1. 서 론
2. 연구 방법
3. 국내 하구 관련 연구 동향
3.1 국내 주요 하구
3.2 물리·화학·생태학적 특성 변화와 관리
3.3 생물학적 특성과 생태 모델
3.4 하구 생태계와 철새 서식지
3.5 하구역 환경관리와 개발
3.6 지속 가능성과 하구 생태계서비스 경제적 가치 평가
3.7 하구 관리의 법·제도적 측면과 통합적 접근
4. 결론 및 제언
1. 서 론
2022년 9월, 허리케인 이언으로 미국 플로리다의 템파 베이와 칼루사하치 강 하구에서는 심각한 홍수가 발생해 많은 사망자와 경제적 손실을 초래했다(Hauptman et al., 2024). 2023년 5월, 74년 만에 최악의 가뭄으로 우루과이는 물 부족 비상사태를 선포하고, 강 하구의 염분 높은 물을 식수로 활용하는 방안을 마련했다(Newstree, 2023). 최근 극단적인 기후 변화로 인해 풍수해 위험이 점차 증가하고 있으며, 하천과 하구에서 발생하는 홍수와 가뭄 문제는 지속 가능한 수자원 관리의 필요성을 더욱 부각시키고 있다. 또한, 예측하기 어려운 기후 변화로 인해 하천에 유입되는 쓰레기와 오염물질의 양이 증가하고 있어, 이를 해결하기 위한 지속 가능한 하구 관리 대책이 요구되는 시점이다.
하구는 육상과 해양생태계가 만나는 복합적이고 역동적인 환경으로, 물리적·화학적·생물학적 특성이 교차해 독특한 생태계를 형성한다. 그러나 과거 급격한 산업화와 도시 확장으로 낙동강, 한강, 금강, 영산강, 섬진강 하구의 생태적 건강성이 크게 훼손되었다. 이를 해결하기 위해 지난 20여 년간 하구의 물리적·화학적 변화, 생물학적 특성, 철새 서식지 보호와 환경 관리에 대한 다양한 연구가 이루어졌으며, 이를 기반으로 하구 복원, 수질 개선, 생태적 연결성 회복을 목표로 한 국내 정책과 사업들이 시행되고 있다.국내 하구는 총 463개로, 이 중 228개, 약 49%는 하굿둑 설치로 인해 물 순환이 차단된 닫힌 하구로 분류된다. 닫힌 하구는 전국적으로 다양한 지역에 분포하며, 홍수 방지와 농업용수 확보 등 여러 이점이 있지만, 물 순환이 차단됨에 따라 수질 악화, 생태계 파괴, 물 이용의 비효율성 등 하구의 자연적 흐름 제한으로 인해 생태계 건강성과 지역 간 물 자원 분배에 부정적인 영향을 미치고 있다. 한편, 2000년대 이후, 하구 관리의 패러다임은 개발 중심에서 생태계 보호 중심으로 전환되면서 생태계서비스의 중요성이 강조되었고, 경제 개발뿐만 아니라 자연 생태계의 유지와 보호가 장기적으로 사회적 이익을 가져온다는 인식이 확산되었다. 이에 따라 하구를 자연 자원으로 인식하고 생태적 기능 보존 관리 방안이 중요하게 강조되고 있다. 더불어 지속 가능한 관리와 복원이 하구 관리의 주요 과제로 부각되었으며, 하구 생태계 회복과 지속 가능한 관리를 위한 연구와 투자의 필요성이 제기되고 있다.
더욱이, 하구 생태계는 수문학적, 생태학적, 화학적, 지형적 연계를 통해 주변 환경과 밀접하게 연결되며, 유역, 하천, 연안 간의 다층적인 상호작용을 포함한다. 이러한 상호작용은 생태계서비스 혜택, 자원의 흐름, 경제적 상호의존성과 얽혀 있어 관리가 매우 복잡하며, 해결이 필요한 중요한 과제이다. 다양한 이해관계자와 행정 기관이 참여하는 다원화된 국내 하구 관리 체계의 한계점이 지적됨에 따라 하구 관련 법제도를 재검토하고, 통합적 하구관리 방안을 마련하는 연구의 중요성이 더욱 강조되고 있다.
따라서, 본 연구는 국내 주요 하구를 대상으로 지난 20여 년간 진행된 연구를 종합적으로 분석하고, 향후 연구와 관리 방향을 제시하고자 한다. 이를 위해 하구의 물리·화학적 특성 변화, 생물학적 특성 및 생태 모델, 하구 생태계와 철새 서식지, 하구역 환경관리와 개발, 지속가능성과 하구 생태계서비스 경제적 가치 평가, 하구 관리의 법·제도적 측면과 통합적 접근으로 구분하여 기존 연구를 검토하였다.
2. 연구 방법
본 연구는 국내 학술논문집에서 하구를 키워드로 기존 연구의 주요 내용을 검토하였다. 이를 위해 DBpia (http://www.dbpia.co.kr)에 수록된 국내 학술논문집을 분석하여, 주요 대표 강 하구에 대한 연구 동향을 살펴보았다. 검색 기간은 2001년부터 2023년 12월까지로, 낙동강 하구, 한강 하구, 금강 하구, 영산강 하구, 섬진강 하구를 검색어로 논문을 찾았으며, 연구 내용의 명확성과 타당성을 확보하기 위해 학술대회 발표집, 심포지엄 초록, 연구보고서 등은 제외하였다.
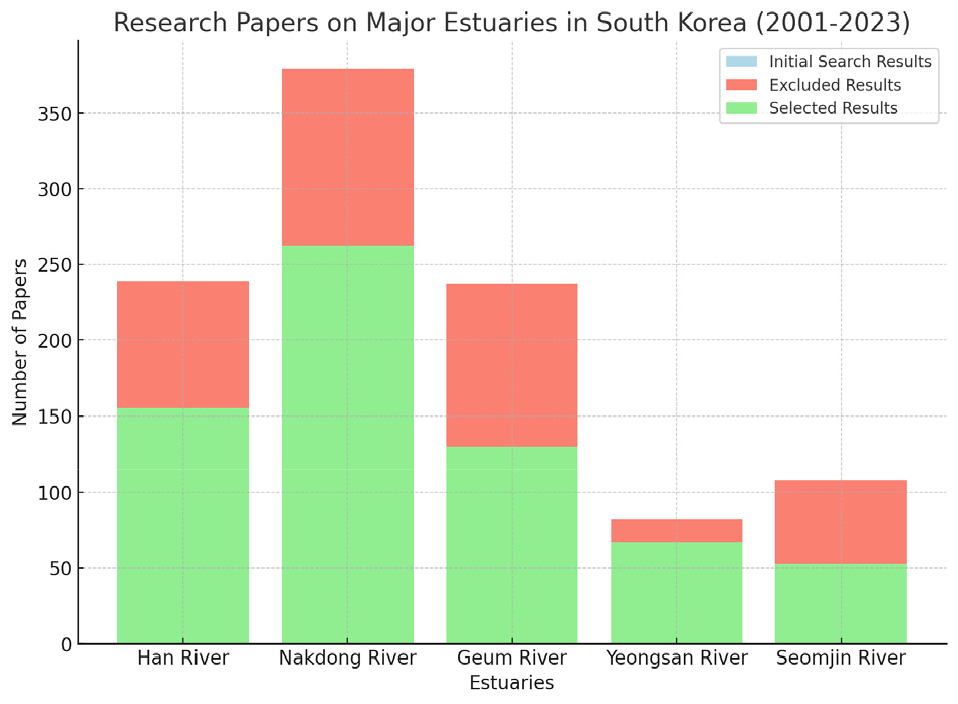
구체적인 검색 결과를 보면, 낙동강 하구는 총 379건 중 학술대회 자료 101건, 전문 잡지 9건, 연구보고서 7건을 제외하였다. 한강 하구는 239건 중 학술대회 자료 48건, 연구보고서 26건, 전문 잡지 9건, 동향 자료 1건을 제외하였다. 금강 하구는 237건 중 학술대회 자료 60건, 학위논문 40건, 연구보고서 2건, 전문 잡지 1건, 기타 4건을 제외하였다. 영산강 하구는 82건 중 학술대회 자료 15건을, 섬진강 하구는 91건 중 학술대회 자료 38건, 학위논문 17건을 제외하였다.
이로써 낙동강 하구 262편, 한강 하구 155편, 금강 하구 130편, 영산강 하구 67편, 섬진강 하구 53편으로 총 667편의 논문을 검토하였고, 이 중 사회, 경제, 환경적 측면을 고려해 총 125편을 선정하여 연구 동향을 분석하였다(Fig. 1).
3. 국내 하구 관련 연구 동향
3.1 국내 주요 하구
낙동강, 한강, 금강, 영산강, 섬진강 하구는 각기 다른 사회적, 경제적, 문화적 배경에 따라 다양한 관리 방식이 적용되고 있다. 각 하구는 농업, 어업, 생태 보전, 관광 등 다양한 사회적 가치를 지니고 있으며, 이러한 가치들이 복합적으로 얽혀 지역 발전과 환경 보존 간의 균형을 맞추는 것이 핵심 과제로 떠오르고 있다. 하천 상류에 건설된 댐과 보, 주요 하구에 설치된 하굿둑으로 인해 물 흐름이 제한되면서 하구 생태계와 수질이 변화하였고, 이에 따른 경제 이익 구조 변화로 다양한 이해관계자가 나타났다. 하굿둑 건설로 농업용수 확보와 홍수 예방 등 경제적 이익에 기여했지만, 어족 자원 감소와 수질 악화 등 생태계에 부정적인 변화도 초래되었다. 이로 인해 환경 보전과 경제 개발 간의 이해관계가 충돌하면서, 지역 사회 내에서 지속적인 갈등이 발생하고 있다.
낙동강 하구는 경상남도 창원시와 부산시에 걸쳐 있으며, 다른 하구와 달리 최근 일부 수문이 시범적으로 개방되어 생태계 회복과 수질 개선을 위한 연구 및 정책 논의가 진행 중이다. 특히 낙동강 하굿둑 수문 개방 시도는 하구 생태계 복원과 지역 경제 및 환경 보전의 균형을 찾기 위한 중요한 이슈로 부각되고 있다. 한강 하구는 서울, 경기, 인천을 포함한 수도권의 중심지로서 남북한을 연결하는 지정학적 중요성이 크며, 남북 관계와 관련하여 그 중요성이 더욱 강조된다. 금강 하구는 전라북도 군산시와 충청남도 서천군을 경계로 하며, 군산항과 서천 연안의 경제 활동과 밀접하게 연관되어 있다. 국내 주요 하구 관리 프로젝트 중 하나였던 금강 하굿둑은 농업용수 확보와 홍수 조절에 긍정적인 역할을 했지만, 어족 자원 감소와 수질 악화 등 환경 문제를 야기했다. 이러한 문제는 지역 생태계에 부정적인 영향을 미치며, 농업과 환경 보전 간의 갈등이 지속되고 있어 해결책이 필요하다. 영산강 하구는 전라남도 목포, 무안, 신안 지역을 중심으로 하굿둑 건설로 인해 감조하천의 특성이 사라지면서 자연 생태계가 크게 변화했다. 이로 인해 수질 악화와 어족 자원 감소, 수질 오염 문제가 심각해졌으며, 지역 주민들의 생활과 밀접하게 연관된 갈등이 존재하고 있다. 반면, 섬진강 하구는 전라남도 광양, 전라북도 순천, 경상남도 하동 지역에 걸쳐 있으며, 하굿둑이 설치되지 않아 비교적 양호한 생태계를 유지하고 있다.
3.2 물리·화학·생태학적 특성 변화와 관리
산업화, 도시화, 하천 정비, 수자원 개발 등 인간 활동은 하구 자연환경에 변화를 일으켜 물리·화학·생태학적 측면에 영향을 미쳤다. 이로 인해 수질, 수량, 염분 농도, 퇴적물 이동 등에 대한 연구가 활발히 이루어졌으며, 닫힌 하구에서는 퇴적물 축적, 생물다양성 감소, 조류 서식지 감소 등 하구 생태계 변화가 관찰되었다(Kim and Lee, 2007).
낙동강 하구와 주변 연안에 대한 연구는 표층 퇴적상과 퇴적환경 변화를 다루고 있다. 예를 들어, 낙동강 하구 갯벌의 사질 퇴적물에서 생지화학적 유기 탄소 순환을 분석하거나, 해양 퇴적토의 중금속 농도를 측정해 오염도를 평가하는 연구들이 있다(Kim and Ha, 2001; Lee et al., 2007b; Park and Ock, 2017; Lee et al., 2020; Shin, 2017). 낙동강 하구에서는 하굿둑 방류가 수질에 미치는 영향에 대한 연구가 지속적으로 이루어졌으며, 방류로 인해 해수질의 시공간적 변화가 관찰되었다(Yoon et al., 2008). 또한, CCHE2D 모형을 이용해 낙동강 하류 유사 특성과 유사량 공식 및 하상변동의 수치모의 결과를 분석한 연구도 있다(Ji et al., 2008). 하굿둑 방류에 따른 해저 변화를 연구하거나(Kim and Kim, 2021), GPS와 위성영상을 이용해 낙동강 하구 사주섬의 식생대를 비교하는 연구도 진행되었다(Lee et al., 2021). 이 외에도 위성영상과 GIS를 활용해 지형 변화와 해안선 변화를 탐지하는 다양한 연구가 있다(Jeon et al., 2021; Kim et al., 2017; Oh et al., 2010; Yoon et al., 2017; Kim et al., 2005; Lee et al., 2011a).
한강 하구 관련 연구는 연안과 경기만의 물리적 특성, 조위 불확실성, 퇴적물의 생태·화학적 반응 등을 다루고 있다(Yoon and Woo, 2012; Kim et al., 2008). 한강 하구역의 수질 및 퇴적물 특성의 공간적 분포를 분석하고, 오염물질 유입 위치와 계절적 요인이 수질에 미치는 영향을 조사한 연구도 있다(Lee and Kim, 2008). 또한, 조석파 전파 특성과 소류사 이동 특성을 분석한 연구가 조사되었고, GIS 기반 통합 수질 모의 시스템을 이용해 한강과 경기만의 수질을 예측하는 연구가 나타났다(Kang and Moon, 2001; Lee and Kim, 2008). QGIS와 LANDSAT 위성사진을 활용해 한강 하구의 하안선 변화를 연구하거나(Youn et al., 2021), 기후 변화와 개발로 인한 하상 구조 변화와 습지 형성을 조사한 연구도 진행되었다(Lee and Youn, 2022). 국내 연안 하구역의 지형적 특성을 분석하거나(Shin et al., 2006), 하구언 수문 작동에 따른 물리적 환경 변화를 다룬 연구도 있다(Lee et al., 2001). 금강 하구에서는 GIS 기법으로 수심 변화와 인공구조물이 수심 및 유속에 미치는 영향을 분석한 연구와 HF 레이더를 이용해 연안 표층 해류 유속을 분석한 연구가 이루어졌다(Hwang et al., 2011; Lee et al., 2007c; Park et al., 2012a; Lee and Um, 2007).
영산강 하구 관련 연구로는 3차원 수치모델(EFDC)을 이용해 여름철 퇴적물 이동 양상을 분석한 연구와 생태·환경 관리를 위한 GIS 기반 통합 DB 관리 시스템 개발 연구가 있다(Bang et al., 2013; Lee et al., 2014a). 하구호와 퇴적물 내 인의 생지화학적 특성을 나타내고 탄소와 질소 안정 동위원소를 비교한 연구도 진행되었다(Choi et al., 2020; Lee et al., 2013b). 섬진강 하구에서는 여름과 겨울철 부유 퇴적물 농도 변화, 부유 퇴적물 특성, 하상 변동 예측 연구가 이루어졌으며, 염분 분포가 부영양화와 수질 변화에 미치는 영향을 다룬 연구도 지속적으로 진행되었다(Kim et al., 2015c; Kim and Lee, 2004; Ceon and Kim, 2009; Noh et al., 2011).
낙동강 하구에서는 머신러닝을 이용한 염분 농도 예측 연구가 진행되었고, 한강 하구에서는 염분 분포와 생태 환경적 특성을 다룬 연구와 수위 관측을 통한 하구 특성 분석과 염분, 유속 분포 연구가 진행되었다(Han et al., 2011; Kim et al., 2010; Shin and Yoon, 2005; Yoon and Woo, 2011). MIKE21 확산 모형을 통해 경기만과 한강 하구의 염분, COD 농도 분포를 예측하고 불확실성을 분석하는 연구도 이루어졌다. 영산강 하구에서는 담수 방류 후 수질 변화를 분석한 연구가 나타났고(Kim and Jin, 2019; Kim and Shin, 2020), 섬진강 하구에서는 3차원 수치모델을 이용해 순환 구조와 염수 침입 특성을 분석한 연구가 나타났다(Kang et al., 2015). 장기적인 영양염류 유출량 변화와 방류량 증가로 인한 염수 침입 저감 효과를 분석한 연구도 진행되었다(Park et al., 2014; Park et al., 2012b). 이처럼 다양한 연구들이 주요 하구의 물리적·생태적 특성을 기반으로 환경 변화를 조사했으나, 미래 예측을 위한 기초 데이터 구축이 여전히 필요한 상황이다. 기존 연구들은 생태, 물리, 화학적 요소 등 각각 집중된 개별 분석이 많아, 통합적이고 지속 가능한 하구 관리 전략을 제시하는 데 한계가 있다(Lim et al., 2020). 더욱이 홍수와 가뭄 등 재해재난 대응과 기후 변화 시나리오를 기반으로 한 하구 수질 변화와 하구 생태계에 미치는 영향에 관한 연구가 상대적으로 부족한 것으로 판단된다.
3.3 생물학적 특성과 생태 모델
하구는 바닷물과 강물이 만나는 특수한 생태적 교차점으로, 염도, 수온, 영양염류 농도가 급격히 변해 플랑크톤 연구에 적합한 지역이다. 농업 활동에서 유입된 영양염류와 산업 폐수는 수질 오염을 일으켜 플랑크톤 군집 분포에 영향을 미치며, 플랑크톤 변화는 하구의 수질과 생태계 건강성을 평가하는 중요한 지표가 된다. 낙동강 하구 기존 연구로는 상류 지역 건설 사업 이후 식물 플랑크톤의 시·공간적 분포를 분석했고, 평수기와 태풍 통과 후 동물 플랑크톤 군집 분포를 비교한 연구가 이루어졌다(Yu et al., 2014; Ryu et al., 2016). 하굿둑 축조 전후의 어류상 변화, 환경적 변화와 계절적 영향을 고려한 생태계 반응 연구도 진행되었다(Ji and An, 2008). 한강 하구에서는 동물 플랑크톤의 행동 양상, 식물 플랑크톤 생체량, 수질 변화를 조사했으며(Sin et al., 2005), 조석에 따른 물리적 환경 변화와 식물 플랑크톤 크기 구조 변동, 여름철 담수 방류 시 Chlorophyll a 농도 변화를 다룬 연구가 나타났다(Yoon et al., 2013; Park and Sin, 2022). 이외에도 생태 하천 복원사업 우선순위를 선정하기 위해 하천의 물리적·화학적·수생태계 건강성 평가지수를 산정한 연구도 진행되었다(Baek et al., 2023). 금강 하구에서는 담수 식물 플랑크톤을 활용해 수생태계 건강성을 평가하고, 하굿둑 부근 미생물 군집 특성을 조사한 연구가 있다(Kim et al., 2018a; Park et al., 2017; Bae et al., 2005). 영산강과 섬진강 하구에서는 식물 플랑크톤 기원 색소 분포 변동 및 식물 플랑크톤과 박테리아 간 관계를 분석한 연구들이 진행되었다(Lee et al., 2017; Shin and Yu, 2018; Min et al., 2012; Na et al., 2012; Shin and Yoon, 2011; Kim and Shin, 2020). 영산강과 섬진강 하구에서는 수달 서식지 이용과 생태계 교란 식물 분포를 다룬 연구(Ha et al., 2020; Kim et al., 2019), 잘피 서식지의 해양 환경 특성과 계절에 따른 거머리말의 탄소·질소 성분 변화 분석(Ji et al., 2014; Kim et al., 2012), 주요 어종의 개체군 생태를 조사한 연구도 이루어졌다(Yang et al., 2012; Lee et al., 2022; Kim et al., 2013). 어류 군집 특성에 관한 연구로는 영산강과 섬진강 유역에서 저수지 크기에 따른 어류 군집 특성을 분석한 연구가 있다(Park et al., 2020; Lee et al., 2013a).
주요 하구에서 동·식물 플랑크톤 군집과 물리적 환경, 수생태계 건강성 간의 연관성을 연구했지만, 복잡한 생물학적 상호작용을 설명하는 데 한계가 있었다. 이를 보완하기 위해 해양-연안-하구가 연계된 정교한 생태 모델 개발과 생물학적 특성을 반영한 연구가 필요하며(Kim et al., 2015b), 하구 생태계의 복잡성과 생물학적 특성을 반영한 연구가 지속적으로 축적될 수 있도록, 현장 조사를 기반으로 한 지역별 연구의 통합적 관리가 필요하다고 판단된다.
3.4 하구 생태계와 철새 서식지
하구는 철새 이동 경로의 중요한 중간 기착지이자 조류의 생태 서식지로, 개발과 간척사업으로 인해 갯벌과 습지 서식지가 축소되었다. 이에 따라 낙동강 하구에서는 천연기념물 조류의 분포, 민물가마우지와 괭이갈매기의 장기적 이동 현황, 지역별 조류 특성을 분석한 연구들이 수행되었다(Hong, 2005, 2004; Hong and Hong, 2023). 특히, 4대강 사업 이전 철새 도래지 현황과 수면성 오리류, 물떼새류, 백로류, 쇠제비갈매기의 이동을 장기 모니터링하여 번식지 변화와 중간 기착지로서의 역할을 파악한 연구가 주목받았다(Kim et al., 2015a; Hong and Lee, 2010).
한강 하구는 재두루미의 주요 월동지이자 중간 기착지로, 재두루미 개체군 감소가 서식지에 미치는 영향을 분석하고, 하구 습지 훼손과 서식지 이용 현황을 다룬 연구들이 있었다(Kim and Lee, 2008). 또한, 한강 하구의 습지 공간 분포와 보호 지역에서 새섬매자기 개체군 감소 원인을 분석하고 복원 방안을 제시한 연구도 진행되었다(Yoo, 2008). 금강 하구에서는 조류 군집 특성, 보호·관리 방안에 대한 연구가 나타났다. 또한 충남 내 철새 도래지로 중요 지역인 유부도 갯벌의 지형적 특성을 나타낸 연구가 조사되었고, 드론과 디지털 표고 모델(DEM)을 활용해 분석한 연구도 수행되었다(Lee et al., 2001; Lee et al., 2014b; Kang et al., 2022).
최근 위성과 드론을 활용한 모니터링 연구가 활발히 진행되었으며, 갯벌 생태계와 철새의 상호작용을 분석한 연구도 수행되었다. 이러한 연구들은 기후 변화가 갯벌의 물리적 구조와 생태계에 미치는 영향을 파악하고, 갯벌 복원과 새로운 서식지 조성의 필요성을 강조하고 있다. 또한, 갯벌 환경을 지속적으로 유지하기 위한 식생 복원과 침식 방지 기술의 중요성도 나타났다. 철새의 갯벌 이용 데이터를 바탕으로 보호구역을 설정하고, 이를 지역 및 국가 계획에 반영할 수 있도록 하는 연구와 개발과 환경의 균형점을 찾기 위해 지역 사회의 협력을 이끌어내는 연구가 필요하다.
3.5 하구역 환경관리와 개발
주요 하구별로 하구 지역 개발과 보전에 관한 연구는 다양하게 진행되었다. 낙동강 하구에서는 항만시설 개발 방안과 서부산권 보전지역 이용 방안에 대한 연구가 진행되었다. 법정보호지역과 비오톱 보전가치 평가를 통해 효율적인 보전과 개발 방안도 모색되었다(Choi et al., 2006; Cha et al., 2010). 또한, 4대강 사업이 하구에 끼친 부정적 영향, 이를 해결하기 위한 통합적 유역 관리 시스템 구축 연구의 필요성도 나타났다(Kim, 2021; Ahn, 2017). 한강 하구는 다른 주요 강과 달리 횡단구조물이 없는 열린 자연 하구로, 남북한 접경지역에 위치한 지리적 특징을 가지고 있다(Youn, 2021; Park, 2004). 이로 인해 주로 남북 관계에서의 한강 하구의 역할을 살펴보고, 남북 공동의 평화적 하구 활용 방안과 협력 방안에 대한 연구가 진행되었다(Park and Kim, 2019; Woo and Mo, 2009; Choi and Han, 2022). 한강 하구 통합 관리 정책의 우선순위와 실행 전략에 대한 연구도 이루어졌다(Park et al., 2022). 수자원 보전과 통합 환경 관리 방안, 친환경적 취수시설의 필요성, 수질과 수량 보전 연구도 중요한 주제로 다루어졌다(Kim et al., 2018b). 한강 하구의 통합 관리와 공간적 디자인의 효율성을 평가하는 연구도 이루어졌으며, 프랙탈 이론을 적용한 양적 평가 분석이 수행되었다(Seo and Maeng, 2016). 영산강 하구에서는 GIS 기반의 통합 데이터 관리 시스템 개발과 관련된 연구가 진행되었고(Lee et al., 2011b), 섬진강 하구와 인근 해양 정보로 모바일 해양지리정보시스템(MGIS) 구축 연구도 이루어졌다(Park et al., 2016). 이러한 연구들은 하구의 물 관리, 생태계 보호, 오염원 관리 등을 전체적으로 운영할 수 있는 통합시스템 구축의 필요성을 시사한다. 또한, 기후 변화로 인한 해수면 상승과 해안 침식이 하구 생태계에 미치는 영향을 예측하고 대응하기 위한 방법론 개발이 필요하다고 판단된다.
3.6 지속 가능성과 하구 생태계서비스 경제적 가치 평가
시대적 패러다임이 지속 가능한 물 관리 정책으로 전환되고, 국내에서 물 관리 일원화 정책이 도입되면서 하구의 지속 가능성과 생태계서비스 가치를 경제적으로 평가하는 연구들이 나타났다. 에머지(Emergy) 방법을 활용해 한강, 금강, 영산강, 섬진강 유역의 자연환경과 사회경제 활동에 대한 평가가 이루어졌으며(Lee, 2018; Kang, 2013, 2007), 사회·경제적 활동으로 인한 개발 압력이 높은 지역, 특히 인구 밀도와 산업 집중도가 높은 지역에서 지속 가능성이 낮게 평가되었다. 다양한 개발 계획이 생태계 보전을 위협할 수 있으며, 환경 수용력을 반영한 정책 수립과 하구 보호가 중요함을 강조하였다. 더불어 지속 가능한 하구 이용을 위해 사전 관리와 예방 조치의 필요성도 제기되었다. 에머지 방법을 통해 한강 하구는 인근 개발 계획과 구상들이 생태계 보전에 위협이 될 수 있음을 확인하였고, 환경 수용력을 고려한 정책과 사전 예방적 접근이 필요함을 시사했다. 또한 경기만 한강 하구역의 지속 가능 발전 지표를 선정하고, 국내·외 사례를 조사한 연구도 나타났다(Kang et al., 2005; Kang et al., 2007). 이외에도 DPSIR 모형을 통해 금강 유역의 조기 경보 지수를 분석한 연구도 진행되었다(Kim and Min, 2017; Kim, 2017; Kang et al., 2007).
2000년대 이후, 국내 하구 생태계 관리에서 재자연화가 중요한 주제로 떠오르며, 하구의 생태적 가치와 더불어 경제적 가치를 평가하는 연구가 일시적으로 활발히 진행되었다. 비시장 가치 평가법을 활용해 낙동강 하구의 경제적 가치를 이중 경계 스파이크 모형을 통해 산출한 바 있으며(Yoo, 2007b), 한강 하구는 남북 공동 이용과 협력으로 인한 경제적 가치를 강조한 연구들이 이루어졌다(Kwon et al., 2013; Kwak et al., 2006). 금강 하구 환경가치 평가를 위해 하구 인근 지역인 전북과 충남지역 주민들을 대상으로 지불 의사액을 추정하였고, 이중 양분 선택형 설문조사를 통해 유산 가치, 존재 가치, 선택 가치, 대리 소비 가치로 구분해 추정한 연구가 있었다(Kwon et al., 2013; Sin et al., 2017). 또한, 영산강과 섬진강 하구의 경제적 가치와 갯벌 보존 가치를 평가한 연구도 진행되었다(Yoo, 2007a; Yoo et al., 2011; Pyo et al., 2001). 이러한 연구들은 하구 생태계 복원을 강조하고, 경제적 이익간의 균형이 필요함을 제시했다. 한편, 기존연구들이 2000년대 초반에 집중되어 있어 최근 연구가 부족하다는 한계가 드러났으며, 이를 보완하기 위해 방법론적 측면에서 개선된 하구 생태계 서비스 가치 평가 연구가 더 많이 필요하다고 판단된다. 공간적·시간적 변동성, 사회·문화적 가치를 반영하고, 장기적 관점에서 생태계 편익을 추정하는 새로운 환경성 평가 방법론의 개발이 필요하다.
3.7 하구 관리의 법·제도적 측면과 통합적 접근
기존 법·제도 관련 연구들은 하구 생태계 보전과 관리를 위해 법제도 재정비의 필요성(Shim, 2017), 지역 간 갈등 해결, 의사결정 지원 시스템 설계, 주민 참여와 제도적 배려의 중요성을 강조하였다. 낙동강 하구 인근의 경우, 개발 압력으로 인해 논 습지 보전과 생태관광지 지정과 관련된 연구가 진행되었으며, 이를 통해 법적 재정비의 필요성이 제기되었다(Im et al., 2010; Shim, 2017, 2018; Kong, 2012). 하구 관리와 보호에 관한 법적 정의와 법률 간의 일관성 부족, 환경적 측면에서의 법적 보호 장치의 필요성을 강조한 연구들도 있었다. 예를 들어, 낙동강 하구 인근에서는 보전법에 따른 규제로 주민 생활이 제한되지만, 보상과 지원이 부족해 주민 참여와 제도적 배려의 필요성이 제기되었다(Kong, 2010). 금강 하구는 물의 이용에 있어 전북과 충남 지역 간 수자원 이용과 수질 확보에 대한 이해가 달라 갈등이 심화되는 문제점이 드러났다. 이를 해결하기 위해 미국의 하구 복원 사례를 제시하며, 법·제도적 측면에서 하구 구역 설정의 한계점을 지적하였다. 또한, 금강 하구역의 환경 변화로 인한 주민 간의 갈등 요인을 분석하고, 이를 해결하기 위한 의사결정 지원 시스템을 제시한 연구도 나타났다(Park et al., 2017; Rhew et al., 2018).
게다가, 환경부, 해양수산부, 농림축산식품부, 국토교통부 등 여러 부처가 동시에 하구와 연안 관리를 함에 따라, 역할 분담 과정에서 발생되는 비효율성 문제가 지적되었다. 하구 인근에 산재된 환경 이슈, 지역별 산발적인 하구 환경정보를 주요 현안으로 다루었다(Lee et al., 2018; Sim, 2018). 또한, 하구 인근의 습지 보호지역 지정과 환경 규제 설정지역의 필요성, 국내 하구의 법적 범위 설정, 전국 하구 관리를 위한 법·제도 간 위계성 확보가 필요하다는 점도 강조되었다(Lee et al., 2007a).
4. 결론 및 제언
본 연구는 2000년부터 2023년까지의 기존 연구를 검토하여, 국내 주요 하구의 물리·화학·생물학적 특성, 생태계와 철새 서식지, 환경 관리와 개발, 지속 가능성, 생태계서비스의 경제적 가치 평가, 하구 관리의 법·제도적 측면을 반영한 연구들을 종합적으로 분석하였다. 이를 통해 하구의 지속 가능한 관리와 균형 잡힌 개발을 위한 다양한 측면이 확인되었다. 하구 통합 관리 기구의 필요성이 제기되었고, 하구 공간 단위의 재정립도 중요하게 다루어졌다. 생태계 기반 접근법과 하구 생태계 가치 평가법 개발이 강조되었다. 이에 따라 다음과 같이 제언 하고자 한다.
첫째, 지역별 하구의 특수성을 반영한 법적 지위를 정립하고, 지역 특성에 부합하는 유연한 하구 정의와 범위 설정이 요구된다. 이를 위해 기존 법률과 제도를 포괄적이고 탄력적으로 재정비할 필요가 있다. 특히, 하구를 단일 공간 개념으로 정의하기보다는 유역, 하천, 연안 지역 간의 연동성을 반영하여 공간적 범위를 설정하는 방안이 논의되어야 한다. 현재 하구 관리의 비일관성은 부처 간의 해석 차이와 법적 지위 부족으로 나타나고 있어 제도적 개선이 요구된다. 국내 하구 관리는 다원화된 구조로, 하구 역할과 중요성을 부처마다 다르게 해석하고 있어, 일관된 정책 수립과 실행 저해 요인으로 작용하고 있다. 주요 강에 맞는 보호지구 지정과 운영 제도 개선, 부처 간 협업을 통해 통합적 관리 체계를 구축하는 것이 필요하다.
둘째, 기후 변화가 하구 생태계에 미치는 영향을 예측하고 대응하기 위해 통합적 생태 모델 개발이 요구된다. 국내 주요 하구 연구는 퇴적 환경, 염분 분포, 생물학적 특성 등 개별적으로 각 요소 분석에 집중되어, 복잡한 상호작용을 통합적으로 이해하는 접근이 부족하다. 이를 극복하기 위해 다학제적 접근을 통한 통합적 생태 모델을 개발하고, 갯벌 복원과 서식지 관리 방안이 요구된다. 장기적 관리 전략을 수립하고, 기후 변화 시나리오를 반영한 GIS 기반의 통합 수질 모의 시스템과 복합성을 반영한 생태 모델을 고도화해야 한다. 또한 철새 서식지 보호를 위한 데이터 기반 정책 수립과 지역 사회와 다양한 이해관계자 간의 협력 모델이 필요하다.
셋째, 하구 생태계 가치를 극대화하기 위해서는 생태계서비스 가치 평가를 위한 새로운 방법론의 개발이 필요하다. 하구의 생물다양성 보존, 탄소 흡수, 수질 정화 등 다양한 생태계서비스 가치를 인식하고 이를 경제적으로 평가하려는 연구들이 시도되었으나, 하구 생태계의 복잡성, 비시장적 특성, 시공간적 변동성, 사회·문화적 가치 등을 종합적으로 고려한 평가 방법은 여전히 부족한 상황이다. 기존의 하구 생태계서비스 가치 평가 방법론은 하구 생태계의 특수성을 반영하는 데 한계점을 가진다. 따라서 수질 정화, 탄소 흡수, 생물다양성 유지, 홍수 조절 등 다양한 기능을 생태계 기능별로 세분화하여 평가하고, 반영한 환경적 편익 분석이 요구된다. 더불어, 하구 생태계의 서비스 가치를 극대화하기 위해 자연기반해법을 통한 통합적 관리 전략이 필요할 것으로 판단된다.
넷째, 지속 가능하고 효율적인 하구 관리를 위해 기술적 접근과 연구의 강화가 요구된다. 하구의 물리적, 화학적, 생태적 특성을 종합적으로 분석하고, 기후 변화 시나리오를 기반으로 한 예측 모델을 개발하여 장기적 대응 전략을 마련하는 것이 중요하다. 이를 지원하기 위해서는 통합 데이터 관리와 시뮬레이션 기술이 요구되며, 자동화된 감시 체계와 오염물질 실시간 추적 및 제거 기술이 요구된다. 더욱이, 하구 지역에 중금속, 영양염류, 해양쓰레기로 인한 환경 문제가 나타나고 있어, 효율적 관리를 위해 고도화된 GIS 기반 통합 수질 관리 시스템이 필요하다. 비점오염원 관리 전략과 저영향 개발(LID) 기법을 지역 특성에 맞게 구체화하여, 농업, 산업, 생활 오염원의 하구 유입을 최소화하는 연구도 필요할 것이다. 기후 변화로 인한 해수면 상승, 강수 패턴 변화, 예상치 못한 태풍과 홍수 빈도 증가는 하구의 물리적 구조와 생태계에 영향을 미치고 있다. 이에 대비하여 해수면 상승과 해안 침식에 따른 하구 생태계 변화를 예측하고, 이러한 변화에 적응할 수 있는 복원과 보호 기술 연구도 요구된다. 드론, 위성영상, 고해상도 DEM 등 최신 모니터링 기법을 도입해 기후 변화에 따른 서식지 변화와 생태적 복원의 필요성을 지역별로 진단할 필요가 있다. 또한, GIS 빅데이터와 AI 기술을 활용한 실시간 모니터링 및 시뮬레이션 시스템을 통해 하구 생태계 변화에 대한 예측과 대응 연구가 지속적으로 필요하다고 판단된다.
본 연구는 기존 연구의 이론과 방법론적 모순점을 충분히 해결하지 못했으며, 국외 관련 하구 사례를 포함하지 않은 한계점을 가지고 있다. 향후 연구에서는 과학적 기초 데이터를 기반으로 통합적 측면의 시사점을 제시하고, 국내·외 하구 관련 연구의 이론적 통합과 방법론적 한계를 분석하여 정책적 측면을 제시할 필요가 있다. 게다가, 하구 환경계획과 국토계획을 연계하여 상호보완적으로 설계하고 실행할 수 있는 통합 관리 시스템 구축 연구가 필요하며, 하구 주변의 개발 가능 지역과 보전지역을 체계적으로 조사하여 최적의 토지 이용 계획을 제시하는 연구가 요구된다. 또한, 물 관리 위험 요소와 수질과 관련된 비점오염원의 중첩 지점을 분석할 필요가 있다. 주변 환경시설과 개발 사업 현황을 고려한 장기적 관점의 다학제적 융복합 연구도 필요하다. 지역개발사업과 연계하여 하구 인접 지역의 공간 변화를 예측하고, 장기적인 하구 관리 방안을 모색할 필요가 있다. 게다가, 하구의 생태계서비스 가치 평가법을 개발하는 연구와 더불어 예비타당성조사 환경성 부문 평가법과 연계 시킨 연구가 기대 된다. 기후위기로 인한 예측 불가능한 홍수, 태풍 등 하구 주변 지역의 잠재 재해 위험성을 분석하고, 국토-환경계획 단계에서 이를 반영한 방재 계획을 수립하는 연구도 요구된다. 인구 감소와 지역 쇠퇴가 수자원 수요와 공급에 미치는 영향을 분석하고, 하구 주변 지역의 수자원 관리 취약점을 조사하는 연구도 필요할 것이다. 더불어, 해양쓰레기와 같은 하구-연안 생태계에 부정적 영향을 미치는 폐기물 처리 문제, 미래 예측이 연계된 물(하구)-에너지-식량 연계(Water-Energy-Food Nexus) 연구에 대한 논의가 향후 중요한 연구 주제로 기대되는 바이다.