-
Research Article
-
Foundation model for waterbody segmentation based on ground camera images
수체 영역 분할을 위한 지상 카메라 이미지 기반 파운데이션 모델 활용 연구
-
Kim, JinyongㆍKim, SoheeㆍJung, Donghwi
김진용, 김소희, 정동휘
- With the increasing flash floods due to climate change, real-time flood detection methods have gained significant attention. For real-time flood detection, ground-based …
기후 변화로 인해 돌발 홍수가 증가함에 따라 실시간 홍수 탐지 방법이 주목받고 있다. 실시간 홍수 탐지 목적으로는 주로 지상 카메라 이미지가 사용되며, …
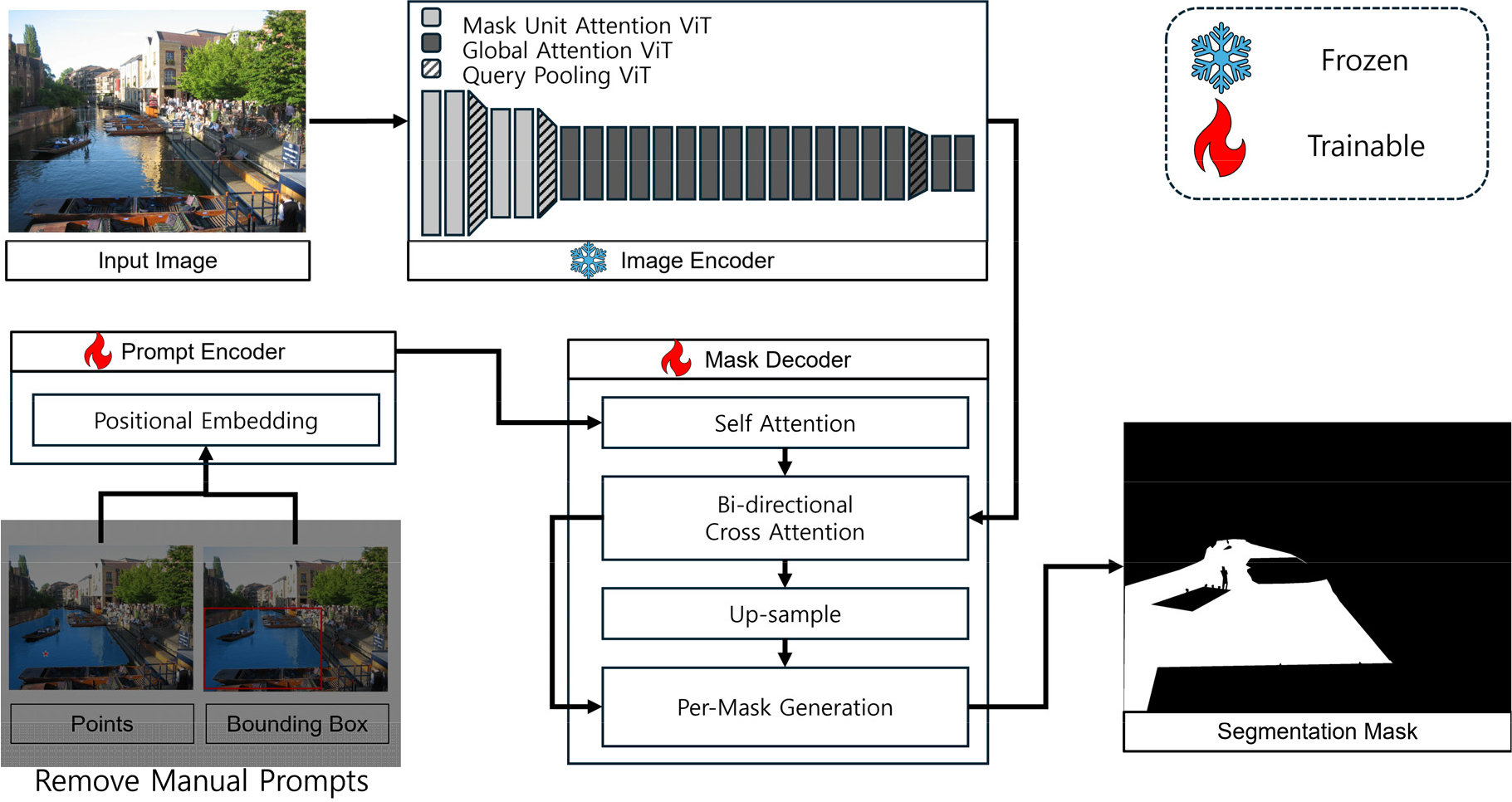
- With the increasing flash floods due to climate change, real-time flood detection methods have gained significant attention. For real-time flood detection, ground-based camera images are primarily used. Unlike satellite images, deep learning-based waterbody segmentation techniques are applied to handle the high variability of waterbody segmentation. To address the challenge of constructing a large volume of ground truth images, Segment Anything Model 2(SAM 2), based on the foundation model and the concept of prompts, has been proposed. Applying this model to flood detection is expected to enable high-accuracy waterbody segmentation with relatively small training datasets through fine-tuning. Therefore, this study proposes an advanced waterbody segmentation model based on SAM 2 and compares their performance with the existing model (V-FloodNet). The improved model, which selectively applies prompts, achieved a 10% improvement in performance compared to the existing model, demonstrating higher accuracy and greater efficiency in the segmentation process.
- COLLAPSE
기후 변화로 인해 돌발 홍수가 증가함에 따라 실시간 홍수 탐지 방법이 주목받고 있다. 실시간 홍수 탐지 목적으로는 주로 지상 카메라 이미지가 사용되며, 위성 이미지와는 달리 변동성이 큰 수체 영역 분할을 위해 딥러닝 기반 수체 영역 분할 기법이 적용되고 있다. 방대한 양의 참값 이미지 구축의 어려움을 해결하기 위해 파운데이션 모델과 프롬프트 개념을 기반으로 한 Segment Anything Model 2(SAM 2)가 제안되었으며, 이를 홍수 탐지에 적용하면 비교적 적은 학습 데이터로도 미세 조정을 통해 높은 정확도의 수체 영역 분할이 가능할 것으로 예상된다. 본 연구에서는 SAM 2 모델의 구조를 개선하여 수체 영역 분할 모델을 구축하고, 기존 모델(V-FloodNet)과의 성능을 비교하였다. 프롬프트를 선택적으로 적용하도록 개선된 모델은 기존 모델 대비 성능이 10% 향상되었으며, 더 높은 정확성과 분할 과정에서의 효율성을 확보한 것으로 확인되었다.
-
Foundation model for waterbody segmentation based on ground camera images
-
Research Article / 우수학생논문상
-
Pedestrian stability assessment and applicability analysis based on human model experiments in inundated flows
인체모형 실험을 통한 침수 흐름 내 보행 안정성 평가 및 적용 가능성 분석
-
Kim, MinjaeㆍPark, JoungjunㆍLee, IlwhaㆍPark, Inhwan
김민재, 박정준, 이일화, 박인환
- Frequent occurrences of heavy rainfall caused by climate change have increased the risk of urban and underground space flooding, posing significant threats …
기후 변화로 인한 집중 강우의 빈번한 발생은 도시 및 지하 공간의 침수 위험을 증가시키며, 지하철역과 같은 지하 공간에서 보행자의 안전성을 심각하게 위협한다. …
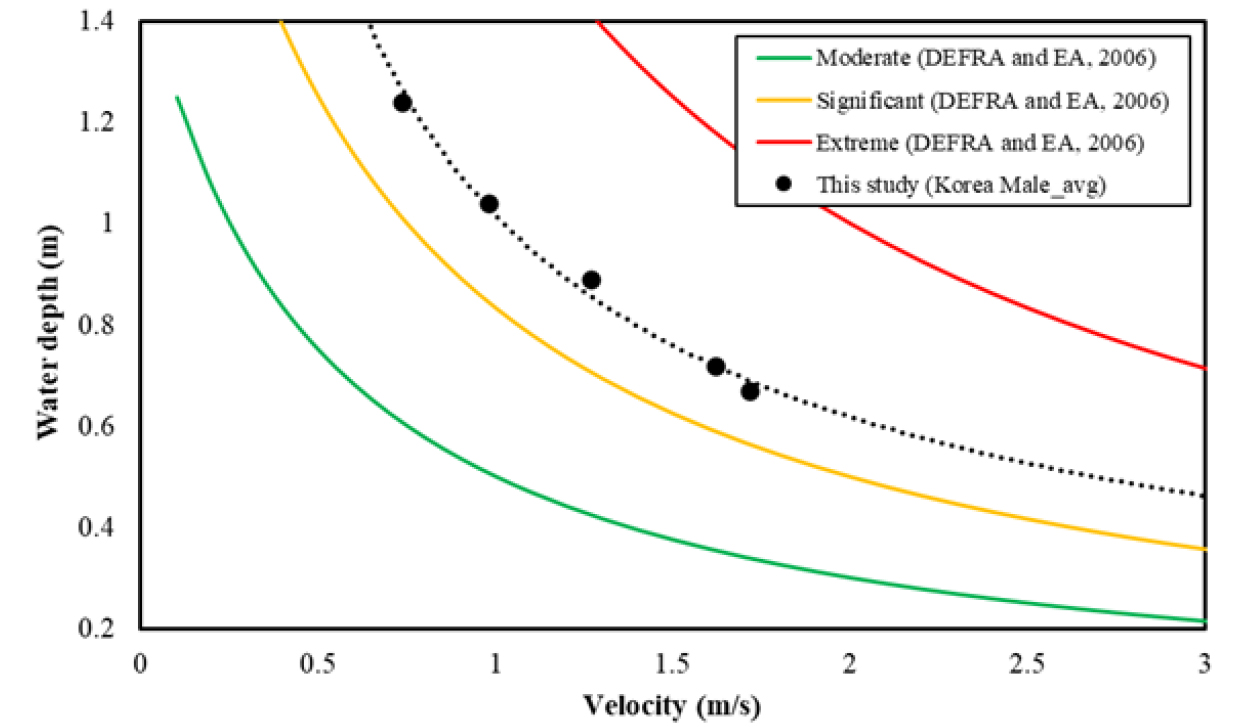
- Frequent occurrences of heavy rainfall caused by climate change have increased the risk of urban and underground space flooding, posing significant threats to pedestrian safety in subway stations. This study conducted lab-scale experiments to derive pedestrian stability conditions on subway platforms under flooding events. To demonstrate the toppling accident of a human body due to inundation flow, a human body model was designed considering mass similitude. By varying the inundation flow conditions, the flow conditions causing a toppling accident were determined, and based on these results, the relationship between walking threshold velocity and water depth (U-H relationship) was derived. The U-H relationship demonstrated a nonlinear decrease in inundation depth with increasing flow velocity. These findings can be utilized to quantitatively assess the threshold conditions by which toppling accidents occur as flow velocity increases. The applicability of the U-H relationship derived from laboratory-scale experiments to real-world inundation flow conditions was evaluated by comparing it with prototype experiments. Compared to previous experiments using human body models, this study presented more appropriate U-H relationship for pedestrian stability.
- COLLAPSE
기후 변화로 인한 집중 강우의 빈번한 발생은 도시 및 지하 공간의 침수 위험을 증가시키며, 지하철역과 같은 지하 공간에서 보행자의 안전성을 심각하게 위협한다. 본 연구에서는 이러한 침수 상황에서 지하철 플랫폼 내 보행자의 보행 안정성을 평가하기 위한 보행 한계 조건 도출을 위한 실험을 수행했다. 실험실 규모에서 침수 흐름에 의해 인체가 균형을 잃고 넘어지는 현상을 재현하기 위해 질량 상사(mass similitude)를 고려한 인체모형을 제작했다. 침수 흐름 조건을 변화시키며 인체모형이 넘어지는 흐름조건을 도출하였으며, 이 결과로부터 보행 한계 유속-수심 관계(U-H 관계)를 제시했다. U-H 관계로부터 유속 증가에 따라 보행 한계 수심이 비선형적으로 감소하는 경향을 보여주며, 이 결과는 보행자가 유속 증가에 따라 안정성을 잃는 조건을 정량적으로 평가하는데 활용 가능하다. 실험실 규모에서 도출된 U-H 관계의 실제 침수 흐름 상황에 대한 적용 가능성 평가를 위해 실규모 보행 안전 실험 결과와 비교하였으며, 기존 인체모형 실험 결과와 비교하여 실제 보행 한계 흐름 조건을 더 적절하게 제시했다.
-
Pedestrian stability assessment and applicability analysis based on human model experiments in inundated flows
-
Research Article
-
Development of a cascade watershed water balance model for agricultural water analysis
농업용수 분석을 위한 유역 연계 물수지 분석 모델 개발
-
Yoon, Dong-HyunㆍNam, Won-HoㆍJung, Suk-JaeㆍOh, Ji-HwanㆍKim, Kyung-MoㆍJo, Young-JunㆍPark, Jin-Hyeon
윤동현, 남원호, 정석제, 오지환, 김경모, 조영준, 박진현
- The quantitative assessment of agricultural water balance is a key component of water management policies for agricultural water resources. However, accurately estimating …
농업용수의 정량적인 물수지 파악은 물관리 정책 및 농업용수의 정량화, 과학적 관리 측면에서 핵심적인 요소이다. 현재 농업용수는 국가 주요 물관리 계획에서 수행되고 있는 …
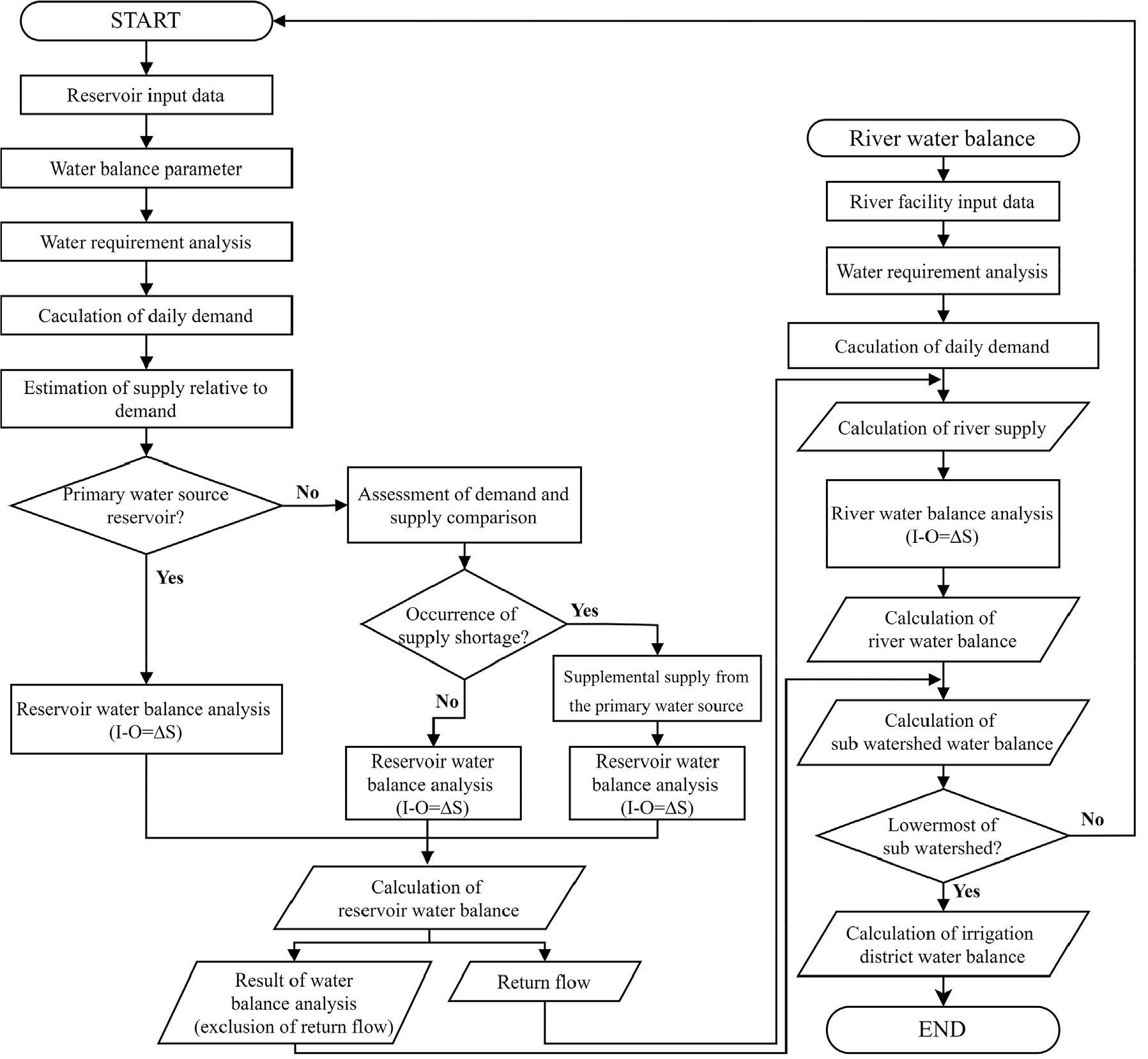
- The quantitative assessment of agricultural water balance is a key component of water management policies for agricultural water resources. However, accurately estimating agricultural water usage remains challenging due to conventional water management practices and the lack of fundamental data. Currently, agricultural water is estimated through water balance analyses conducted as part of major national water management plans. However, these analyses have methodological and data limitations, which can be categorized into three major issues. First, the agricultural water analysis in the First National Water Management Plan does not distinguish between water sources, such as reservoirs and river facilities, leading to an unrealistic representation of agricultural water supply and causing distortions in the estimation of water deficits and return flows. Second, the application of a uniform return flow rate results in inaccuracies in both supply and return flow estimations. Third, the Agricultural and Rural Water Use Rationalization Plan excludes river water balance assessments, overlooking the interconnections between facilities and river-based water systems. This study aims to develop a model that addresses these limitations. The research focuses on the mid-watershed of Anseongcheon, establishing the topological relationships of individual facilities based on river flow within sub-watersheds and constructing a water balance network that reflects watershed connectivity. The annual water demand and return flow rates, derived from rural water district water balance analyses, were integrated into the national water supply model, allowing for the incorporation of daily demand patterns on an annual scale for agricultural water balance analysis. Finally, the applicability of the developed model was assessed by comparing conventional MODSIM analysis results with integrated analysis results for the Anseongcheon mid-watershed.
- COLLAPSE
농업용수의 정량적인 물수지 파악은 물관리 정책 및 농업용수의 정량화, 과학적 관리 측면에서 핵심적인 요소이다. 현재 농업용수는 국가 주요 물관리 계획에서 수행되고 있는 물수지 분석을 통해 추정하고 있으나 기초자료 확보 및 방법론적 측면에서 한계가 있다. 주요한 한계점으로 첫째, 제1차 국가물관리계획 내 농업용수 분석은 저수지와 하천시설과 같은 수원공 구분이 적용되지 않아 실제와는 다른 농업용수 공급 개념이 반영되어 있으며, 이에 따라 부족량 및 회귀량 산정에 왜곡이 발생하고 있다. 둘째, 순물소모량 개념의 일률적 회귀율 반영으로 농업용수 공급량의 왜곡 및 하천 물수지에서의 회귀량 왜곡이 발생하고 있다. 셋째, 농어촌용수 이용 합리화계획의 경우 하천 물수지를 배제하여 시설물 및 하천 기반의 연계가 누락되어 있다. 본 연구에서는 이러한 한계점을 개선하고자, 기존 모델의 네트워크 및 주요 인자 개선과 하천 물수지 알고리즘을 포함한 모델을 개발하고 국가 물수지 모델인 MODSIM 연계를 통해 활용성을 평가하고자 한다. 안성천 중권역을 대상으로 소유역 내 하천 흐름에 따른 개별 시설물의 위상 관계를 정립하였으며, 유역 연계 기반 물수지 네트워크를 구축하였다. 용수구역 내 수원공별 물수지 분석 결과 중 연별 수요량과 회귀율 결과를 국가 물수급 모델에 연계 적용하였으며, 연 단위 일별 수요 패턴을 반영하여 농업용수 물수지를 분석하였다. 또한, 안성천 중권역을 대상으로 용수구역 내 수원공별 물수지 분석 결과 중 연별 수요량과 회귀율 결과를 MODSIM에 연계 적용하였다.
-
Development of a cascade watershed water balance model for agricultural water analysis
-
Research Article
-
Optimal implementation of LID facilities in the mid-upper Youngsan River basin for runoff reduction performance and economic efficiency
유출 저감 성능 및 경제적 효율성을 고려한 영산강 중상류 유역의 최적 LID 시설 적용 방안
-
Kim, MinjeongㆍPark, InhwanㆍChae, Seung Taek
김민정, 박인환, 채승택
- This study aims to determine the optimal Low Impact Development (LID) implementation strategies considering runoff reduction performance and economic efficiency in the …
본 연구에서는 영산강 중상류 유역을 대상으로 유출 저감 성능과 경제성을 고려한 최적 Low Impact Development (LID) 적용 방안을 결정하였다. 강우-유출 및 LID …
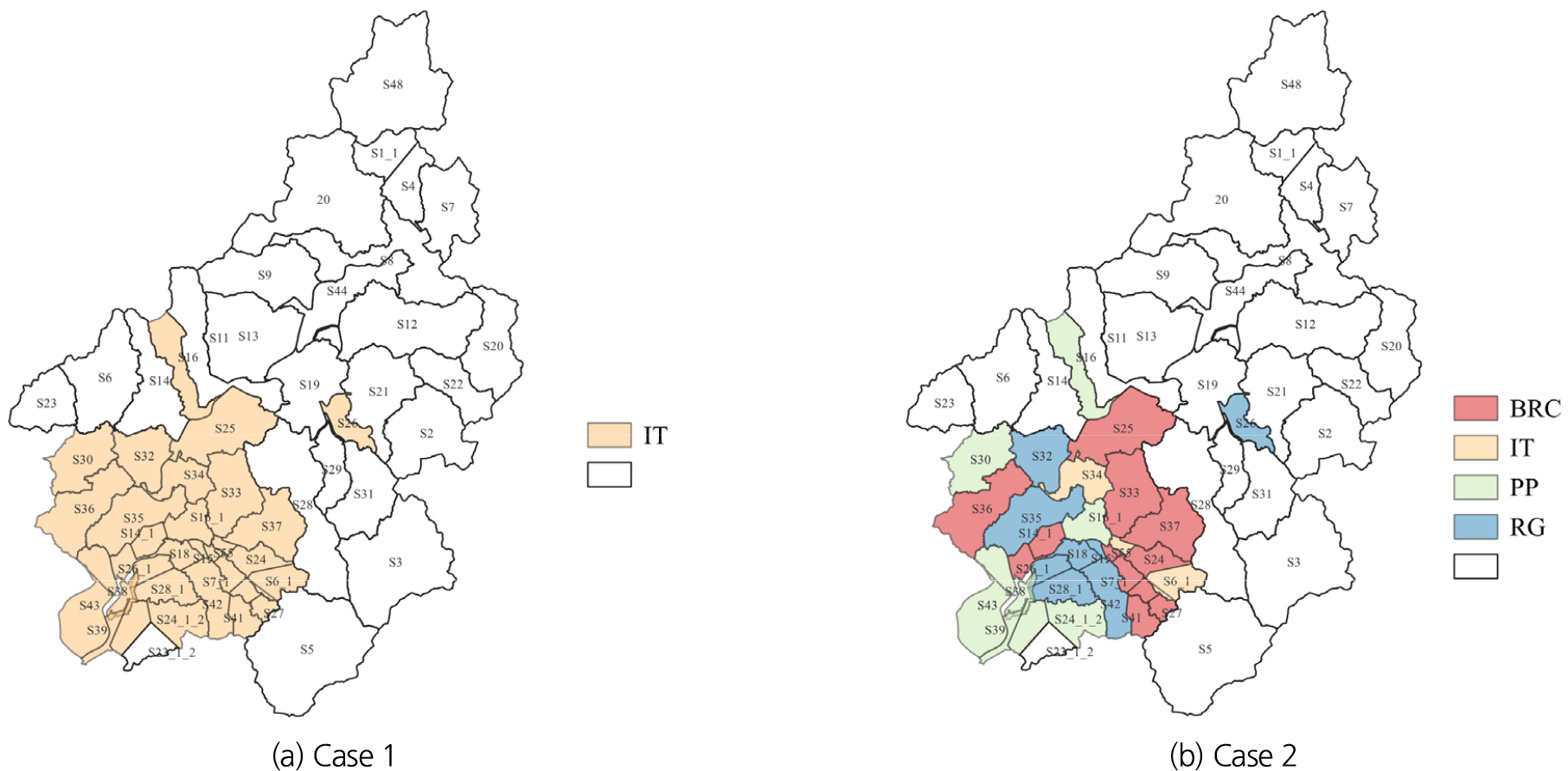
- This study aims to determine the optimal Low Impact Development (LID) implementation strategies considering runoff reduction performance and economic efficiency in the mid-upper region of the Youngsan River basin. The Storm Water Management Model (SWMM) was used to simulate rainfall-runoff processes and LID implementation strategies. The study focused on areas with an impervious surface ratio exceeding 50%, comparing the optimal design parameters and runoff reduction performance of Permeable Pavement (PP), Infiltration Trench (IT), Bio-Retention Cell (BRC), and Rain Garden (RG). To optimize the design parameters of these LID facilities two approaches were applied: (Case 1) determining a single design parameter minimizing total runoff across the entire study area and (Case 2) determining individual design parameters that minimize runoff for each sub-watershed. The comparison of runoff reduction performance between the two cases showed that Case 2 showed superior runoff reduction performance compared to Case 1. In Case 1, IT was identified as the optimal facility in all sub-watersheds, whereas Case 2 resulted in different optimal LID facility types depending on the runoff characteristics of each sub-watershed. In Case 2, BRC was determined as the most frequently selected facility. When considering the economic efficiency of construction and maintenance costs, RG demonstrated the highest cost-effectiveness in runoff mitigation for both cases. Consequently, applying the optimal LID facility allocation strategy that accounts for both runoff reduction performance and economic efficiency resulted in a total runoff reduction of 6.36% in Case 1 and 7.16% in Case 2.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 영산강 중상류 유역을 대상으로 유출 저감 성능과 경제성을 고려한 최적 Low Impact Development (LID) 적용 방안을 결정하였다. 강우-유출 및 LID 적용 전략을 모의하기 위해 Storm Water Management Model (SWMM)을 사용하였으며, 불투수면적 비율 50% 이상 지역에 대해 Permeable Pavement (PP), Infiltration Trench (IT), Bio-Retention Cell (BRC), Rain Garden(RG)의 최적 설계 인자 결정 및 유출 저감 성능을 비교했다. 최적 설계 인자는 영역 전체의 유출량을 최소화하는 단일 설계 인자를 결정하는 방법(Case 1)과 개별 소유역의 유출량을 최소화하는 개별 설계 인자를 결정하는 방법(Case 2)을 각각 적용하여 결정했다. Case 1과 Case 2에서 결정된 최적 설계 인자를 적용하여 유출 저감 성능을 비교한 결과, Case 1보다 Case 2의 설계 인자를 적용했을 때 유출 저감 능력이 향상되었다. Case 1의 설계 인자를 적용했을 때 모든 소유역에서 IT가 최적 시설로 결정됐고 Case 2에서는 유역의 유출 특성에 따라 서로 다른 최적 LID 시설 유형이 결정됐고 이중 BRC가 가장 많은 소유역에서 최적 시설로 결정됐다. LID의 설치 및 유지관리 비용의 경제성을 함께 고려한 경우에는 Case 1과 Case 2 모두 RG의 비용 대비 홍수 저감 효율이 다른 시설에 비해 효과적인 것으로 나타났다. 이에 따라 유출 저감 성능과 경제성을 모두 고려한 LID 시설 최적 배치안을 적용한 경우 Case 1에서는 6.36%, Case 2에서 7.16%의 총유출량 저감 효과를 나타냈다.
-
Optimal implementation of LID facilities in the mid-upper Youngsan River basin for runoff reduction performance and economic efficiency
-
Research Article
-
Analysis of flow rate variation by mixed flow in a drainage pipe using numerical simulation
수치모의를 이용한 배수관로의 혼합 흐름에 의한 유량 변동성 해석
-
Lee, Du HanㆍRhee, Dong Sop
이두한, 이동섭
- This study analyzes the characteristics of mixed flow occurring in a drainage pipe due to unsteady inflow using a numerical model. The …
본 연구는 부정류 유입 흐름으로 배수관로에서 발생하는 혼합 흐름 특성을 수치모형을 이용하여 분석하였다. 수치모형은 OpenFoam의 interIsoFoam 솔버를 이용하여 공기와 물의 경계면을 보다 …
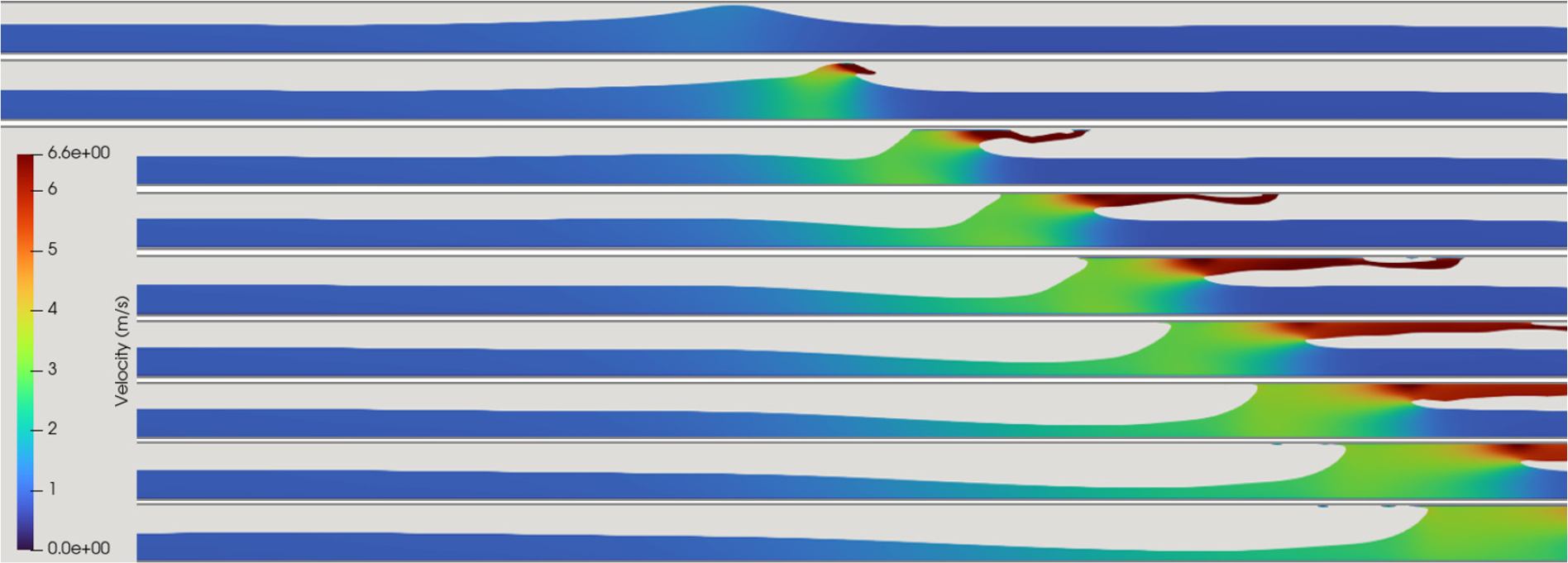
- This study analyzes the characteristics of mixed flow occurring in a drainage pipe due to unsteady inflow using a numerical model. The numerical model utilizes the interIsoFoam solver in OpenFOAM to more accurately simulate the interface between air and water. To validate the model, it is applied to a slug flow experiment, demonstrating that the model effectively reproduces slug formation caused by water surface surges, as well as the movement and development of slugs. The characteristics of mixed flow in the pipe are simulated in a two-dimensional vertical plane under various air and water inflow conditions. To reproduce the unsteady nature of the water surface at the inlet boundary, a sinusoidal vertical velocity boundary condition is applied. Additionally, to analyze the flow rate variability induced by the mixed flow, the maximum outflow rate is calculated and compared against the inflow rate. Nine different mixed flow conditions are simulated. The results show that when both water and air velocities are sufficiently high, slugs formed and developed, leading to a maximum flow rate variability of 112.5%. In three-dimensional simulations, pressure flow is found to be more dominant, and the formation and development of the air layer differed from the two-dimensional results. In drainage pipes, the unsteady fluctuations in the inlet water level increase the likelihood of mixed flow formation. However, for mixed flow to persist along the pipeline and result in significant flow rate variability, sustained slug formation and development are necessary. This persistence depends on both the magnitudes of water and air velocities and their relative proportions.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 부정류 유입 흐름으로 배수관로에서 발생하는 혼합 흐름 특성을 수치모형을 이용하여 분석하였다. 수치모형은 OpenFoam의 interIsoFoam 솔버를 이용하여 공기와 물의 경계면을 보다 정확하게 모의하고자 하였다. 모형 검증을 위해 슬러그 흐름 실험에 적용하였으며, 수면 처오름에 의한 슬러그 형성과 슬러그의 이동 및 발달 과정을 잘 재현하는 것으로 나타났다. 다양한 공기와 물의 유입 조건에 따라 관로 내의 혼합 흐름 특성을 연직 2차원으로 모의하였다. 유입 경계에서 수면의 부정류 특성을 재현하기 위하여 사인함수 형태의 연직 유속 경계를 설정하였으며 혼합 흐름에 의한 유량 변동성을 해석하기 위하여 유입 유량에 대한 최대 유출 유량을 계산하여 비교하였다. 9개 조건의 혼합 흐름 모의를 수행하였으며 모의 결과에 의하면 물 유속과 공기 유속이 어느 정도 큰 경우 슬러그가 형성되어 발달하게 되며 이 경우에 유량 변동성이 최대 112.5%로 크게 나타났다. 3차원 모의에서는 압력 흐름이 보다 지배적이며 공기층의 형성과 발달이 상이함을 확인하였다. 배수관로는 유입 경계의 수위 요동으로 혼합 흐름이 형성될 가능성이 높으나 관로를 따라 혼합 흐름이 지속되고 유량 변동성이 커지기 위해서는 슬러그의 지속 또는 발달이 필요한데, 이는 물 유속과 공기 유속의 크기와 두 유속의 상대적 크기에 의존하는 것으로 판단된다.
-
Analysis of flow rate variation by mixed flow in a drainage pipe using numerical simulation
-
Policy Note
-
Current status and prospects of Korea’s implementation of the integrated water resources management indicator (SDG 6.5.1)
우리나라 통합물관리 지표(SDG6.5.1)의 이행 현황과 전망
-
Chung, Il-MoonㆍLee, Jeong Eun
정일문, 이정은
- This study aims to assess and improve Korea's integrated water management governance by focusing on the SDG 6.5.1 indicator, as outlined in …
본 연구는 2024년 발간된 유엔환경계획(United Nations Environment Programme, UNEP)의 SDG 6.5.1 지표 보고서를 중심으로, 한국의 통합물관리 거버넌스를 진단하고 개선 방향을 제시한 것이다. …
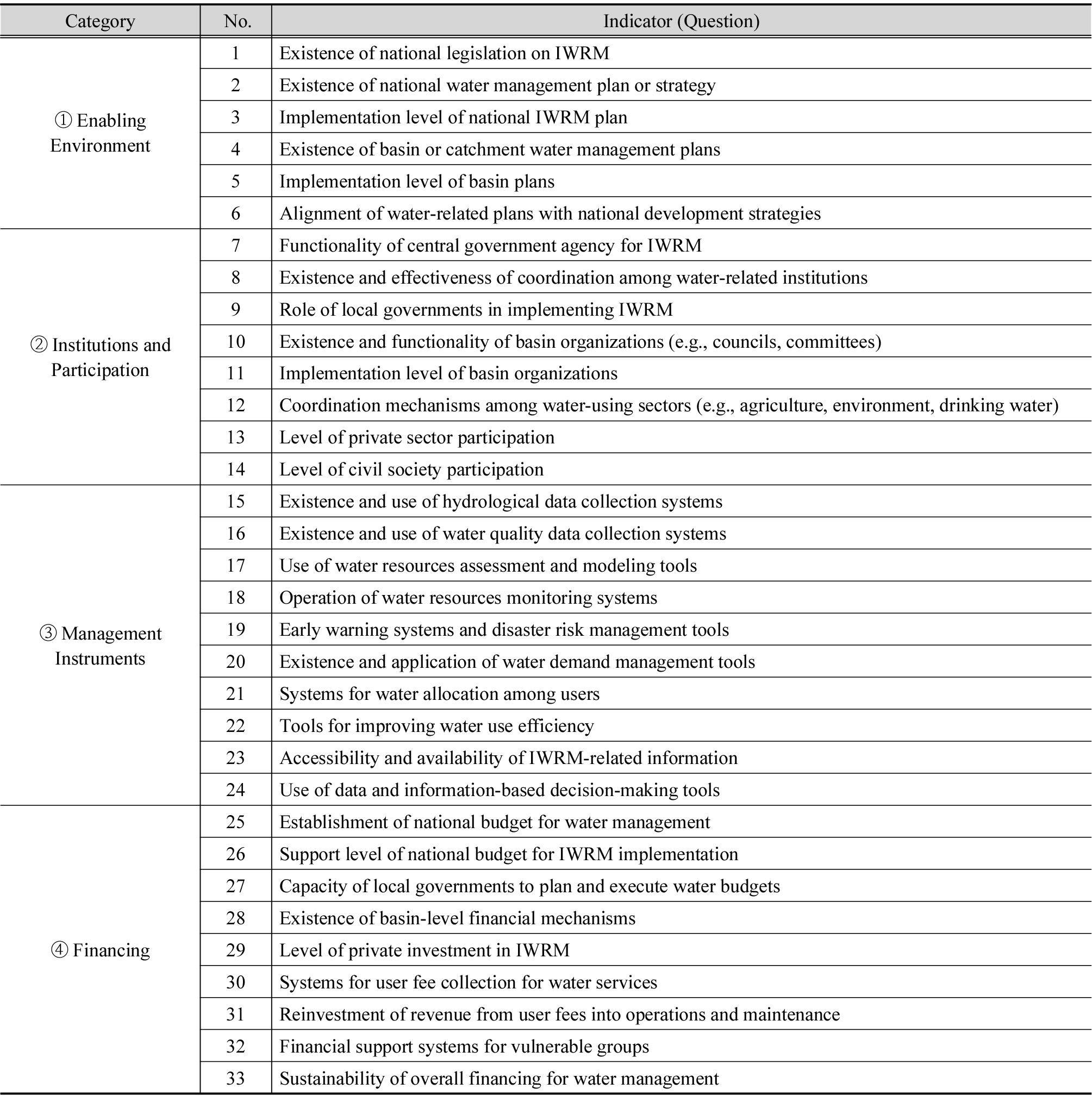
- This study aims to assess and improve Korea's integrated water management governance by focusing on the SDG 6.5.1 indicator, as outlined in the latest 2024 report published by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). The analysis is structured around four key components: (1) global implementation trends of the SDG 6.5.1 indicator, (2) Korea’s year-by-year performance and structural characteristics, (3) category-based comparison and SWOT analysis, and (4) formulation of policy recommendations. While Korea achieved high scores in institutional arrangements and policy frameworks, limitations were identified in local implementation capacity, diversification of financial mechanisms, and the internalization of participatory governance. Globally, the progress toward achieving SDG 6.5.1 remains insufficient, suggesting that current trends may fall short of the 2030 target. Therefore, the study calls for mid- to long-term strategies that go beyond short-term performance-driven approaches. Furthermore, the study highlights the potential of the SDG 6.5.1 indicator not only as a reporting tool but also as a framework for evaluating national water policies and facilitating international cooperation.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 2024년 발간된 유엔환경계획(United Nations Environment Programme, UNEP)의 SDG 6.5.1 지표 보고서를 중심으로, 한국의 통합물관리 거버넌스를 진단하고 개선 방향을 제시한 것이다. 이를 위해 (1) SDG 6.5.1 지표에 대한 글로벌 이행 동향 분석, (2) 우리나라의 연도별 점수 변화 및 특성 평가, (3) 범주별 비교 및 SWOT 분석, (4) 정책적 시사점 도출을 수행하였다. 분석 결과, 한국은 제도 정비와 정책 체계 부문에서 높은 점수를 기록했으나, 지방정부의 실행 역량, 재정 구조의 다양성, 시민 참여 기반의 거버넌스 확보 측면에서는 한계가 확인되었다. 또한 전 세계적으로 SDG 6.5.1 지표의 이행 속도는 목표 연도인 2030년 달성을 보장하기 어려운 수준이며, 이에 따라 단기 성과주의를 넘는 중장기 전략의 수립이 필요함을 제언한다. 또한 본 연구는 SDG 6.5.1 지표가 단순한 보고 지표를 넘어, 국내 물 정책 평가와 국제 협력의 매개로 활용될 수 있는 가능성도 제시하고자 한다.
-
Current status and prospects of Korea’s implementation of the integrated water resources management indicator (SDG 6.5.1)
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of Korea Water Resources Association
Journal of Korea Water Resources Association
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of Korea Water Resources Association
Journal of Korea Water Resources Association