율 그리고 ‘좋은물’ 변화율을 활용한 새로운 수질평가 프레임워크를 제안하였다. 한강 청미천 유역을 대상으로, 개발한 프레임워크를 이용한 수질평가를 실시하여 다수질기준 부하지속곡선의 실제 수질평가에의 적용가능성을 검토하였다. 그 결과, 다수질기준 부하지속곡선을 통해 관측부하량의 수질등급 분포와 오염정도를 직관적으로 확인할 수 있었다. 또한, 수질등급비율을 통해 특정 수질기준을 초과하는 수질등급비율의 지속 발생 여부와 하천 수질 변화추세를 파악할 수 있고, 지점 간 수질 차이를 고려하여 하천 수질 특성을 파악할 수 있었다. 나아가, 개선된 프레임워크를 적용하여 다양한 유량구간 구분에 따라 하천 수질을 평가한 결과, 비점오염원 분석에 유량구간 설정 방식에 따른 ‘좋은물’ 비율 차이는 미미한 것으로 나타났다. 본 연구는 다수질기준 부하지속곡선이 기존 부하지속곡선보다 하천수질 상태에 대한 보다 다양하고 유용한 정보를 제공할 수 있음을 보여주었고, 이는 다수질기준 부하지속곡선이 하천 수질평가와 정책 의사결정 과정에서 유용한 도구로 사용될 수 있음을 시사한다.
-
Development of a water quality assessment framework using multistandard load duration curves
-
Research Article
-
High-resolution soil moisture estimation using a multiple linear regression model based on remote sensing data
원격탐사 자료 기반 다중선형회귀 모형을 활용한 고해상도 토양수분 추정 기법
-
Park, HeejunㆍHwang, SeokhwanㆍKang, NaraeㆍYoon, Jungsoo
박희준, 황석환, 강나래, 윤정수
- Accurate soil moisture observation is essential for understanding hydrological processes and supporting disaster response under climate change. However, in South Korea, the …
정확한 토양수분 관측은 수문 과정 이해와 기후 변화에 따른 재해 대응에 필수적이다. 그러나 한반도 지역은 복잡한 지형과 식생 조건으로 인해 기존 위성 …
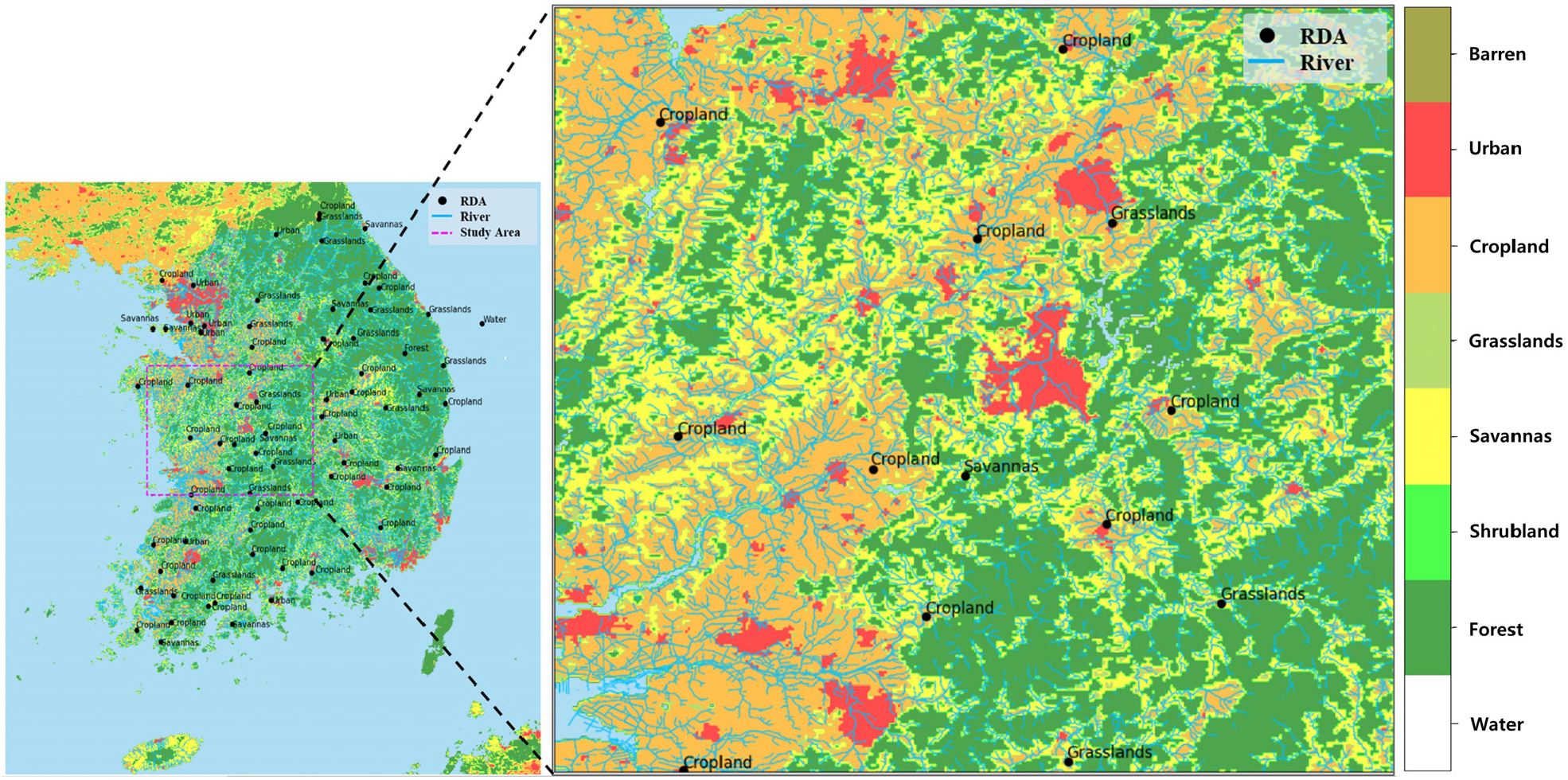
- Accurate soil moisture observation is essential for understanding hydrological processes and supporting disaster response under climate change. However, in South Korea, the complex topography and vegetation conditions limit the accuracy of satellite-based soil moisture estimation. This study, conducted from January 2020 to June 2025, aimed to produce high resolution soil moisture data using a multiple linear regression (MLR) model based on remote sensing data. Key input variables included the VV-polarized backscattering coefficient from Sentinel-1A, cumulative 1, 2, and 3day precipitation derived from Korea Meteorological Administration (KMA) radar data, and consecutive dry days. The model was validated against in situ soil moisture observations at 13 stations in the Chungcheong region provided by the Rural Development Administration (RDA), showing high performance (MAE: 2.49~10.3, R: 0.517~0.768). The model also highly reproduced soil moisture variations across different land cover types, reflecting the influence of both surface conditions and precipitation patterns. These results demonstrate that remotely sensed based data can effectively complement ground observations. The developed model provides a reliable foundation for various applications, including drought monitoring, agricultural productivity assessment, landslide prediction, and flood hazard evaluation.
- COLLAPSE
정확한 토양수분 관측은 수문 과정 이해와 기후 변화에 따른 재해 대응에 필수적이다. 그러나 한반도 지역은 복잡한 지형과 식생 조건으로 인해 기존 위성 기반 토양수분 산출의 정확도에 한계가 존재한다. 본 연구는 2020년 1월 부터 2025년 6월 까지 기간동안 원격탐사 자료를 활용한 다중선형회귀(Multiple Linear Regression, MLR) 모형을 구축하여 고해상도 토양수분 자료를 생산하는 것을 목표로 수행되었다. 주요 입력 변수로 Sentinel-1A 위성의 VV 편파 후방산란계수, 기상청 합성 레이더 기반 1일,2일,3일 누적 강우량, 그리고 연속 무강우일수를 활용하였다. 모형은 농촌진흥청(RDA)의 충청권 13개 지점 토양수분 관측자료를 이용해 검증하였으며, 높은 성능(MAE: 2.49~10.3, R: 0.517~0.768)을 나타내었다. 또한 토지피복 유형별 분석에서도 모형은 지표 특성과 강우 패턴에 따른 토양수분 변화를 안정적으로 재현하였다. 이는 원격 탐측 자료가 지상관측 토양수분 자료를 효과적으로 보완, 대체 할 수 있음을 의미하며, 개발된 모형은 가뭄 모니터링, 농업 생산성 평가, 산사태 및 수문재해 예측 등 다양한 분야의 기초자료로 활용될 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
High-resolution soil moisture estimation using a multiple linear regression model based on remote sensing data
-
Research Article
-
River monitoring using Sentinel-2 imagery and deep learning-based object detection models
Sentinel-2 영상과 딥러닝 기반 객체 탐지 모델을 활용한 하천 모니터링
-
Cho, ShinhyeonㆍKim, Wanyub, Choi, Minha
조신현, 김완엽, 최민하
- Efficient water system monitoring is an essential element for securing stable water resources and preventing water-related disasters. The significance of monitoring has …
효율적인 수계 모니터링은 안정적인 수자원 확보와 수재해 예방을 위해 필수적인 요소이며, 최근 기후변화로 인한 가뭄 및 홍수 발생의 빈도가 증가함에 따라 모니터링의 …
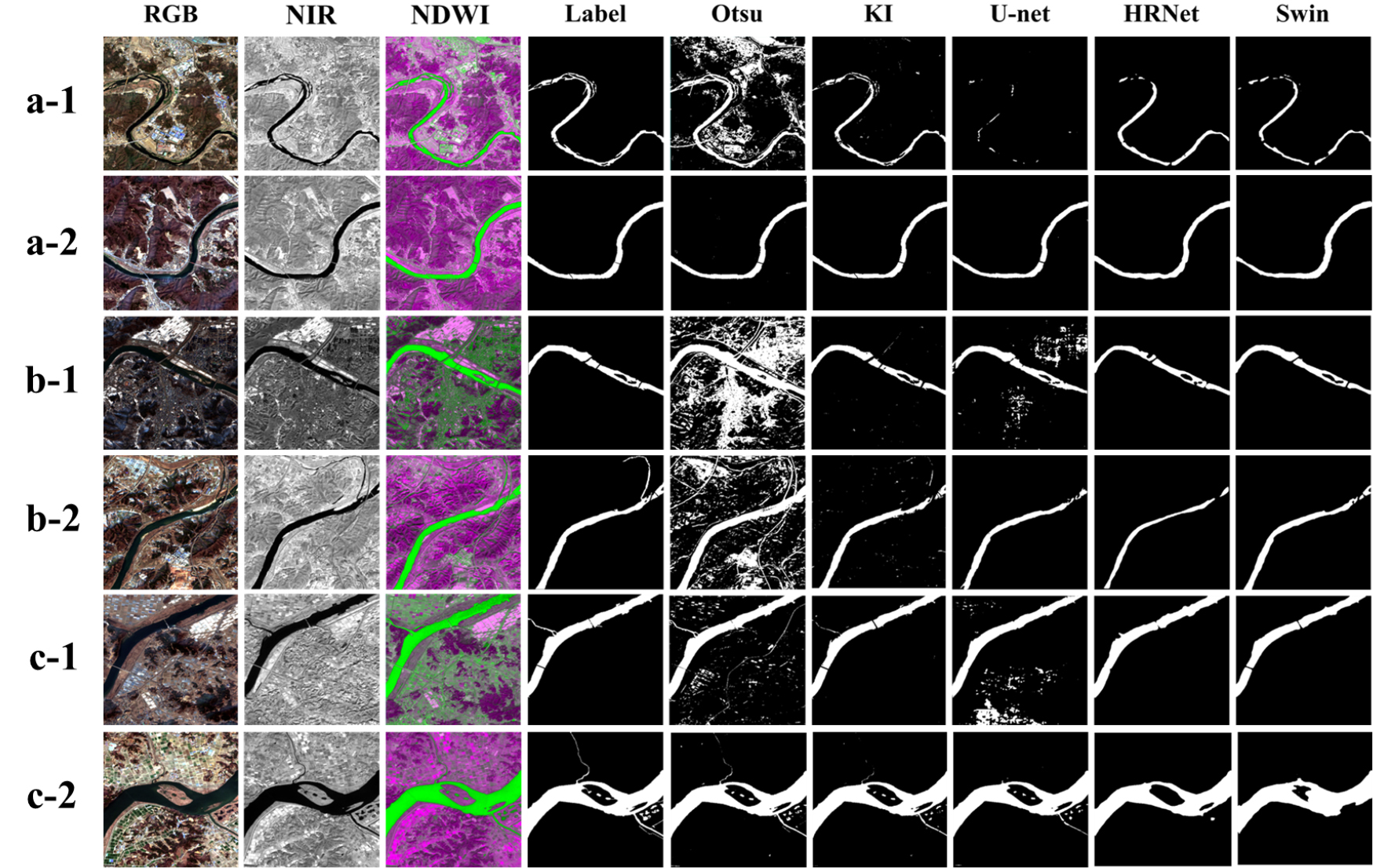
- Efficient water system monitoring is an essential element for securing stable water resources and preventing water-related disasters. The significance of monitoring has increased in the context of rising frequencies of droughts and floods, a phenomenon attributable to recent climate change. Satellite remote sensing, in particular, has become a core tool in water resource management due to its ability to enable periodic detection across a wide spatial range. Accordingly, the present study was conducted with the objective of detecting water bodies, with a focus on domestic rivers. The study employed Sentinel-2 satellite imagery with a resolution of 10 meters and the Swin-Transformer model. The objective of the study was to identify alterations resulting from watershed monitoring and to assess the model's applicability. Initially, a comparative analysis was conducted among the classical water body detection techniques Otsu, Kittler-Illingworth (KI), and the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)-based models U-net and High-Resolution Network (HRNet). These techniques were evaluated against a set of manually digitized and labeled images. The Swin-Transformer model demonstrated optimal performance, achieving an accuracy of 0.99, an Intersection over Union (IoU) of 0.88, and an F1-score of 0.87. Furthermore, the Swin- Transformer model, when employed for the purpose of evaluating the performance of watercourse change detection, demonstrated a high degree of efficacy, as evidenced by the high values obtained when evaluating the model's performance against labeled images. The model demonstrated an accuracy of 0.99, an IoU of 0.83, and an F1-score of 0.90. While changes in broad watercourse areas can be detected with high accuracy, limitations existed in detecting water bodies at the boundary edges of sandbars within thin tributaries and watercourse areas with complex structures. The Swin-Transformer model is expected to enable stable monitoring of water systems across diverse terrains, even in medium-to-low resolution satellite imagery. It is anticipated that the utilization of this technology will be effective in detecting changes in water systems and in disaster response.
- COLLAPSE
효율적인 수계 모니터링은 안정적인 수자원 확보와 수재해 예방을 위해 필수적인 요소이며, 최근 기후변화로 인한 가뭄 및 홍수 발생의 빈도가 증가함에 따라 모니터링의 중요성이 증대된다. 특히, 위성 원격 탐사는 넓은 공간적 범위를 주기적으로 탐지가 가능한 장점으로 인해 수자원 관리 분야에서 핵심적인 도구로 자리 잡고 있다. 이에 따라 본 연구에서는 10 m급 해상도를 지닌 Sentinel-2 위성 영상과 Swin-Transformer모델을 활용하여 국내 하천을 대상으로 수체 탐지를 진행하였으며, 수계의 모니터링으로 인한 변화 탐지 및 모델의 활용성을 평가하고자 하였다. 우선, 수체 탐지의 고전 기법인 Otsu, Kittler-Illingworth (KI) 와 Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) 기반의 U-net, High-Resolution Network (HRNet) 모델과 Tranformer 기반의 Swin-Transformer 모델을 수작업으로 디지타이징한 레이블 영상과 비교 및 검증한 결과, Swin-Transformer 모델에서 Accuracy 0.99, Intersection over Union (IoU) 0.88, F1-score 0.87로 가장 우수한 결과가 도출되었다. 추가적으로 Swin-Transformer 모델을 활용한 수계 변화탐지 성능을 레이블 영상과 비교하여 평가한 결과, Accuracy 0.99, IoU 0.83, F1-score 0.90으로 높은 수치가 도출되었다. 넓은 수계 영역에서의 변화는 높은 정확도로 탐지가 가능하지만, 얇은 지류 및 복잡한 구조를 지는 수계영역에서는 모래톱의 경계 가장자리 부분에서의 수체 탐지의 한계점이 존재하였다. 향후 Swin-Transformer 모델을 기반 수체 탐지는 중·저해상도 위성 영상에서도 다양한 지형에서의 수계 모니터링을 안정적으로 탐지할 수 있으며, 수계 변화탐지 및 재해 대응에 효과적으로 활용될 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
River monitoring using Sentinel-2 imagery and deep learning-based object detection models
-
Review Article
-
Analysis of flood inundation simulation according to terrain resolution and interpolation methods
지형 해상도 및 보간 기법에 따른 홍수범람 모의 특성 분석
-
Kim, MieunㆍJang, SuhyungㆍKang, ShinukㆍChoi, Hyungu
김미은, 장수형, 강신욱, 최현구
- The frequency of floods caused by extreme weather events is increasing, and accurate flood innundation information is required when establishing related plans …
극단적 이상 기후로 인한 홍수의 빈도는 증가하는 추세이고, 홍수로 인한 피해를 저감시키기 위하여 관련 계획 수립 시 정확한 홍수범람 정보가 필요하다. 홍수범람 …
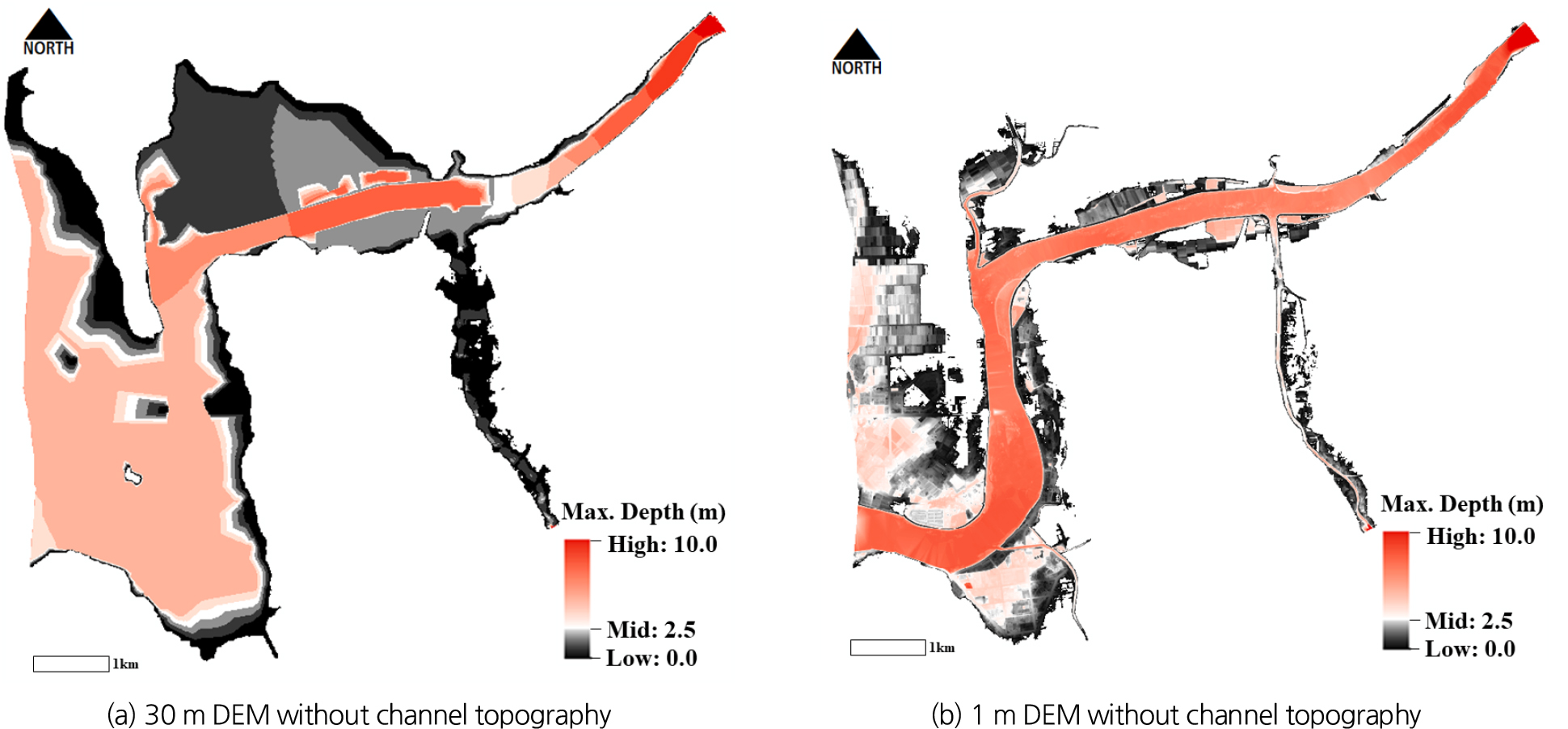
- The frequency of floods caused by extreme weather events is increasing, and accurate flood innundation information is required when establishing related plans to mitigate flood damage. Accurate flood inundation information is essential for developing plans to minimize flood damage. In flood inundation analysis, the resolution of topographic data is the most critical factor. This study interpolated river channel terrain using cross-sectional survey data from river master plans, and refined the topographic data by subdividing grids along levee lines and river centerlines in RAS Mapper. To compensate for the absence of measured data, the two-dimensional HEC-RAS model was validated using design flood discharge. A comparison of inundation areas before and after channel interpolation, classified by water depths above and below 2 meters, revealed approximately 96% reduction in high-depth areas (≥2 m) and approximately 93% reduction in low-depth areas (<2 m). These results demonstrate that flood inundation analysis outcomes vary significantly depending on whether topographic information of the river channel is incorporated, highlighting the importance of direct and indirect model calibration and verification processes. This study is expected to enable more accurate identification of high-risk areas when establishing flood risk management plans, thereby preventing flood damage in advance.
- COLLAPSE
극단적 이상 기후로 인한 홍수의 빈도는 증가하는 추세이고, 홍수로 인한 피해를 저감시키기 위하여 관련 계획 수립 시 정확한 홍수범람 정보가 필요하다. 홍수범람 분석은 지형자료의 해상도가 가장 중요한 요소이다. 본 연구는 RAS Mapper에서 하천기본계획 수립 시의 횡단측량 자료를 이용하여 하도 구간 내 지형을 보간하고, 제방선과 하천 중심선을 따라 격자를 세분화하여 지형자료를 생성하였다. 실측 자료의 부재를 보완하기 위해 하천의 계획홍수량을 적용하여 2차원 HEC-RAS 모형을 검증하였다. 하도구간 보간 전과 후의 침수범위를 수심 2 m 이상과 미만으로 구분하여 침수면적을 비교한 결과, 2 m 이상의 고수심에서는 약 96% 감소하였고 2 m 미만 저수심에서는 약 93% 감소하였다. 이는 홍수범람 분석 시 하도 구간의 지형 정보에 반영 유무에 따라 범람 범위의 분석 결과가 상이함으로 직·간접적 모형의 검보정 단계가 중요하다. 본 연구를 통해 향후 홍수 위험에 대한 계획 수립 시 보다 정확한 위험지역 선정으로 범람으로 인한 피해를 사전에 예방할 수 있을 것으로 기대한다.
-
Analysis of flood inundation simulation according to terrain resolution and interpolation methods
-
Research Article
-
Spatial distribution of reverse flow with three-dimensional in-situ hydraulic measurements at the Dumulmeori in Paldang Lake
3차원 현장 수리계측을 통한 팔당호 두물머리 합류부 역류 공간분포 분석
-
Yongmuk Kang, Dongsu Kim, Suin Choi, Sehwi Park, Youngdo Kim
강용묵, 김동수, 최수인, 박세휘, 김영도
- This study aimed to investigate seasonal reverse flow phenomena in the upstream confluence zone of Paldang Lake, a river-type reservoir. Five field …
본 연구는 하천형 호소인 팔당호 상류 두물머리에서 발생하는 계절별 역류 현상을 정밀 분석하고자 하였다. 이를 위하여 2023년부터 2024년까지 총 5회의 현장 계측을 …
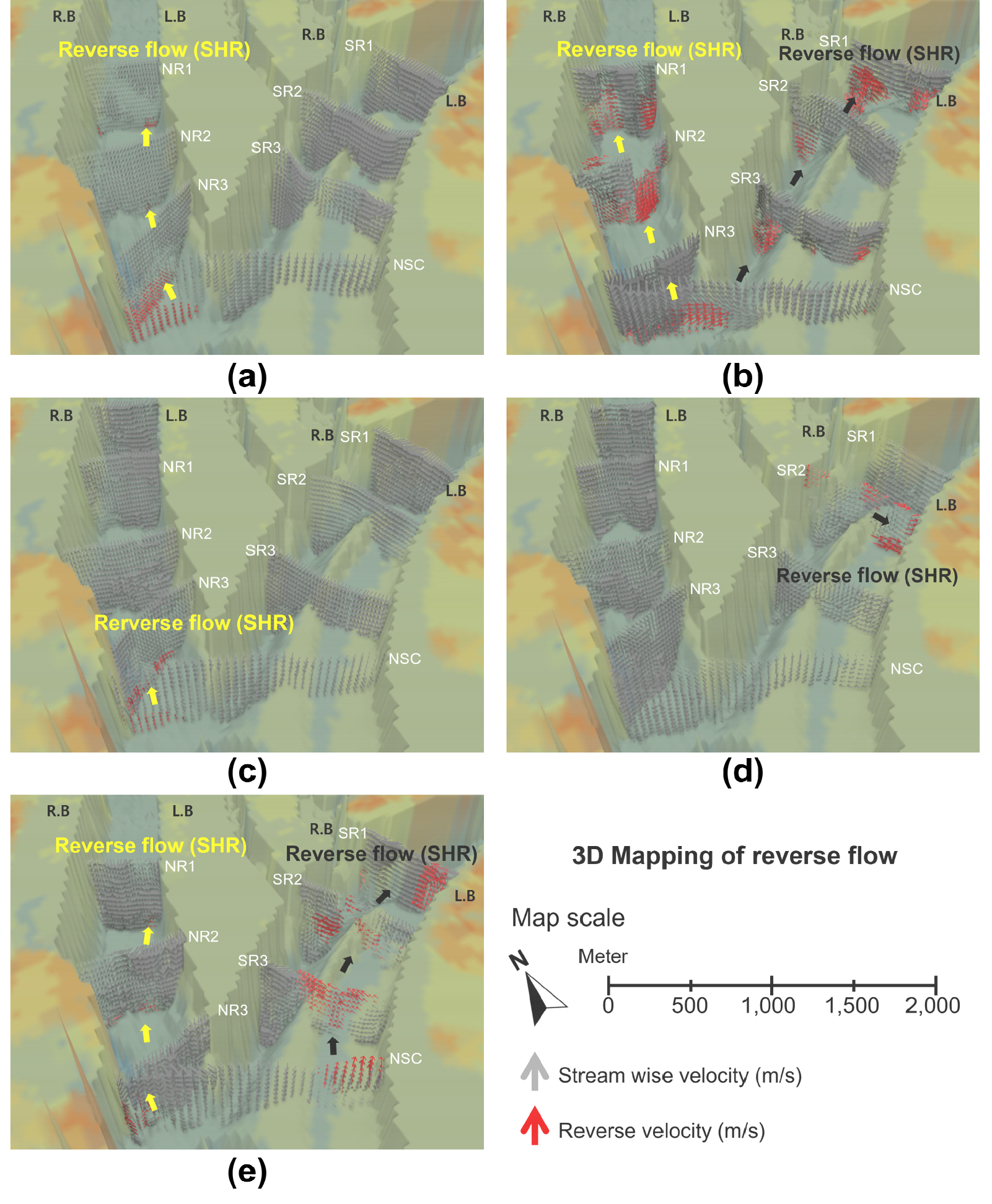
- This study aimed to investigate seasonal reverse flow phenomena in the upstream confluence zone of Paldang Lake, a river-type reservoir. Five field surveys were conducted from 2023 to 2024, focusing on discharge, flow momentum of the North Han River and South Han River, as well as vertical profiles of temperature and electrical conductivity at the confluence. Results showed that reverse flow from the South Han River into the North Han occurred consistently across all cases, regardless of momentum dominance, with its spatial extent varying seasonally. In contrast, inflow from the North Han into the South Han was limited and primarily influenced by localized stagnant zones formed by channel curvature, rather than by dynamic reverse flow. Stratified reverse flows were particularly evident under combined conditions of discharge imbalance and thermal contrast, indicating the influence of density gradients. The findings provide a useful foundation for understanding hydraulic complexity and mass movement within compound river confluence systems.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 하천형 호소인 팔당호 상류 두물머리에서 발생하는 계절별 역류 현상을 정밀 분석하고자 하였다. 이를 위하여 2023년부터 2024년까지 총 5회의 현장 계측을 수행하였으며, 북한강과 남한강의 유량 및 흐름 운동량, 합류부 단면의 수온과 전기전도도(EC) 분포를 바탕으로 역류의 발생 조건과 공간적 특성을 고찰하였다. 분석 결과, 남한강 수체가 북한강 방향으로 역류하는 현상은 흐름 운동량의 상대적 우세와 무관하게 모든 계측 사례에서 반복적으로 발생하였고, 계절 및 유속 조건에 따라 그 범위는 달라졌다. 반면, 북한강 수체의 남한강 방향 유입은 국지적 만곡지형에 따른 사수역 영향으로 제한적으로 나타났으며, 구조적인 역류보다는 정체 유역의 특성이 강조되었다. 특히 방류량 차이와 수온 차가 동시에 존재하는 조건에서는 밀도구배에 따른 성층적 역류 양상이 뚜렷하게 확인되었다. 본 연구 결과는 복합 합류부의 수리적 특성과 수체 거동을 이해하는 데 기초자료로 활용될 수 있다.
-
Spatial distribution of reverse flow with three-dimensional in-situ hydraulic measurements at the Dumulmeori in Paldang Lake
-
Research Article
-
Evaluation of scattering efficiency and suspended sediment concentration accuracy for fine sediments using acoustic backscatter intensity: Validation based on a full-scale river experimental flume
초음파 산란도를 활용한 세립질 부유사 산란 효율 및 부유사 농도 산정 정확도 평가: 실규모 하천 실험 수로 기반 검증
-
Jeong, BoseongㆍKim, DongsuㆍChoi, SuinㆍLee, SeogyeongㆍKang, Yongmuk
정보성, 김동수, 최수인, 이서경, 강용묵
- This study comparatively evaluated the scattering characteristics and accuracy of suspended‐sediment concentration (SSC) estimation for fine sediment by operating a SonTek ADCP …
본 연구는 한국건설기술연구원 안동하천실센터 급경사수로에서 SonTek ADCP M9과 AquaSCAT 1000R을 병행 운용하여 세립질 부유사의 산란 특성과 농도(SSC) 산정 정확도를 LISST-200X(기준값)와 비교 평가하였다. …
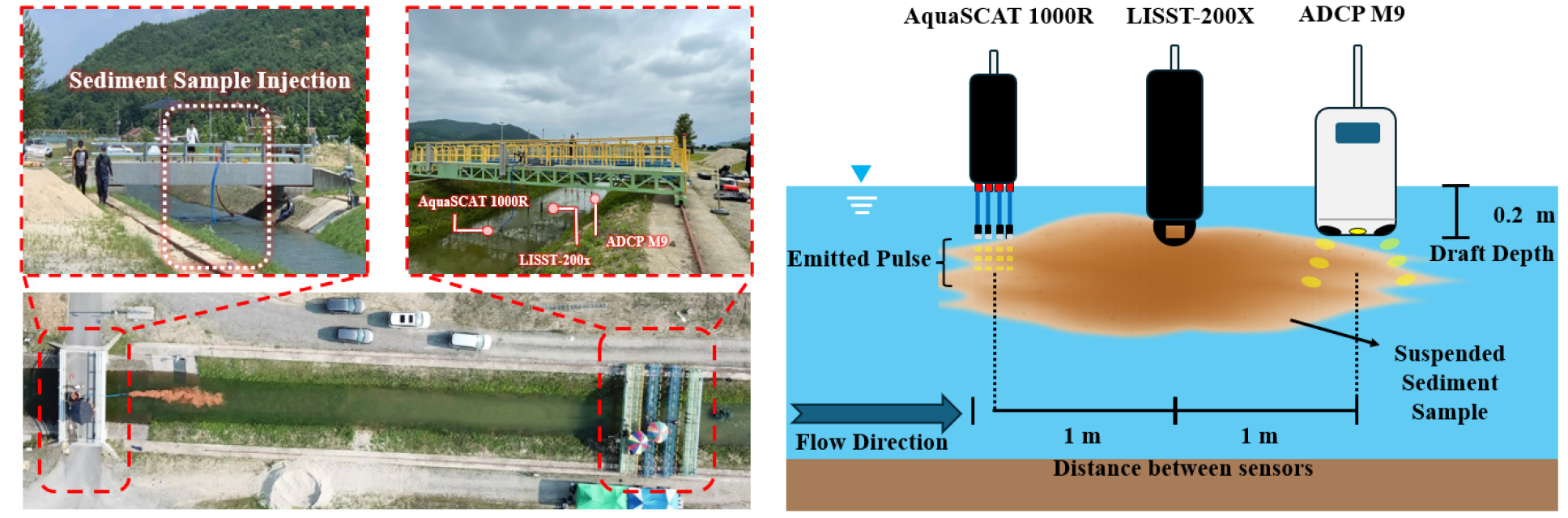
- This study comparatively evaluated the scattering characteristics and accuracy of suspended‐sediment concentration (SSC) estimation for fine sediment by operating a SonTek ADCP M9 and an AQUAscat 1000R in parallel at the steep-slope channel of the KICT Andong River Experiment Center, using a LISST-200X as reference. The analysis of frequency-particle-size dependency revealed that 2.5-5 MHz (ABS) and 3 MHz (ADCP) provided stable detection within the Rayleigh regime. Both instruments consistently captured the spatio-temporal SSC distribution under yellow loess and mixed-sediment conditions, showing high agreement with LISST-200X (R2=0.85-0.95). Quantitatively, errors were MAPE 13-54% and PBIAS -3.6 to +4.6% for the loess case, and MAPE 6-8% and PBIAS -2.0 to +2.1% for the mixed case. While AQUAscat-based particle-size estimates showed differences from LISST-200X, they were effective for qualitatively identifying particle-size trends during plume passage. The findings provide practical guidance on effective frequency bands, attenuation and near-field corrections, and integration of independent particle-size data for river applications, and they motivate expansion to broader grain-size/SSC regimes and multi-frequency operations.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 한국건설기술연구원 안동하천실센터 급경사수로에서 SonTek ADCP M9과 AquaSCAT 1000R을 병행 운용하여 세립질 부유사의 산란 특성과 농도(SSC) 산정 정확도를 LISST-200X(기준값)와 비교 평가하였다. 주파수-입경 의존성 분석 결과, 레일리 영역에서는 2.5-5 MHz와 3 MHz가 안정적인 탐지 성능을 제공하는 것으로 나타났다. 이를 바탕으로 두 장비는 황토 단독 및 혼합토 실험 조건 모두에서 부유사의 시간·공간 분포를 일관되게 포착하였으며, SSC 상관성은 R2=0.85-0.95 수준이었다. 정량 오차는 황토 조건에서 MAPE 13-54%, PBIAS -3.6~+4.6%였고 혼합토 조건에서 MAPE 6-8%, PBIAS -2.0~+2.1%로 확인되어 높은 상관성과 허용 가능한 오차 범위를 동반하였다. 또한 AquaSCAT 1000R의 입경 산정은 LISST-200X 대비 정량 차이가 있으나 통과 과정의 입경 변화 경향을 정성적으로 규명하는 데 유효했다. 본 연구 결과는 국내 하천 적용을 위한 유효 주파수 대역, 감쇠·근거리 보정, 입경 정보 결합의 실무 기준을 제시하며, 향후 다양한 입도·농도 조건 및 다중 주파수 운용으로의 확대를 제안한다.
-
Evaluation of scattering efficiency and suspended sediment concentration accuracy for fine sediments using acoustic backscatter intensity: Validation based on a full-scale river experimental flume
-
Research Article
-
Estimation of manning’s roughness coefficients at automatic discharge gauging stations using the continuous slope–area method
연속 경사 면적법을 통한 자동유량관측소에서의 실측 조도계수 산정
-
Lee, IkhanㆍKim, DongsuㆍKim, KyeongdongㆍRoh, Youngsin
이익한, 김동수, 김경동, 노영신
- River discharge is a key indicator for water resources management and flood forecasting, but the traditional single stage–discharge rating curve produces systematic …
하천 유량은 수자원 관리와 홍수 예보의 핵심 지표이나, 이를 산정하는 전통적 단일 수위–유량곡선은 하천의 비정상류 조건에서 이력현상으로 체계적 오차가 발생한다. 본 연구는 …
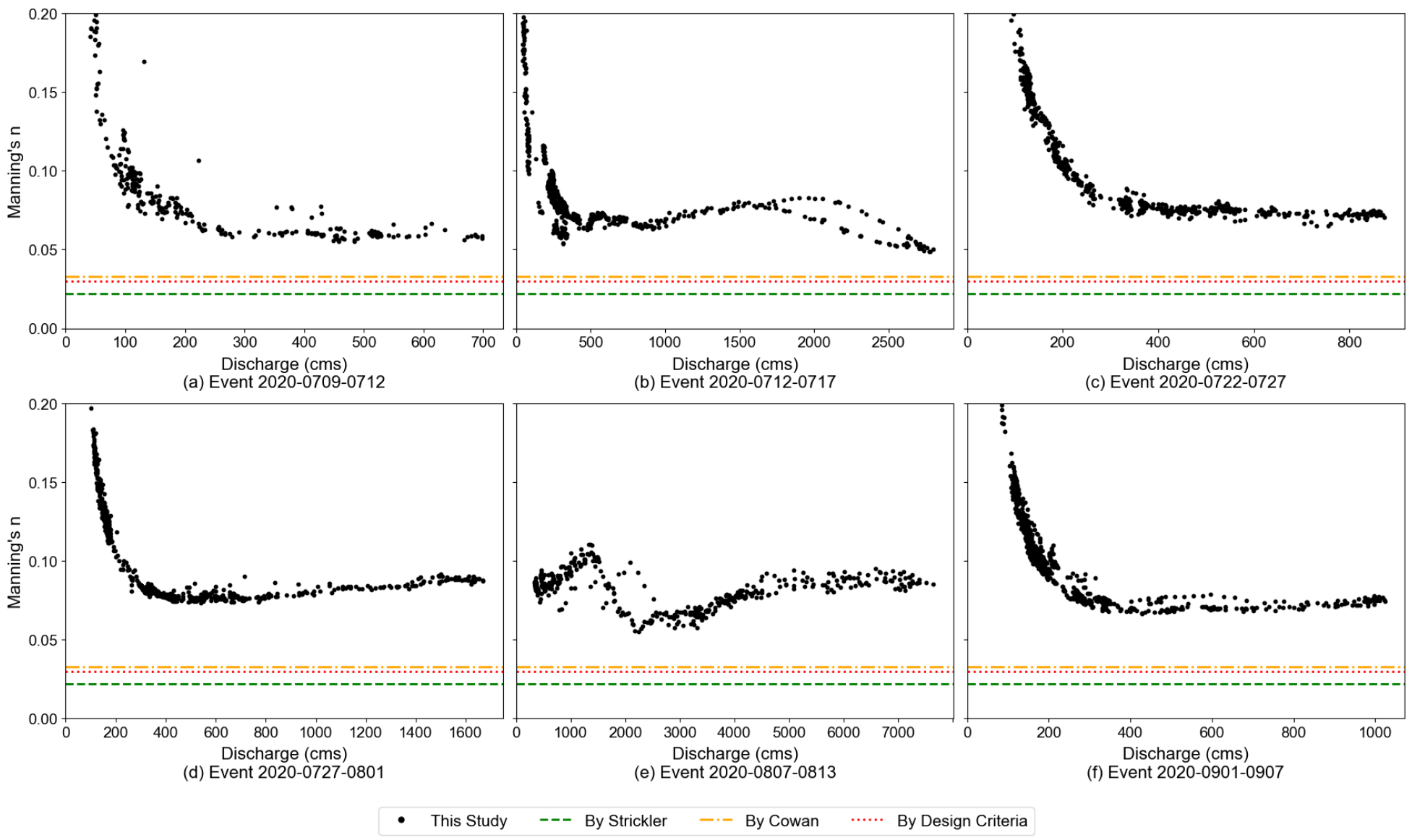
- River discharge is a key indicator for water resources management and flood forecasting, but the traditional single stage–discharge rating curve produces systematic errors under unsteady flow due to hysteresis. This study applies the inverse continuous slope–area (CSA) method at Naju Bridge on the Yeongsan River by combining H-ADCP (Horizontal Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler) measured discharges with upstream and downstream water-surface slopes. Time-series Manning’s roughness coefficients (n) were estimated at 10-minute intervals for the 2020 flood events, segmented by stage to reflect cross-sectional characteristics, and applied to recalculate and validate CSA discharges for the 2019 and 2021 events. The estimated n shows a common pattern: rapid decrease at low stages, convergence at intermediate stages, an inflection before rapid expansion, and increase again at high stages, converging to values higher than conventional empirical or design criteria (reaching n ≈ 0.08~0.09 during extreme floods). Using the segmented n, the CSA method reproduced hysteresis in six flood events with R2 ≥ 0.94 and peak error ≤ 3%, although nRMSE exceeded 10% under low-flow conditions. Overall, time-series estimation and stage-wise application of measured n significantly improve the performance of the CSA method and enhance the practical applicability of field-based roughness estimation and CSA-based discharge computation in natural rivers.
- COLLAPSE
하천 유량은 수자원 관리와 홍수 예보의 핵심 지표이나, 이를 산정하는 전통적 단일 수위–유량곡선은 하천의 비정상류 조건에서 이력현상으로 체계적 오차가 발생한다. 본 연구는 영산강 본류에 위치한 나주시(나주대교)에서 H-ADCP (Horizontal-Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler) 실측유량과 상·하류 수면경사를 결합하여 연속 경사-면적법(CSA)을 역산하고, 2020년 홍수사상에 대해 10분 간격의 실측 Manning 조도계수 n을 산정한 뒤 단면 특성을 반영해 수위별 구간화 후 2019, 2021년 홍수사상에서 CSA 유량을 재산정 및 검증하였다. n은 저수위 급감–중수위 수렴–급확대 직전 변곡–고수위 재상승의 공통 패턴을 보였고, 기존 경험식이나 설계기준에서 사용되는 고정값보다 크게(극한 홍수 시 n≈0.08~0.09) 수렴하였다. 구간화한 n을 적용한 CSA는 6개 홍수사상에서 이력현상을 효과적으로 재현하여 결정계수 R2≥0.94, 첨두오차 ≤3%의 성능을 보였으나 저유량에서는 nRMSE가 10% 이상으로 증가하였다. 결론적으로, 실측 n의 시계열 추정과 구간 적용은 CSA의 재현성을 유의하게 향상시켜, 여러 하천에서 실측 조도계수 산정과 CSA의 실무 적용 가능성을 한층 높일 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
Estimation of manning’s roughness coefficients at automatic discharge gauging stations using the continuous slope–area method
-
Research Article
-
Identifying Gibbs’ characteristics of urban drainage networks using flow matrix tool
FMT를 이용한 도시 배수관망의 깁스 특성 분석
-
Seok, MinsooㆍPark, ChangminㆍSeo, Yongwon
석민수, 박창민, 서용원
- Gibbs' Model, one of the stochastic drainage network models, serves as a useful tool for characterizing drainage network properties. This study developed …
추계학적 배수망 모형의 하나인 깁스모형(Gibbs’ Model)은 배수망의 특성을 나타내는 유용한 도구이다. 본 연구에서는 깁스모형의 적용 과정에 필요한 격자망 재구성을 자동으로 수행할 수 …
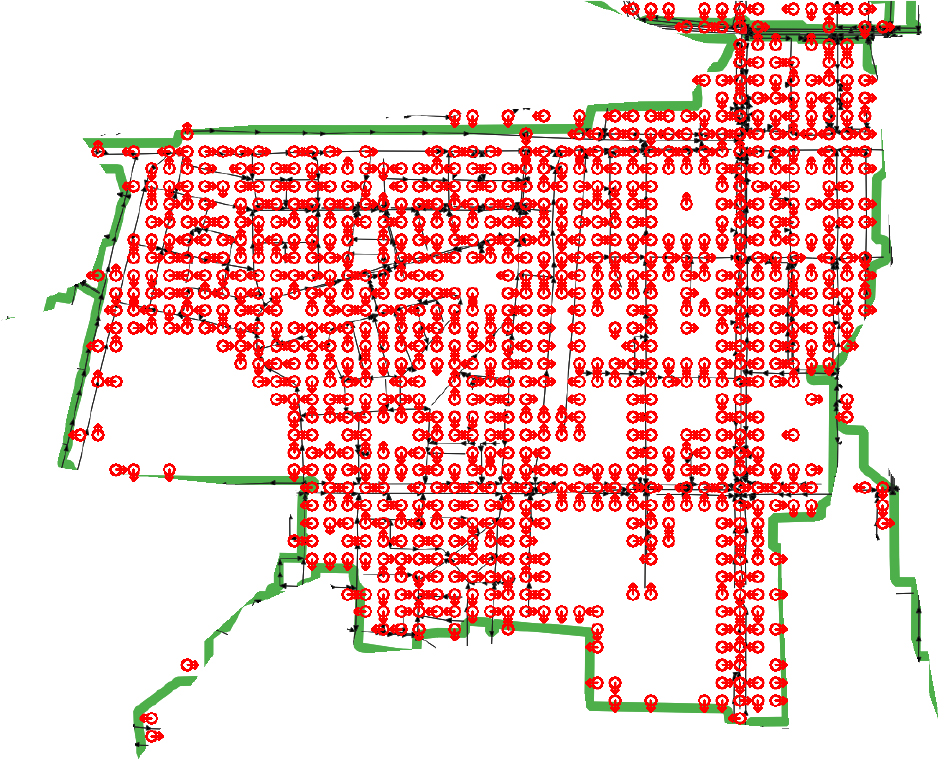
- Gibbs' Model, one of the stochastic drainage network models, serves as a useful tool for characterizing drainage network properties. This study developed a computational process called Flow Matrix Tool (FMT) that automatically performs the grid reconstruction required for applying Gibbs' Model. FMT recognizes the flow direction in drainage networks of arbitrary basins presented as images using image recognition (ROI), weighted voting, and breadth-first search (BFS), and automatically reconstructs the pipe network on a grid. Users can finely adjust parameters such as thresholds, kernel size, color range, and cell size through settings. The FMT developed in this study was applied to the Seocho 4 district to verify its applicability. The results confirmed that drainage pipe networks presented as images can be quickly and stably reconstructed onto a given grid with high accuracy using FMT. Additionally, since users can arbitrarily adjust the desired grid size, it is deemed applicable to various fields. It is expected to be significantly helpful for computational analysis of existing drainage pipe networks in drawing formats.
- COLLAPSE
추계학적 배수망 모형의 하나인 깁스모형(Gibbs’ Model)은 배수망의 특성을 나타내는 유용한 도구이다. 본 연구에서는 깁스모형의 적용 과정에 필요한 격자망 재구성을 자동으로 수행할 수 있는 전산 과정(Flow Matrix Tool, FMT)을 개발하였다. FMT는 이미지 상태로 제시된 임의 유역의 배수망을 이미지 인식(ROI), 가중투표와 너비우선탐색(BFS)을 이용하여 흐름의 방향을 인식하고 관망을 자동으로 격자 위에 재구성한다. 또한 설정을 통해 사용자가 임계값, 커널 크기, 색상 범위, 셀 크기 등을 세밀하게 조정할 수 있도록 하였다. 본 연구에서 개발한 FMT를 서초4분구에 적용하여 그 적용성을 검증하였다. 적용 결과 이미지 상태로 제시된 배수관망을 FMT를 통해 빠르고 안정적으로 높은 정확도로 주어진 격자에 관망을 재구성할 수 있음을 확인하였다. 또한 사용자가 원하는 격자 크기를 임의로 조정할 수 있어 다양한 분야에 적용가능 할 것으로 판단된다. 도면 형태로 이루어진 기존 배수관망의 전산 해석에도 큰 도움이 될 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
Identifying Gibbs’ characteristics of urban drainage networks using flow matrix tool
-
Research Article
-
Enhancing agricultural reservoir water body monitoring through the integration of optical and SAR remote sensing
광학 및 SAR 영상 기반 농업용 저수지 수체의 시·공간적 변화 모니터링
-
Lee, Hee-JinㆍNam, Won-HoㆍYang, Mi-HyeㆍLee, Hosun
이희진, 남원호, 양미혜, 이호선
- Changes in water bodies are critical indicators for diagnosing and predicting extreme hydrological hazards, and the ongoing decline in storage across dams …
저수지 수체의 변화는 극한 수문 재해 발생 및 상황을 진단하고 예측하는 데 핵심적인 지표이다. 대규모 댐, 저수지 저수량의 지속적인 감소는 수자원 부존량에 …
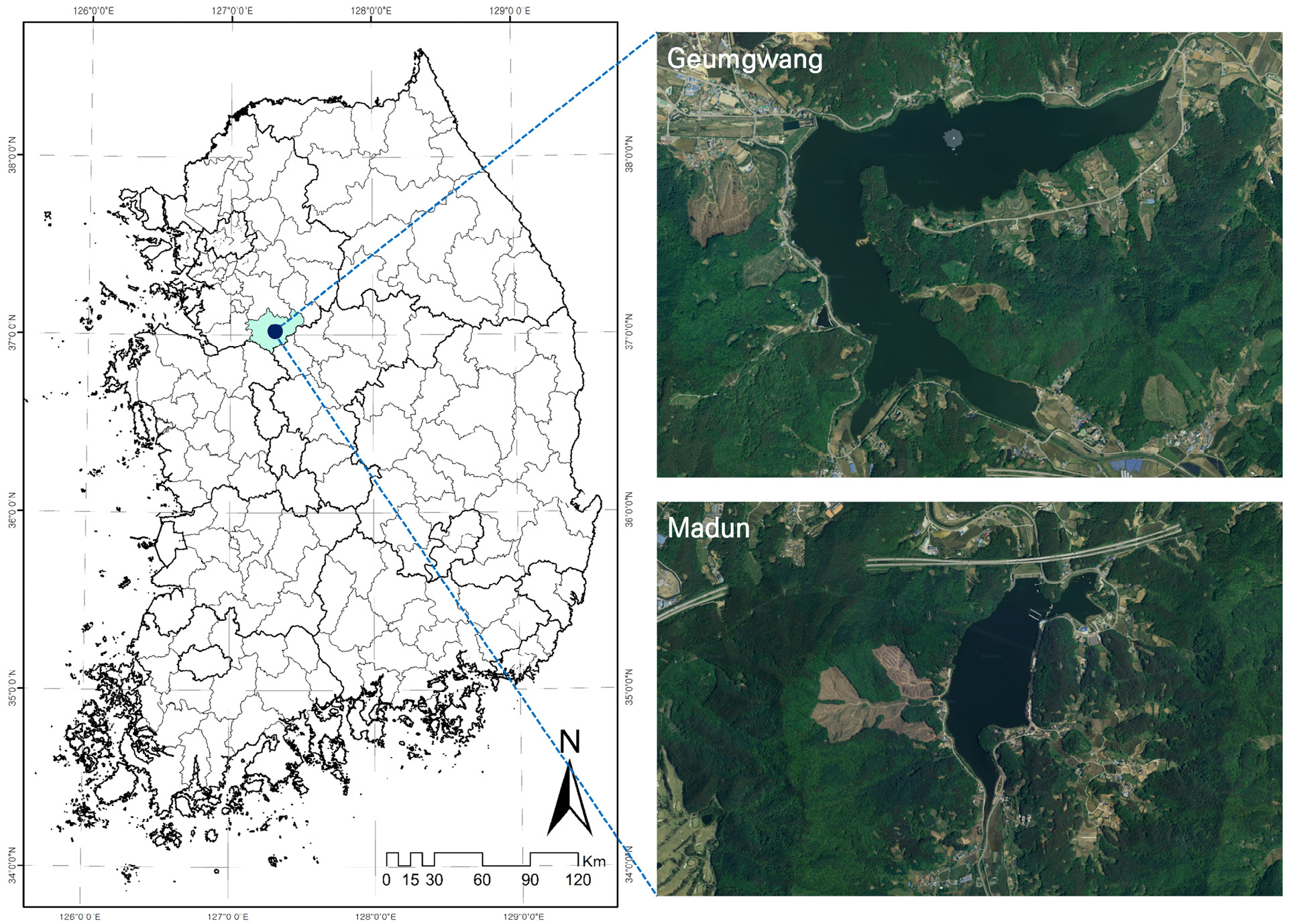
- Changes in water bodies are critical indicators for diagnosing and predicting extreme hydrological hazards, and the ongoing decline in storage across dams and reservoirs has recently posed significant challenges for water resource management. As a result, there is a growing demand for reliable systems capable of monitoring the spatiotemporal dynamics of reservoir water bodies. In this study, we quantitatively compared optical and SAR-based methods for monitoring reservoir dynamics using Sentinel imagery processed on the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform. The optical indices—the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) and the Modified Normalized Difference Water Index (MNDWI)—generally produced lower RMSE values and closely matched observed water surface areas; however, their reliability diminished during periods of reservoir drawdown due to indistinct boundaries and data gaps. In contrast, Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR)-based approaches—including the Kittler-Illingworth (KI), Chan-Vese (CV), and K-means (KM) algorithms—offered greater year-round data availability and more stable time-series detection. Among these, the CV method provided the best balance between accuracy and robustness, yielding an R² of 0.7 for the Geumgwang Reservoir, an RMSE of 7.6 ha for the Madun Reservoir, and an overall classification accuracy of 87% relative to observed water surface areas. Overall, both optical- and SAR-based approaches effectively captured reservoir variations during periods of rising water levels, though performance declined under stable or decreasing conditions. Future research should focus on developing segment-specific corrections and integrating optical and SAR imagery to establish a continuous monitoring framework for medium- to large-scale agricultural reservoirs, with potential application as a core component of national hazard monitoring systems.
- COLLAPSE
저수지 수체의 변화는 극한 수문 재해 발생 및 상황을 진단하고 예측하는 데 핵심적인 지표이다. 대규모 댐, 저수지 저수량의 지속적인 감소는 수자원 부존량에 직접적인 영향을 미치기 때문에 수리시설물 수체의 시공간 변동에 대한 모니터링이 필요하다. 본 연구에서는 구글어스엔진(GEE) 기반 Sentinel 영상 자료를 활용하여 광학 영상 기반 정규수분지수(NDWI) 및 수정정규수분지수(MNDWI)와 합성개구레이더(SAR) 기반 Kittler-Illingworth (KI), Chan-Vese (CV), K-Means clustering (KM)의 수체 변화 모니터링 성능을 비교하였다. 광학 기반 추정은 실제 수표면적에 근접하였으나, 수위 감소 구간에서 경계 불명확성과 관측 공백으로 변화 탐지 신뢰도가 저하되었다. SAR 기반 추정은 연중 가용성이 높고 시계열 패턴 포착이 안정적이었으며, 특히 CV는 금광 저수지에 대한 R2는 0.7, 마둔 저수지에 대한 RMSE는 7.6 ha로 정확성 및 가용성에 대한 균형이 우수하였다. 또한, 실제 수표면적 대비 수체 분류 정확도는 87%로 가장 높은 정확도를 나타내었다. 광학 및 SAR 기반 수체 분류는 수위 상승 구간에서 안정적인 수체 변화 정보를 제공하지만, 수위 감소 및 유지 구간에 대해서는 미흡한 것으로 판단된다. 본 연구의 결과는 향후 수위 구간에 따른 보완과 광학 및 SAR 이미지와의 융합을 통해 중규모 이상의 농업용 저수지에 대한 상시 수체 모니터링 체계를 구축할 수 있으며, 국가 단위 수자원 재해 감시 네트워크의 핵심 모듈로 확장될 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
Enhancing agricultural reservoir water body monitoring through the integration of optical and SAR remote sensing
-
Research Article
-
Application of an ensemble watershed model for simulation of suspended sediment generation and transport under extreme rainfall events
이상강우에 의한 부유사 발생 및 유출 모의를 위한 앙상블 유역모델의 적용
-
Lee, TaehwanㆍCho, Hong-LaeㆍJeong, Euisang
이태환, 조홍래, 정의상
- In recent years, the frequency and intensity of extreme rainfall events have increased due to climate change, leading to recurring occurrences of …
최근 기후변화로 인한 이상강우의 빈도와 강도가 증가함에 따라, 소양호에서는 매년 탁수 현상이 반복적으로 발생하고 있다. 본 연구는 이상강우 발생시 부유물질(Suspended sediment, SS)의 …
- In recent years, the frequency and intensity of extreme rainfall events have increased due to climate change, leading to recurring occurrences of turbid water in the Soyang Lake watershed. This study aimed to improve the prediction accuracy of suspended sediment (SS) generation and transport during extreme rainfall events by developing an ensemble watershed model based on the physically based STREAM model, and by evaluating its predictive performance and uncertainty reduction compared with a single model. The ensemble model was constructed by combining different physical formulations for evapotranspiration, soil water retention and hydraulic conductivity, infiltration, and sediment transport processes, resulting in 72 ensemble watershed models (18 hydrologic models × 4 sediment models). Simulations were performed for the upper Soyang Lake watershed using an hourly time step for the 2017-2024 period. As a result, the ensemble mean discharge showed improved performance, with PBIAS decreasing from 45.5% to 38.8% compared to the base single STREAM model. For SS concentration, the ensemble median achieved an R2 of 0.26, RMSE of 146.4 mg/L, and PBIAS of 6.9%, which markedly outperformed the single model (R2=0.17, RMSE=209.0 mg/L, PBIAS=-87.2%). These results indicate that the ensemble approach can enhance predictive reliability and stability while reducing the time and uncertainty associated with complex parameter calibration in traditional physically based models. Therefore, the proposed ensemble watershed modeling framework can serve as an efficient alternative for turbidity prediction under extreme rainfall conditions, and its integration with data-driven techniques is expected to further advance the accuracy of ensemble-based predictions.
- COLLAPSE
최근 기후변화로 인한 이상강우의 빈도와 강도가 증가함에 따라, 소양호에서는 매년 탁수 현상이 반복적으로 발생하고 있다. 본 연구는 이상강우 발생시 부유물질(Suspended sediment, SS)의 발생과 유출을 보다 정확히 예측하기 위해 물리기반 유역모델 STREAM을 기반으로 한 앙상블 유역모델을 구축하고, 단일 모델 대비 예측 성능과 불확실성 저감 효과를 평가하였다. 증발산, 토양수분함량 및 수리전도도, 침투, 유사이동 과정을 서로 다른 물리식으로 조합하여 총 72개의 앙상블 유역모델(18개 수문모델 × 4개 유사모델)을 구성하였으며, 북한강 상류 소양호 유역을 대상으로 2017-2024년 기간 동안 1시간 간격으로 모의를 수행하였다. 그 결과, 기준 STREAM 단일모델에 비해 앙상블 모델의 평균값 적용 시 유량은 PBIAS가 45.5%에서 38.8%로 개선되는 모습을 보였으며, SS 농도의 경우 72개 모델의 중앙값 적용 시 R2=0.26, RMSE=146.4 mg/L, PBIAS= 6.9%로 단일모델(R2=0.17, RMSE=209.0 mg/L, PBIAS=-87.2%) 대비 크게 향상되었다. 이는 앙상블 접근법이 복잡한 매개변수 보정 과정에 소요되는 시간과 불확실성을 줄이면서도, 단일 물리기반 모델 이상의 예측 신뢰도와 안정성을 확보할 수 있음을 보여준다. 따라서 제안된 앙상블 유역모델은 이상강우 발생시 탁수 예측의 효율적 대안으로 활용될 수 있으며, 향후 데이터 기반 기법과의 결합을 통해 더욱 고도화된 예측체계 구축이 가능할 것으로 기대된다.
-
Application of an ensemble watershed model for simulation of suspended sediment generation and transport under extreme rainfall events
-
Research Article
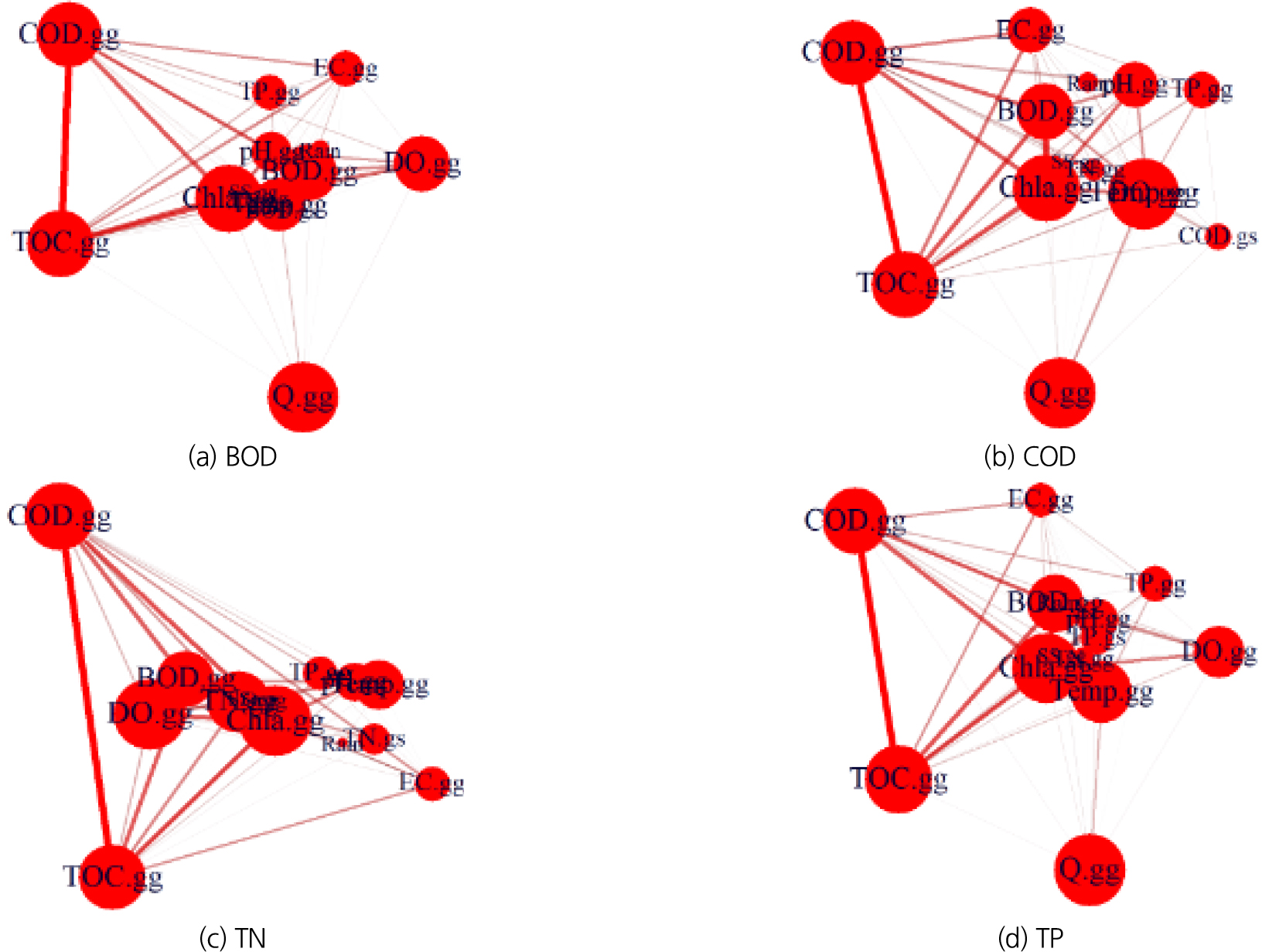
-
Network-based contribution approach for analyzing water quality fluctuation characteristics in NakdongMilyang mid-watershed
네트워크기반 기여율 분석을 활용한 수질변동 특성 분석 - 낙동밀양 중권역을 대상으로
-
Jo, BugeonㆍKo, Joo SukㆍKim, Young DoㆍLyu, SiwanㆍRhee, Dong SopㆍPark, Moon Hyeong
조부건, 고주석, 김영도, 류시완, 이동섭, 박문형
- Recent environmental changes driven by climate change have made it increasingly difficult to identify the causes of water quality degradation in river …
최근 기후변화로 인한 환경변화는 하천에서의 수질악화의 원인을 파악하는데 더욱 어려움을 주고있다. 도시화 및 산업화로 인한 비점오염물질의 증가 또한 수질악화에 영향을 미친다. 하천에서의 …
- Recent environmental changes driven by climate change have made it increasingly difficult to identify the causes of water quality degradation in river systems. The expansion of urbanization and industrial activities has further intensified water quality deterioration by increasing non-point source pollutants. Understanding the underlying causes is essential for preventing water quality decline however, research applying multivariate techniques to quantify the contributions of multiple interacting factors remains limited. Therefore, this study aimed to perform a network-based contribution analysis to examine the complex factors influencing river water quality. The Nakdong-Milyang mid-watershed, located upstream of the major intake points in the Nakdong River, was selected as the study area due to its importance in regional water quality management. Contribution analyses were conducted to identify the major pollution sources affecting water quality in the principal tributaries—Gyesung Stream, Hwapocheon Stream, and Juchoen River. By quantifying the degree to which each factor influences water quality conditions in these tributaries, the study seeks to provide a scientific basis for establishing management priorities and improving the effectiveness of watershed-scale water quality management.
- COLLAPSE
최근 기후변화로 인한 환경변화는 하천에서의 수질악화의 원인을 파악하는데 더욱 어려움을 주고있다. 도시화 및 산업화로 인한 비점오염물질의 증가 또한 수질악화에 영향을 미친다. 하천에서의 수질악화를 방지하기 위해서는 원인을 파악하는 것이 중요하며 따라서 본 연구에서는 수질에 영향을 미치는 복합적인 요소를 다변량 분석을 통한 기여도분석을 수행하였다. 본 연구에서는 복합적 요소에 대한 네트워크기반의 기여도 분석을 수행하고자 하였다. 낙동밀양 중권역은 낙동강 주요 취수지점 상류에 위치하여 수질관리에 중요한 지점으로 해당지역을 연구대상지역으로 설정하여 주요 지류하천에서의 수질악화에 대한 오염원인에 대한 기여율을 분석하였다. 계성천, 화포천, 주천강에 대하여 하천 수질에 영향을 미치는 대상에 대한 기여율 분석을 수행하여 수질에 미치는 영향을 정량화하고 관리 우선순위를 설정하고 수질관리에 기여하고자 한다.
-
Network-based contribution approach for analyzing water quality fluctuation characteristics in NakdongMilyang mid-watershed
-
Research Article
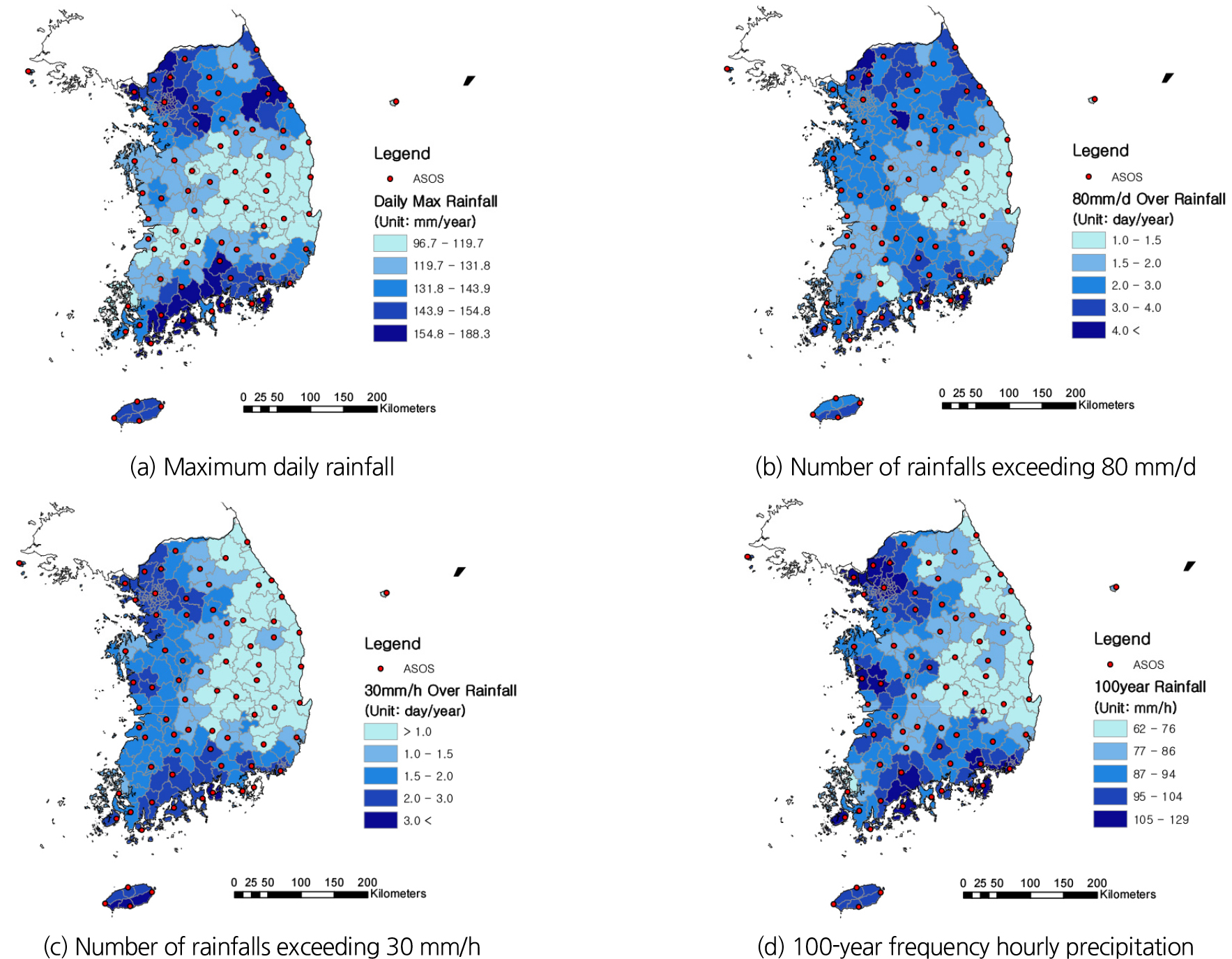
-
Integrated flood risk assessment of domestic local governments using the Delphi-AHP technique
Delphi-AHP 기법을 활용한 국내 지자체 통합홍수 위험도 평가
-
Yoon, Sun-KwonㆍYoon, JunseoㆍChoi, HyeonseokㆍKim, MinseokㆍHwang, Sung-Hwan
윤선권, 윤준서, 최현석, 김민석, 황성환
- This study aims to develop and validate a mid- to long-term integrated flood risk assessment model to address the growing flood hazards …
본 연구는 기후변화로 인한 홍수 위험의 증대에 대응하여 기존의 단기·사건 중심적 접근의 한계를 보완할 수 있는 중·장기적 통합 홍수 위험 평가 모델을 …
- This study aims to develop and validate a mid- to long-term integrated flood risk assessment model to address the growing flood hazards driven by climate change and to overcome the limitations of conventional short-term, event-focused approaches. To this end, a multi-criteria decision-making framework was constructed by combining the Delphi method and the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP). A multidimensional assessment system was then established, comprising three major categories—meteorological/climatic, socio- economic, and policy/institutional factors—and twelve detailed indicators. The proposed model distinguishes itself from hazard history–based assessments by comprehensively incorporating climate prediction uncertainties, societal structural vulnerabilities, and institutional response capacities. AHP results indicate that the meteorological/climatic category carries the highest weight (0.512), identifying it as the primary driver of flood risk variability, while “variability in mid- to long-term precipitation forecasts” emerged as the most influential indicator (0.203). Furthermore, analysis using the integrated risk index revealed that flood risk increases by more than 15% during El Niño phases compared to normal conditions, quantitatively demonstrating the impact of seasonal and climatic fluctuations on disaster management. The study is expected to provide an effective foundation for scientifically integrating mid- to long-term climate prediction information into disaster management decision-making.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 기후변화로 인한 홍수 위험의 증대에 대응하여 기존의 단기·사건 중심적 접근의 한계를 보완할 수 있는 중·장기적 통합 홍수 위험 평가 모델을 개발·검증하는 것을 목적으로 하였다. 이를 위해 델파이(Delphi) 기법과 계층분석기법(AHP)을 결합한 다중기준 의사결정 프레임워크를 구축하고, 기상·기후, 사회·경제, 정책·제도 등 3개 대분류와 12개 세부 지표로 구성된 다차원적 평가 체계를 정립하였다. 본 모델은 기후 예측의 불확실성, 사회 구조적 취약성, 제도적 대응 역량을 통합적으로 반영함으로써 재해 발생 이력 기반 평가 방식과 차별성을 갖는다. AHP 분석 결과, ‘기상·기후’ 부문이 가장 높은 가중치(0.512)를 보이며 핵심 영향 요인으로 확인되었고, ‘중장기 강수량 예측 변동성’이 최우선 세부 지표(0.203)로 도출되었다. 또한 통합 위험 지수를 활용한 분석에서 엘니뇨 단계 발생 시 홍수 위험 지수가 평년 대비 15% 이상 상승함을 확인하여, 계절·기후 변동성이 재난 관리에 미치는 정량적 영향을 제시하였다. 본 연구는 중·장기 기후 예측 정보를 재난 관리 의사결정에 과학적으로 통합할 수 있는 실효적 기반을 제공할 것으로 기대한다.
-
Integrated flood risk assessment of domestic local governments using the Delphi-AHP technique
-
Research Article
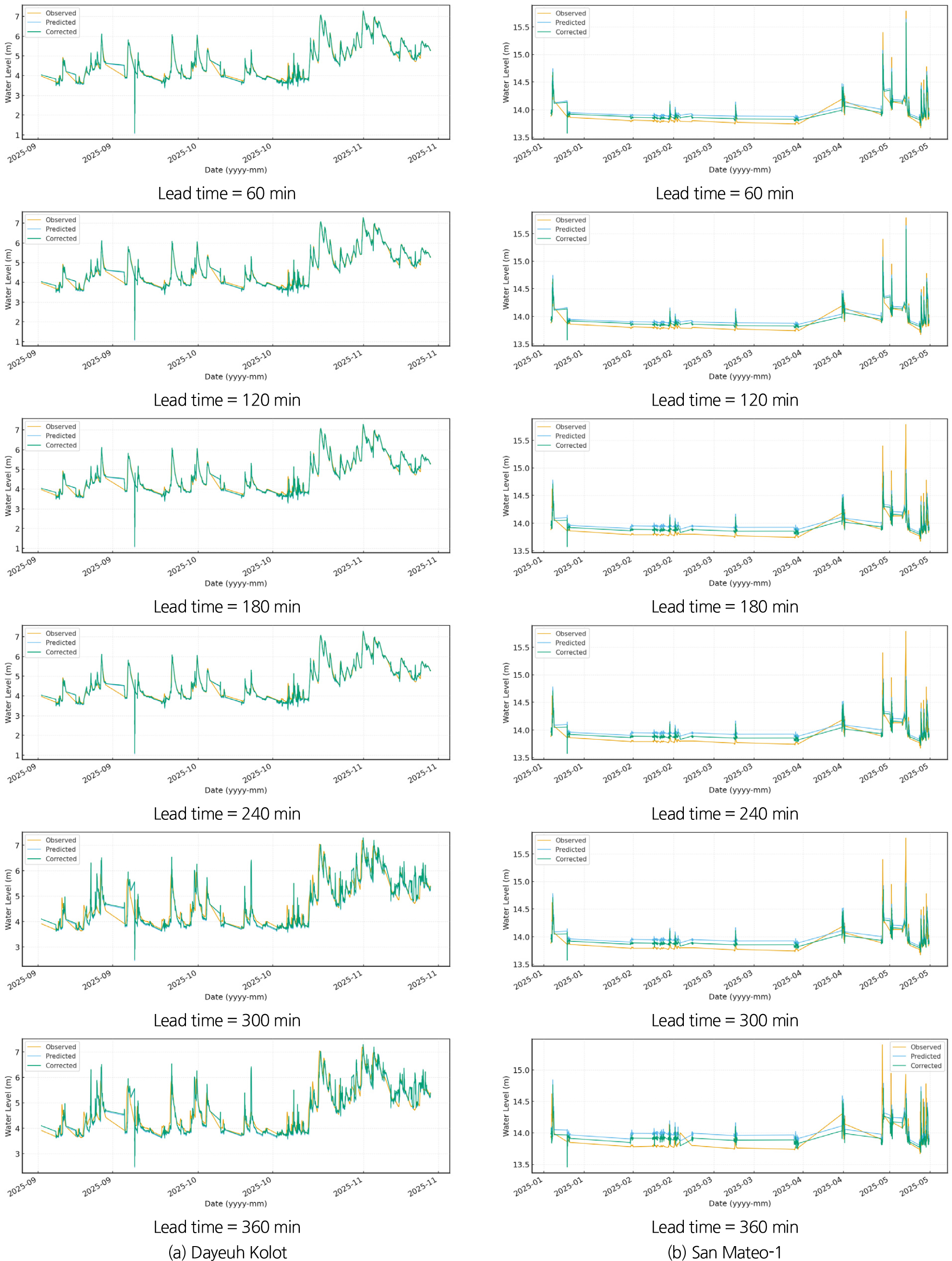
-
Real-time reliability assessment and RMSE-based correction for LSTM flood forecasting models
LSTM 홍수예측모형의 실시간 신뢰도 평가 및 RMSE 기반 보정기법 개발
-
Lee, SeunghoㆍKim, SooyoungㆍLim, JaeyeonㆍYoon, Kwang Seok
이승호, 김수영, 임재연, 윤광석
- This study proposes an RMSE-based continuous bias-correction method to evaluate real-time reliability and improve prediction accuracy of LSTM-based flood forecasting models. Although …
본 연구에서는 LSTM 기반 홍수예측모형의 실시간 신뢰도 평가 및 예측 정확도 향상을 위해 RMSE(Root Mean Squared Error)를 활용한 연속 편의 보정 기법을 …
- This study proposes an RMSE-based continuous bias-correction method to evaluate real-time reliability and improve prediction accuracy of LSTM-based flood forecasting models. Although the Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency (NSE) is effective for evaluating the overall fit of a complete time series, it often over-represents low-flow periods and fails to accurately reflect prediction performance during flood events. To address this limitation, the real-time prediction error RMSE was computed by integrating forecast errors across all lead times (10–360 min) at each prediction time. A real-time performance index was then defined based on the relative magnitude of RMSE compared with the reference error RMSE. In addition, a continuous error-correction equation incorporating lead-time-dependent prediction bias was applied to derive real-time corrected water-level forecasts. Application of the proposed method using observed and predicted water-level datasets demonstrated that RMSE decreased by approximately 1~5% at the Dayeuh Kolot station and by more than 10% during rapid rising-limb conditions at the San Mateo station. These results indicate that the proposed reliability-based correction method effectively improves prediction accuracy under diverse hydrological conditions. Owing to its lightweight structure, the method can be readily integrated as a post-processing module into real-time flood forecasting and warning systems using single-model LSTM architectures.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 LSTM 기반 홍수예측모형의 실시간 신뢰도 평가 및 예측 정확도 향상을 위해 RMSE(Root Mean Squared Error)를 활용한 연속 편의 보정 기법을 제안하였다. 기존의 NSE(Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency coefficiency)는 전체 시계열의 평균 적합도를 평가하는 데에는 유효하나, 저수위 구간의 영향이 과대하게 반영되어 홍수사상에 대한 예측 성능을 정확히 표현하지 못하는 한계가 존재한다. 이를 보완하기 위해 본 연구에서는 예측시점에서 예측선행시간별(10~360분)의 예측오차를 통합한 RMSE를 산정하고, 이를 활용하여 레퍼런스 RMSE를 산정하고 비교하여 실시간 예측 성능지표를 정의하였다. 또한 예측선행시간별 평균 편의(Bias)를 반영한 연속 오차보정식을 적용하여 실시간 보정 예측값을 산출하였다. 관측 자료와 예측 결과를 활용한 적용성 평가 결과, 인도네시아 Dayeuh Kolot 수위관측소 지점에서는 약 1~5% 정도의 RMSE값 감소가 있었고, 필리핀 San Mateo-1 수위관측소 지점에서는 급격한 수위 상승 구간에서 10% 이상의 감소가 확인되어, 제안된 기법이 다양한 수문학적 조건에서 예측 정확도를 개선시키는데 효과적임을 확인하였다. 본 연구에서 제안한 실시간 성능지표 기반 보정기법은 단일 LSTM 구조에 직접 적용 가능한 경량 후처리 방식으로, 향후 국내·외 홍수예경보 시스템의 실시간 예측 신뢰도 향상에 활용될 수 있다.
-
Real-time reliability assessment and RMSE-based correction for LSTM flood forecasting models
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of Korea Water Resources Association
Journal of Korea Water Resources Association
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of Korea Water Resources Association
Journal of Korea Water Resources Association