-
Research Article
-
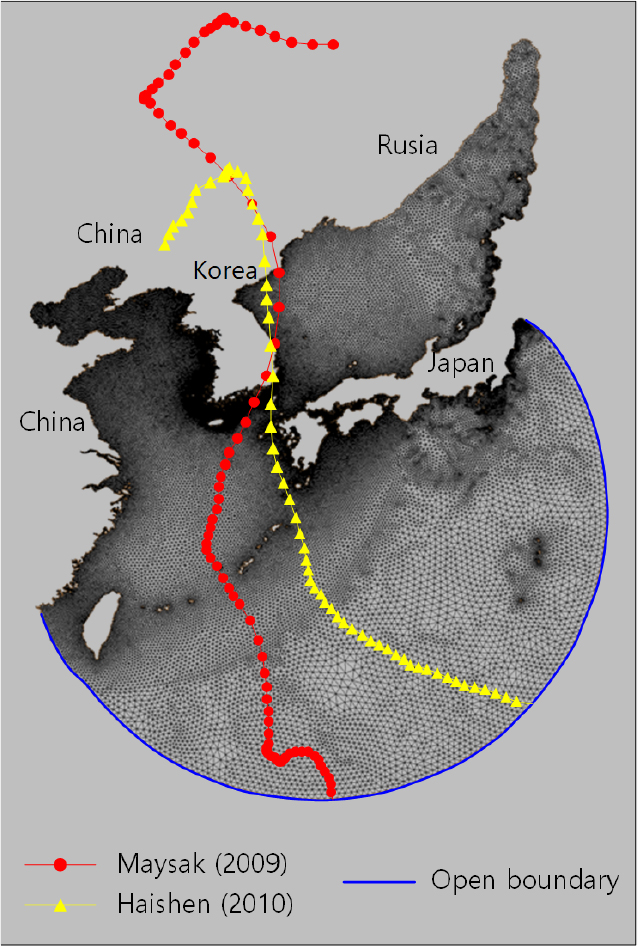
Simulation of storm surges and waves using the coupled ADCIRC–SWAN model based on JMA-MSM meteorological fields: A case study of typhoons Maysak (2009) and Haishen (2010)
JMA-MSM 기상장 기반 ADCIRC-SWAN 연성모델을 이용한 폭풍해일 및 폭풍파 모의: 태풍 마이삭(2009)과 하이선(2010)을 대상으로
-
Taegeon Hwang, Hyeon-Jeong Kim, Byung-Il Min, Sang-Yeop Lee, Woo-Dong Lee
황태건, 김현정, 민병일, 이상엽, 이우동
- This study employed the coupled ADCIRC–SWAN model driven by meteorological fields from the Japan Meteorological Agency Meso - Scale Model (JMA-MSM) to …
본 연구는 일본기상청 중규모모델(JMA-MSM) 기상장을 외력으로 적용하여 ADCIRC-SWAN 연성해석을 수행하였다. 대상 태풍은 2020년 한반도를 연이어 강타한 태풍 마이삭(2009)과 하이선(2010)이며, 내습 시기의 폭풍해일 …
- This study employed the coupled ADCIRC–SWAN model driven by meteorological fields from the Japan Meteorological Agency Meso - Scale Model (JMA-MSM) to simulate and analyze storm surges and waves induced by Typhoons Maysak (2009) and Haishen (2010), which successively struck the Korean Peninsula in 2020. Model performance was verified through quantitative comparisons with observed water levels, in-situ wave data, and hindcast results, confirming the physical validity and predictive reliability of the coupled surge–wave interaction analysis. The results revealed that the temporal evolution and spatial distribution of storm surges and waves varied significantly depending on the typhoon tracks and the locations of strong wind fields. The simultaneous effects of surge-induced water level rise and wave radiation stresses produced complex coupled behaviors in coastal regions. Benefiting from the accurate representation of large-scale pressure and wind variations in the JMA-MSM fields, the model successfully reproduced high storm waves in regions severely affected by overtopping and inundation, including the southeastern and eastern coasts, Ulleungdo, and Dokdo. These findings demonstrate the practical applicability of high-resolution reanalysis or forecast meteorological data with coupled modeling for precise prediction of compound coastal hazards under changing climate conditions.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 일본기상청 중규모모델(JMA-MSM) 기상장을 외력으로 적용하여 ADCIRC-SWAN 연성해석을 수행하였다. 대상 태풍은 2020년 한반도를 연이어 강타한 태풍 마이삭(2009)과 하이선(2010)이며, 내습 시기의 폭풍해일 및 폭풍파를 추산하고 그 특성을 분석하였다. 먼저, 관측 수위, 관측 파랑, 후측 파랑 자료와의 정량적 비교를 통해 폭풍해일-파랑 비선형 상호작용 해석의 타당성과 모델의 유효성을 확인하였다. 연성해석 결과, 태풍의 경로와 강풍역의 위치에 따라 해일과 파랑의 발달 및 소멸 시점과 공간분포가 상이하게 나타났다. 특히, 해일 상승에 따른 수심 변화와 파랑 복사응력에 의한 해면상승이 동시에 작용함으로써 연안역의 수위와 파고가 상호 영향을 주는 복합 거동을 보였다. JMA-MSM 기상장은 태풍 전후의 광역 기압 및 풍속 변동을 반영하고 있기 때문에 두 태풍 내습 시에 월파 및 침수 피해가 심각했던 남해 동부, 동해 남부와 북부, 울릉도 및 독도 해역에서 높은 폭풍파가 추산되었다. 이러한 결과는 복합 해양 재해 예측에 성공적으로 적용될 수 있음을 보여줌과 동시에, 기후 변화에 따른 태풍 피해에 대응하기 위한 월파ㆍ침수 등 연안 재해 평가에 고해상도 재분석/예측 기상장 적용 및 연성해석의 중요성을 시사한다.
-
Simulation of storm surges and waves using the coupled ADCIRC–SWAN model based on JMA-MSM meteorological fields: A case study of typhoons Maysak (2009) and Haishen (2010)
-
Research Article / 우수학생논문상
-
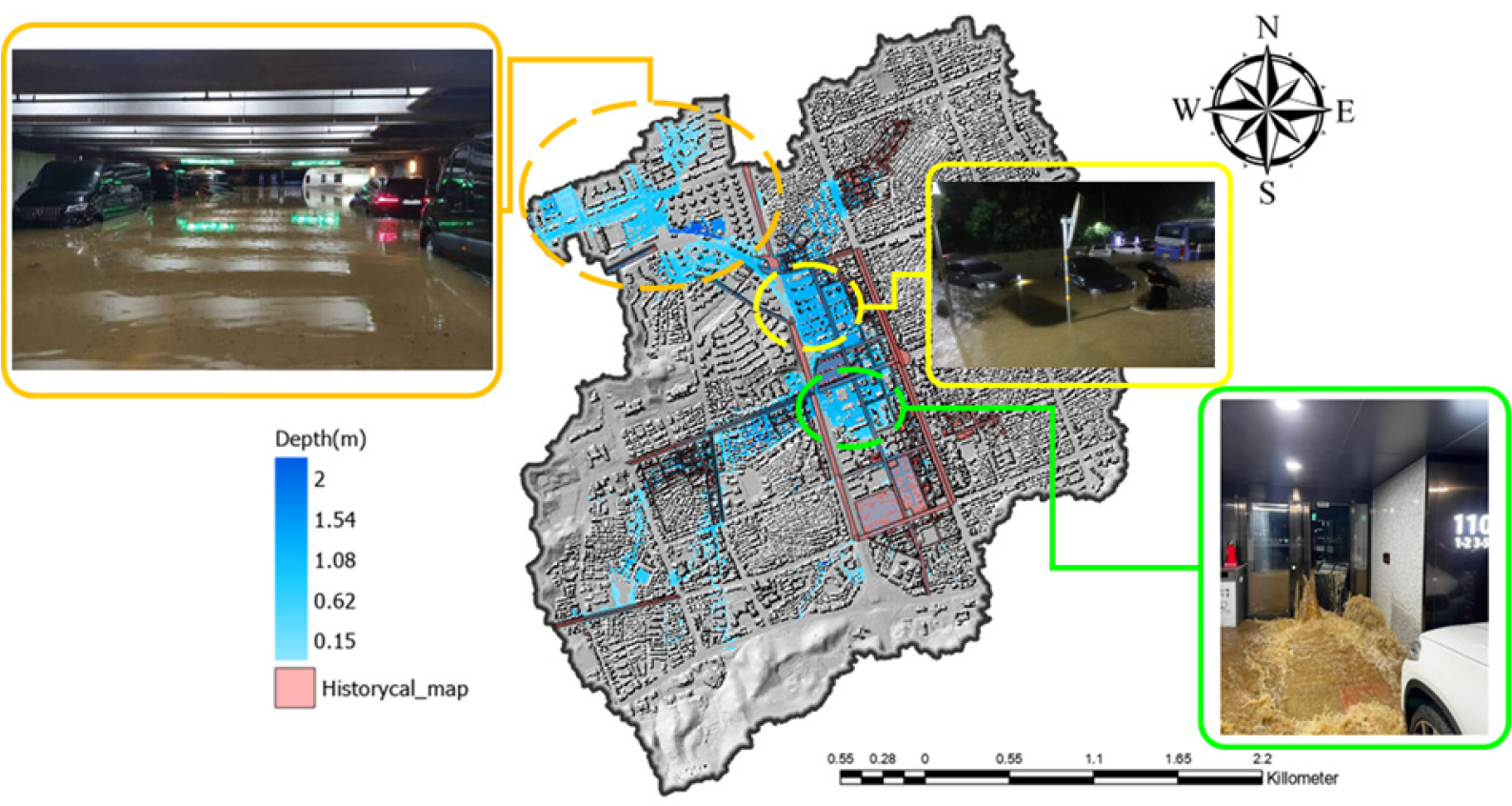
An impact-based evaluation methodology for identifying manholes contributing to urban underground flooding
도시 지하공간 침수에 기여하는 맨홀의 영향도 기반 평가 방법론
-
Seongcheon Kwon, Giha Lee, Jinhyeong Lee, Seungsoo Lee
권성천, 이기하, 이진형, 이승수
- This study presents an impact-based evaluation methodology to quantitatively identify manholes with the highest influence on underground flooding among numerous urban drainage …
본 연구는 서울시 교대역 일대를 대상으로, 도시 내 다수의 맨홀 중 지하공간 침수에 미치는 영향이 높은 맨홀을 정량적으로 선별하기 위한 영향도 기반 …
- This study presents an impact-based evaluation methodology to quantitatively identify manholes with the highest influence on underground flooding among numerous urban drainage nodes in the vicinity of Seoul’s SNUniv. of Education Station. A coupled modeling framework integrating SWMM and a two-dimensional inundation model was employed to simulate various rainfall scenarios with different return periods (30-500 years) and durations (60-180 minutes). Key hydraulic parameters, including distance to subway entrances, overflow onset time, and cumulative overflow volume, were utilized to assess the relative influence of each manhole. Results indicated that manholes 8201, 2112, and 4100 near SNUniv. of Education Station consistently exhibited high impact, functioning as critical nodes that govern flood propagation in underground spaces. The proposed methodology provides a quantitative and practical framework that can support scientific decision-making for flood warning systems and priority management of manholes in urban drainage networks.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 서울시 교대역 일대를 대상으로, 도시 내 다수의 맨홀 중 지하공간 침수에 미치는 영향이 높은 맨홀을 정량적으로 선별하기 위한 영향도 기반 평가 방법론을 제시하였다. 이를 위해 SWMM과 2차원 침수모형을 연계하여 다양한 재현기간(30-500년)과 지속기간(60-180분)의 강우 시나리오를 모의하였으며, 지하철 출입구 주변 맨홀의 거리, 역류 시점, 누적 월류량 등을 주요 변수로 활용하였다. 분석 결과, 교대역 인근의 맨홀 8201, 2112, 4100이 모든 조건에서 높은 영향도를 보이며 지하공간 침수 확산에 핵심적인 역할을 수행하는 것으로 나타났다. 제안된 방법론은 정성적 판단에 의존하던 기존 체계에 정량적 근거를 제공함으로써, 향후 지하공간 침수 예·경보 및 우선관리 대상 맨홀 선정을 위한 과학적이고 합리적인 의사결정 지원체계로 활용될 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
An impact-based evaluation methodology for identifying manholes contributing to urban underground flooding
-
Research Article
-
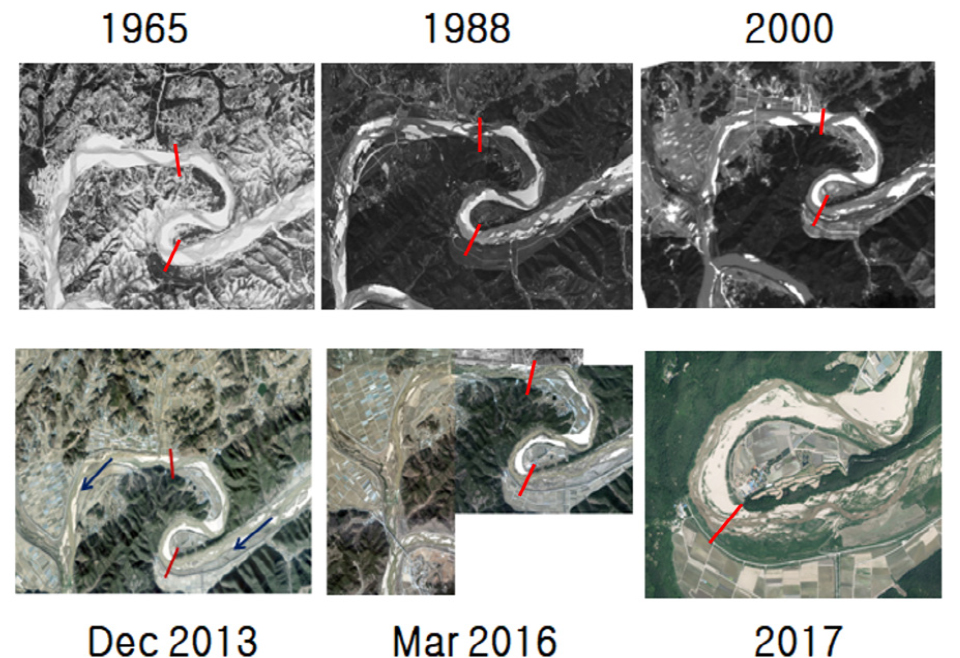
Estimation of the vegetation mortality conditions on a riparian sand bar using the field observation and numerical simulation - A case of herbaceous plant in Korea
야외관측 및 수치해석을 이용한 하천 사주 상 식생 사멸조건의 추정 - 초본류 사례
-
Hyoseop Woo, Chang-Lae Jang, Chanjoo Lee, Hyung-jin Cho, Sung-uk Choi
우효섭, 장창래, 이찬주, 조형진, 최성욱
- Riparian plants recruited by hydrochory often experience high mortality during their early growth period, primarily due to three factors: 1) insufficient soil …
하안식생은 수매작용으로 이입, 활착하는 과정에서 보통 1) 토양수분 부족, 2) 장기간 침수, 3) 흐름 및 유사 이동으로 인한 서식지 표면의 물리적 불안정(침식, …
- Riparian plants recruited by hydrochory often experience high mortality during their early growth period, primarily due to three factors: 1) insufficient soil moisture, 2) excessive duration of inundation, and 3) physical instability of their habitat caused by flow and sediment transport processes such as excavation, uprooting, and burial. In this study, we investigated the critical mortality conditions associated with physical instability during the recruitment stage of the herbaceous riparian species Persicaria nodosa (node smartweed), a common pioneer plant in Korean sand-bed rivers, using field observations in conjunction with numerical analysis. We monitored germination, seedling establishment, and subsequent growth of the species within a selected reach of a sand-bed river in Korea. To assess the flow conditions under which plants are likely to survive or die, we conducted numerical simulations of the reach to obtain two-dimensional distributions of bed shear stress. A validated hydraulic model was used to reproduce critical flow periods observed during the monitoring years. In the analysis, we assumed that the Shields number (dimensionless shear stress) could serve as an indirect indicator of the physical threshold for plant survival. Our results show that the Shields number associated with physical mortality varies markedly with plant age. For two-month-old seedlings, the threshold lies between 0.19 and 0.24, whereas four-month-old plants require values exceeding 0.37. These findings differ substantially from the common assumption in vegetation-dynamics models that mortality of recruitment-stage plants can be represented using the critical Shields threshold of approximately 0.04-0.06. The results clearly demonstrate that age-dependent resistance must be considered when modelling mortality of pioneer vegetation on riparian sand bars.
- COLLAPSE
하안식생은 수매작용으로 이입, 활착하는 과정에서 보통 1) 토양수분 부족, 2) 장기간 침수, 3) 흐름 및 유사 이동으로 인한 서식지 표면의 물리적 불안정(침식, 뿌리 뽑힘, 매몰) 등 이유로 사멸할 수 있다. 본 연구에서는 국내 모래하천에 흔히 서식하는 초본식물인 명아자여뀌를 대상으로 물리적 불안정성으로 인한 사멸의 한계조건을 특히 식생 이입기에 초점을 맞추어 현장 관찰과 수치 분석을 통해 조사했다. 이를 위해 낙동강 제1지류인 내성천의 한 구간에서 대상 식물의 발아 및 생장 과정을 관찰했다. 다음, 식물이 서식하는 하안사주의 물리적 불안정성으로 인해 식생 이입기에 사멸할 수 있는 흐름 조건을 추정하기 위해 2차원 흐름 수치모의를 수행했다. 본 연구에서 식생과 하상의 물리적 불안정성에 의한 사멸의 간접적 지표로서 Shields 수를 이용하였다. 그 결과 이입기인 2개월 자란 7 cm 높이 명아자여뀌 사멸조건은 Shields 수로 0.19보다 크나 0.24보다 작으며, 4개월 된 50 cm 높이 식생의 경우 0.37보다 큰 것으로 나타났다. 이 결과는 Shields 수 0.04-0.06 를 보통 하안식생의 초기 사멸기준으로 사용하는 현 식생동역학 모델링의 실무 값과 큰 차이를 보여준다. 또한, 하안사주 상 초기식생의 생존과 사멸을 평가하기 위해서는 생장시기 별 한계조건을 고려하여야 한다.
-
Estimation of the vegetation mortality conditions on a riparian sand bar using the field observation and numerical simulation - A case of herbaceous plant in Korea
-
Research Article
-
Impact of oversampling on the predictive performance of machine learning models: Empirical analysis of algal bloom prediction
오버샘플링이 머신러닝 모델 예측성능에 미치는 영향: 녹조예측 실증분석
-
Junhaeng Lee, Choongsung Yi, Jewan Ryu, Sunghoon Kim
이준행, 이충성, 류제완, 김성훈
- The aim of this study is to quantitatively evaluate how oversampling affects regression-based predictive performance in highly imbalanced time series, such as …
본 연구의 목적은 남조류 세포수 데이터셋과 같이 고농도 샘플이 극히 희소한 불균형 시계열에서 오버샘플링이 회귀 기반 예측성능에 미치는 영향을 정량적으로 분석하는데 있다. …
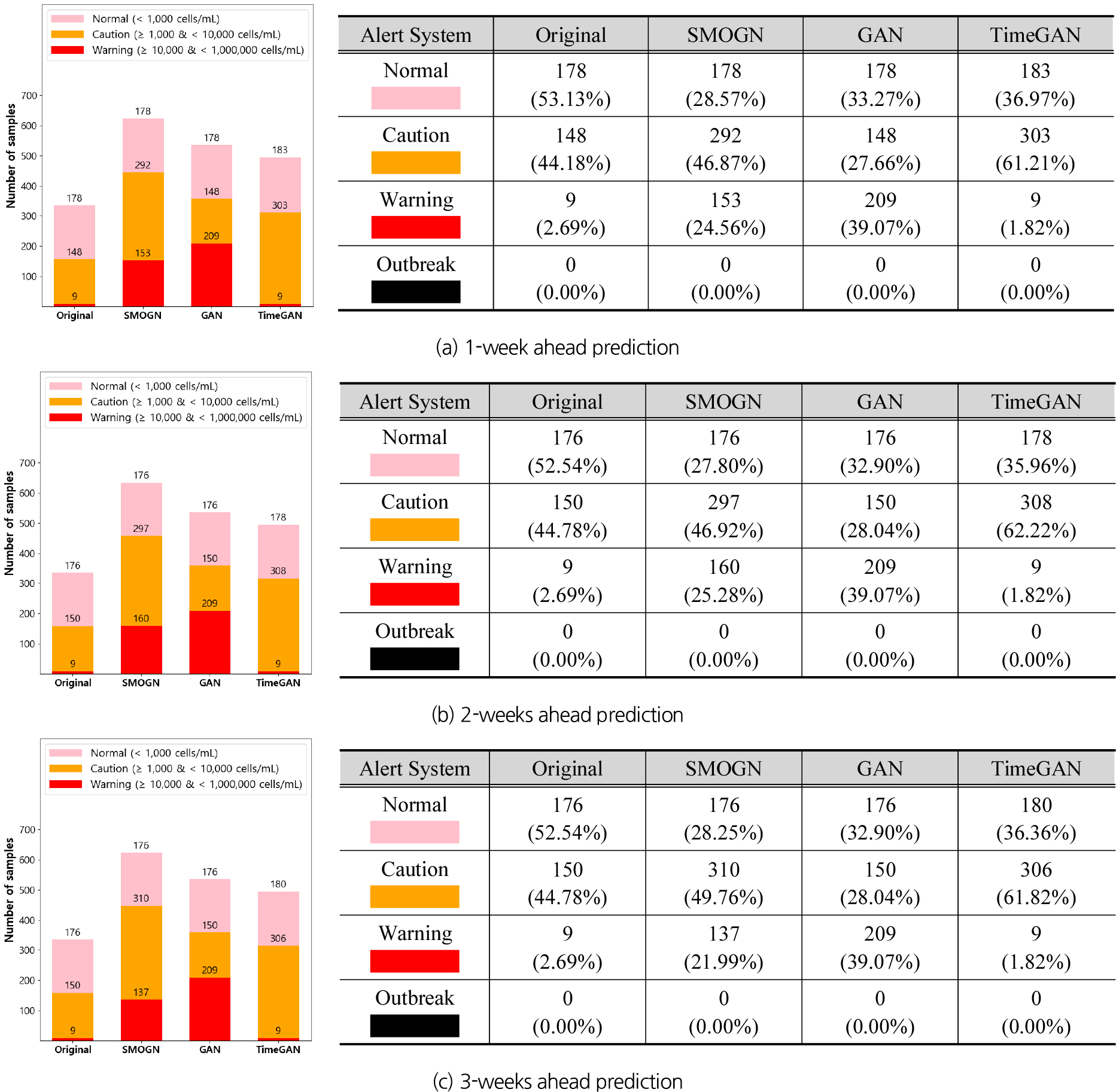
- The aim of this study is to quantitatively evaluate how oversampling affects regression-based predictive performance in highly imbalanced time series, such as cyanobacterial cell density datasets with extremely rare high-concentration samples. Using Daecheong Reservoir as a case study, we compiled weekly data for 2005-2024 by integrating cyanobacterial, water quality, hydrologic, and meteorological variables, built random forest models with 1-3 week lead times, and compared SMOGN, GAN, and TimeGAN oversampled training sets against the original data using multiple performance metrics. SMOGN, by preserving the continuous distribution while selectively reinforcing rare regions according to local density, reduced errors in high-concentration ranges and yielded consistent improvements across most metrics compared with the original data. In contrast, GAN and TimeGAN better preserved the original distribution and temporal structure but showed limited ability to rebalance toward extremely rare high-concentration regimes. These results suggest that, for hydrologic and environmental time series with rare extremes and severe imbalance, regression-oriented oversampling strategies that jointly preserve the target distribution and strengthen sparse regions can effectively enhance the predictive performance of forecasting models.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구의 목적은 남조류 세포수 데이터셋과 같이 고농도 샘플이 극히 희소한 불균형 시계열에서 오버샘플링이 회귀 기반 예측성능에 미치는 영향을 정량적으로 분석하는데 있다. 대청호를 대상으로 2005-2024년 주간 자료로 남조류, 일반수질, 수리·수문, 기상변수를 통합하고, 리드타임 1~3주별로 랜덤포레스트 예측모형을 구축한 뒤, SMOGN, GAN, TimeGAN을 적용한 훈련 데이터셋과 원본 데이터셋의 성능을 다양한 성능 평가 지표로 비교하였다. 그 결과 SMOGN은 연속형 분포를 유지하면서 국소 밀도에 따라 희소 구간을 선택적으로 강화함으로써 고농도 구간 오차를 줄이고, 오버샘플링 미실행 대비 대부분의 평가 지표에서 일관된 성능 개선을 보였다. 반면 GAN과 TimeGAN은 원본 분포 및 시계열 구조 보존에는 유리하나, 극히 희소한 고농도 구간을 목표로 분포를 재조정하는 데에는 한계를 나타냈다. 이러한 결과는 극단값이 드물고 불균형이 심한 수문·환경 시계열에서 단순 데이터 증대가 아닌 분포 보존과 선택적 밀도 강화를 결합한 회귀형 오버샘플링 전략이 예측모형 성능 향상에 유용함을 시사하는 기초적 근거로 활용될 것으로 기대된다.
-
Impact of oversampling on the predictive performance of machine learning models: Empirical analysis of algal bloom prediction
-
Research Article
-
Development and performance evaluation of LSTM-based multi-points water level forecasting model for downstream region of Yongdam Dam
LSTM을 활용한 용담댐 하류 다중지점 시간 단위 하천 수위 예측 모델 개발과 성능평가
-
HyunSeok Yang, YoungDon Choi, SungHoon Kim, JunSeok Lee
양현석, 최영돈, 김성훈, 이준석
- This study developed a multi-point water level forecasting model for 21 observation stations located between Yongdam Dam and Daecheong Dam in the …
본 연구는 금강 유역 용담댐부터 대청댐까지 21개 수위관측소를 대상으로 상·하류 상관관계를 고려한 다중지점 수위 예측 모델을 구축하였다. 강우, 수위, 댐 방류량을 입력자료로 …
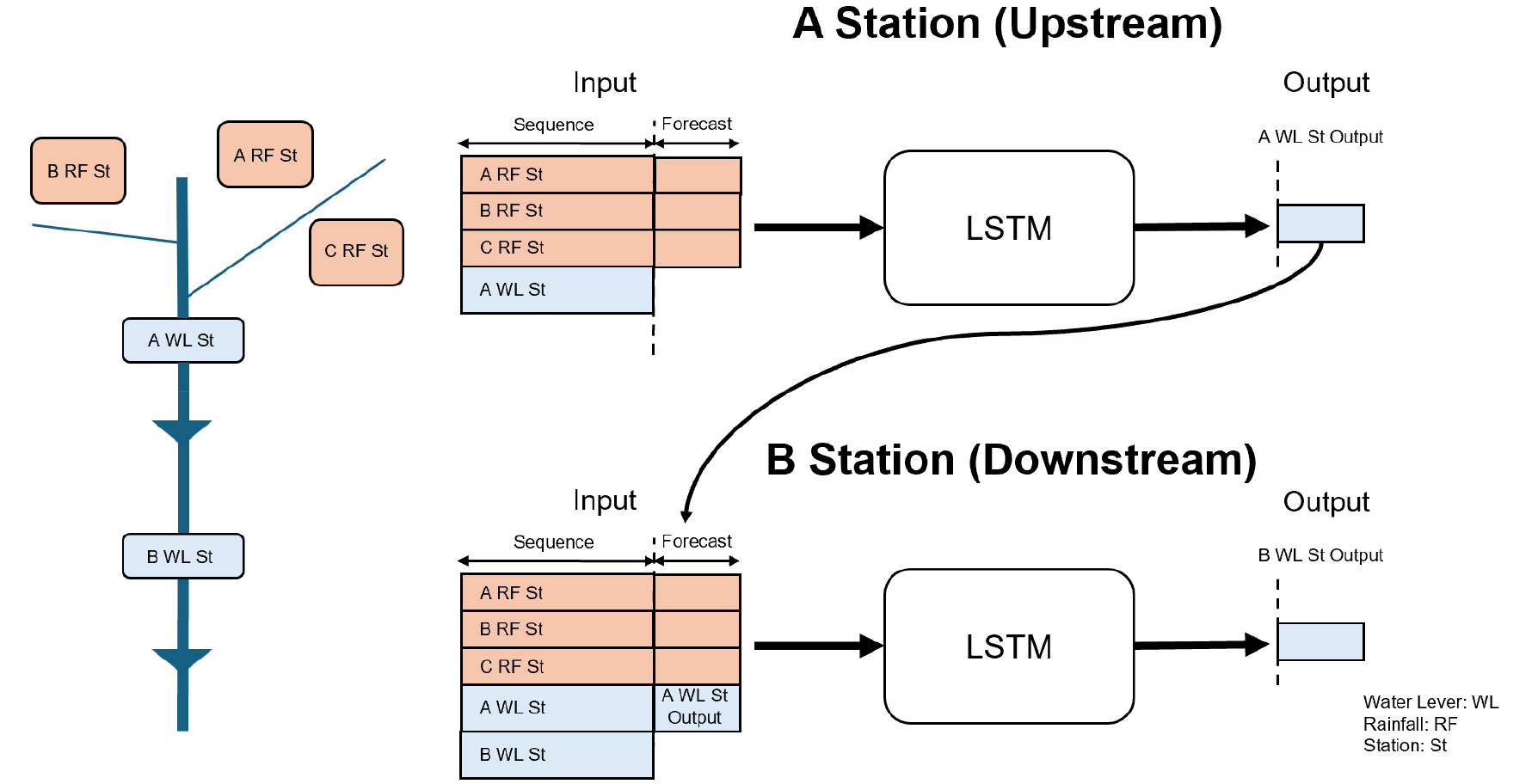
- This study developed a multi-point water level forecasting model for 21 observation stations located between Yongdam Dam and Daecheong Dam in the Geum River Basin, considering upstream-downstream hydrological connectivity. Rainfall, water level, and dam discharge data were used as input variables, and station-specific forecasting models were constructed using the CUDA-LSTM framework provided by NeuralHydrology. A configuration-based structure was implemented to sequentially propagate upstream predictions to downstream models. Model performance during the development phase was evaluated using the higher NSE value between the validation and testing periods, while the forecasting phase assessed 72-hour water level predictions—consistent with the operational flood forecasting procedure—using both NSE and RMSE. As a result, 18 stations during the development phase and 14 stations during the forecasting phase achieved NSE values of 0.6 or higher, demonstrating stable performance at more than half of the observation stations. These findings confirm the practical applicability of the proposed multi-point water level forecasting model for real-world flood forecasting operations, and its effectiveness was verified.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 금강 유역 용담댐부터 대청댐까지 21개 수위관측소를 대상으로 상·하류 상관관계를 고려한 다중지점 수위 예측 모델을 구축하였다. 강우, 수위, 댐 방류량을 입력자료로 활용하고 NeuralHydrology의 CUDA-LSTM을 적용하여 관측소별 예측 모델을 개발하였으며, Configuration 파일을 기반으로 상류 예측값이 하류 모델의 입력으로 순차 반영되는 구조를 구현하였다. 모델 개발 단계에서는 Validation과 Testing 중 더 높은 NSE 값을 기준으로 성능을 평가하였고, 예측 단계에서는 실제 홍수예측 절차와 동일하게 72시간 수위 예측을 수행하여 NSE와 RMSE로 예측성능을 검증하였다. 그 결과, 개발 단계에서는 21개 관측소 중 18개 관측소에서, 예측 단계에서는 14개 관측소에서 NSE 0.6 이상의 성능이 확인되었으며, 이를 통해 다중지점 하천수위 예측 모델의 실제 적용 가능성을 검증하였다.
-
Development and performance evaluation of LSTM-based multi-points water level forecasting model for downstream region of Yongdam Dam
-
Research Article
-
Evaluation of GR4J streamflow simulations incorporating snow accumulation and snowmelt
적설 및 융설 영향을 반영한 GR4J 모형의 유출 모의 평가
-
Seo Gyun Lee, Moon Hyung Park, Subin Kang, Hyun Han Kwon
이서균, 박문형, 강수빈, 권현한
- This study aims to evaluate and improve the reproducibility of winter–spring (December–April) streamflow using a GR4J-SN model that explicitly accounts for snow …
본 연구의 목적은 융·적설 과정을 고려한 GR4J-SN 모형을 활용하여 겨울-봄(12~4월) 유량 재현성을 평가 및 개선하는 데 있다. 이를 위해 강수, 기온, 댐 …
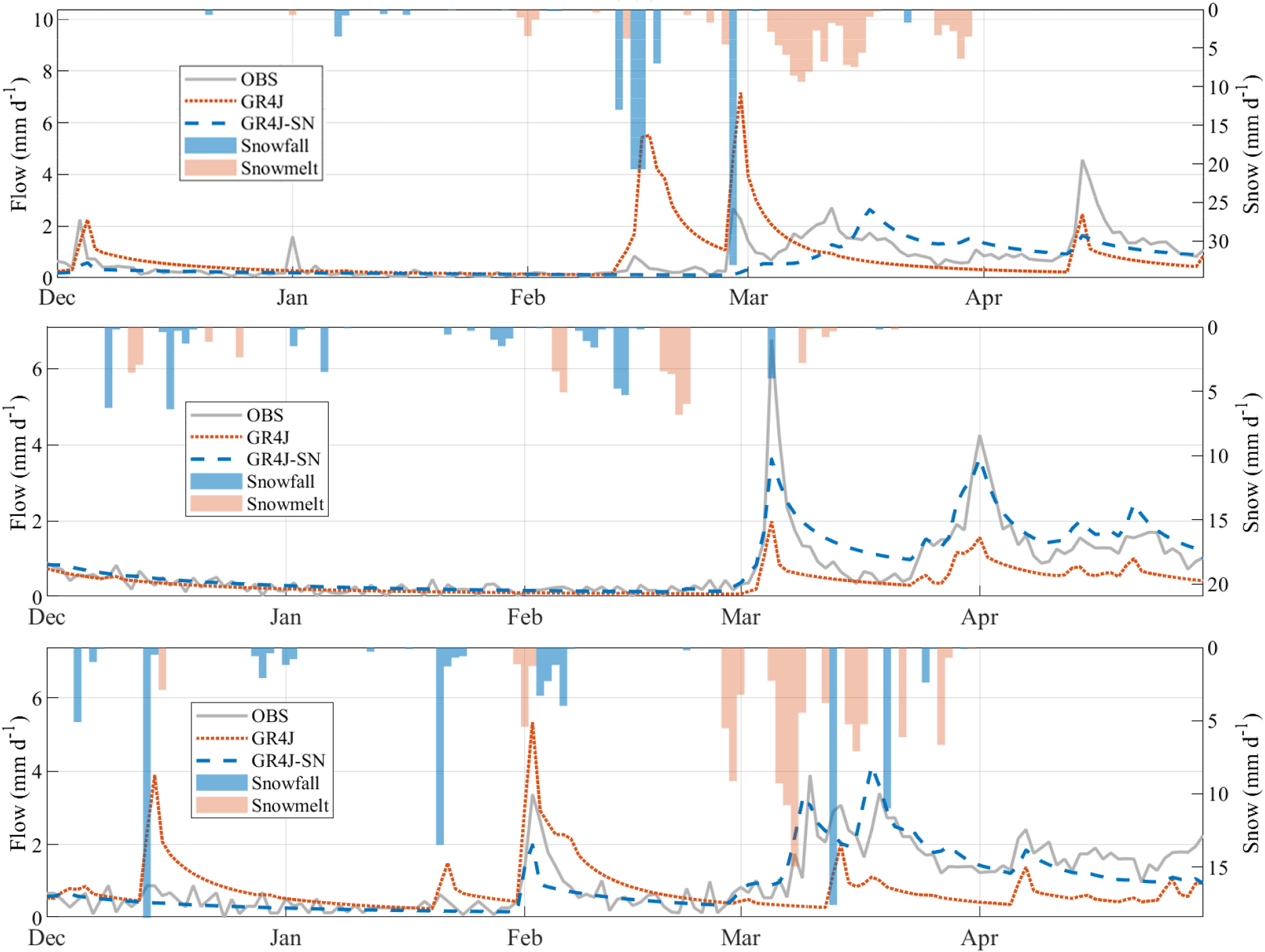
- This study aims to evaluate and improve the reproducibility of winter–spring (December–April) streamflow using a GR4J-SN model that explicitly accounts for snow accumulation and melt. Precipitation, air temperature, and dam‐inflow data were used to estimate seasonally varying parameter sets for three regimes—December–February, March–April, and May–November—via a multi-objective function combining the Kling–Gupta efficiency (KGE) with RMSE computed separately for low and high flows. Model skill was assessed for the full period and by month using KGE, Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE), correlation coefficient (CC), RMSE, and PBIAS. In addition, standardized anomaly plots and conditional probability analysis were employed to examine temperature–runoff response characteristics. Results show that in March–April, when snowmelt strongly influences runoff, KGE improved from 0.400 and 0.471(GR4J) to 0.754 and 0.767(GR4J-SN) and NSE from 0.145 and 0.576 to 0.562 and 0.578, indicating clear gains in reproducing both peak flows and low-flow conditions. The systematic overestimation of winter flows was also alleviated, while annual KGE and NSE remained ≥0.90, demonstrating that the December–April improvements were achieved without degrading performance in other seasons. These findings suggest that a snow-aware GR4J-SN model provides sufficient reliability for dam-inflow simulation and offers practical support for spring flow forecasting and water-resources management in snow-affected mountainous basins.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구의 목적은 융·적설 과정을 고려한 GR4J-SN 모형을 활용하여 겨울-봄(12~4월) 유량 재현성을 평가 및 개선하는 데 있다. 이를 위해 강수, 기온, 댐 유입량 자료를 이용하여 KGE와 저·고유량을 분리한 RMSE로 구성된 다목적 함수를 활용해 12~2월, 3~4월, 5~11월 구간별 매개변수를 추정하였다. 모형 성능 평가는 전체 기간과 월별 KGE, NSE, CC, RMSE, PBIAS를 통해 수행하였으며, 표준화 아노말리 및 조건부 확률 분석을 통해 기온 변화에 따른 유량 반응 특성을 검토하였다. 그 결과, 3~4월과 같이 융설이 유출에 주요하게 작용하는 시기에서 기존 GR4J 모형 대비 KGE가 0.400, 0.471에서 0.754, 0.767로, NSE가 0.145, 0.576에서 0.562, 0.578로 향상되었으며, 봄철 첨두유량 및 저유량 구간의 재현성이 뚜렷이 개선되었다. 또한 겨울의 유량 과대 추정 경향이 완화되고, 연간 KGE 및 NSE는 0.9 이상으로 유지되어 타 계절의 모의 성능 저하 없이 12월~4월 유량 성능을 개선하였다. 이러한 결과는 융·적설 영향을 반영한 GR4J-SN 모형이 댐 유입량 모의에 충분한 적용성을 가지며, 향후 봄철 유량 예측 및 산지 유역 수자원 관리에 중요한 정보를 제공할 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
Evaluation of GR4J streamflow simulations incorporating snow accumulation and snowmelt
-
Research Article
-
An evaluation of subcatchment delineation methods for enhanced accuracy in urban flood analysis
도시침수 분석 정확성 향상을 위한 소유역 분할 기법 평가
-
Geumchae Shin, Junghwan Lee
신금채, 이정환
- With accelerating climate change and urbanization, urban flooding caused by localized extreme rainfall has become more frequent, increasing the need for accurate …
기후변화와 도시화의 가속화로 도시침수 발생 빈도가 증가함에 따라, 도시 배수 시스템의 침수 거동을 정확히 재현하기 위한 수치모형 기반 분석의 중요성이 커지고 있다. …
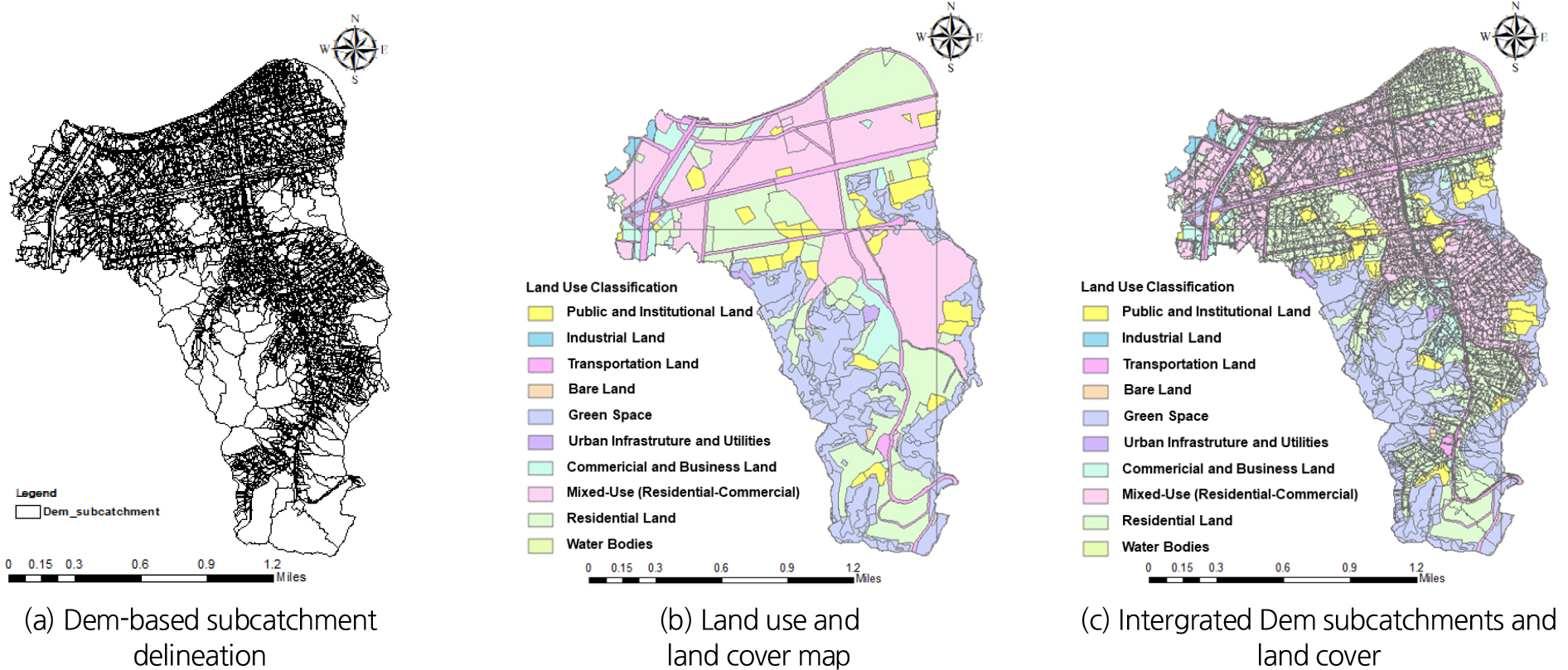
- With accelerating climate change and urbanization, urban flooding caused by localized extreme rainfall has become more frequent, increasing the need for accurate numerical modeling of urban drainage systems. This study evaluates the impact of subcatchment delineation methods on urban flood simulations by comparing DEM-based and Thiessen polygon-based approaches. A coupled 1D-2D hydrologic-hydrodynamic model was developed using InfoWorks ICM, and simulations were conducted under identical rainfall, drainage network, and pump operation conditions. Model outputs were quantitatively compared using the coefficient of determination (R2), Nash-Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE), and root mean square error (RMSE), and simulated inundation extents were validated against observed flood trace maps. The results show that subcatchment delineation has a limited effect on overall inundation magnitude at the watershed scale, but significantly influences the reproduction of localized flow dynamics and flood-prone areas. These findings highlight the importance of selecting an appropriate delineation strategy based on the objectives of urban flood analysis and provide useful insights for future flood modeling and urban drainage planning.
- COLLAPSE
기후변화와 도시화의 가속화로 도시침수 발생 빈도가 증가함에 따라, 도시 배수 시스템의 침수 거동을 정확히 재현하기 위한 수치모형 기반 분석의 중요성이 커지고 있다. 본 연구는 도시침수 모의 과정에서 핵심적인 전처리 단계인 소유역 분할 방식에 주목하여, DEM (Digital Elevation Model) 기반 소유역 분할과 Thiessen 다각형 기반 소유역 분할이 도시침수 해석 결과에 미치는 영향을 비교·분석하는 것을 목적으로 하였다. InfoWorks ICM을 활용하여 1D-2D 연계 수리·수문 모형을 구축하였으며, 두 소유역 분할 방식에 대해 동일한 강우 조건과 하수관망 및 펌프 운영 조건을 적용하여 도시 배수 및 침수 모의를 수행하였다. 분할 방식에 따른 결과 차이를 정량적으로 평가하기 위해 결정계수(R2), Nash-Sutcliffe 효율계수(NSE), RMSE를 활용하였고, 모의된 침수 분포는 침수 흔적도와 비교하여 공간적 타당성을 검토하였다. 분석 결과 소유역 분할 방식은 펌프 토출량 규모에는 큰 영향을 미치지 않는 것으로 분석되었다. 반면, 국지적인 유량 변화 및 침수 취약 구간의 세부 재현에는 분할 방식에 따라 차이가 발생하여, 침수 위치와 흐름 특성의 공간적 표현에 영향을 미치는 것으로 확인되었다. 이는 도시침수 해석에서 분석 목적에 따라 소유역 분할 방식을 합리적으로 선택하는 것이 중요함을 시사한다.
-
An evaluation of subcatchment delineation methods for enhanced accuracy in urban flood analysis
-
Research Article
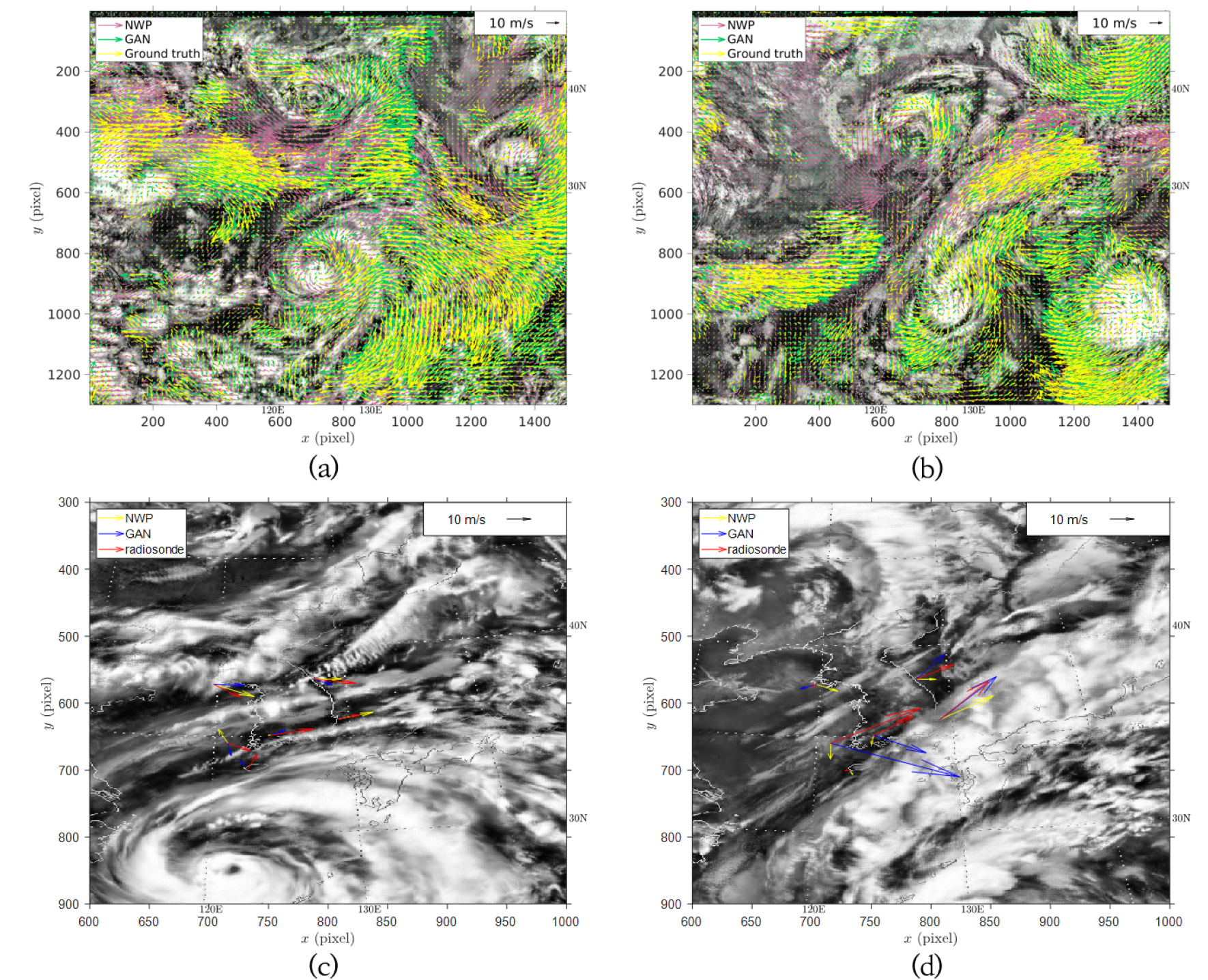
-
Atmospheric motion vector derivation technique using generative AI–based satellite image prediction
생성형 AI 기반 위성사진 예측을 활용한 대기운동벡터 산출 기법 연구
-
Dongjae Nam, Jongtak An, Byoungjoon Na
남동재, 안종탁, 나병준
- In this study, a method for deriving atmospheric motion vectors (AMVs) by combining generative AI–based satellite image frame prediction with a cross-correlation …
본 연구에서는 생성형 AI 기반 위성영상 프레임 예측과 상호연관 기법을 결합하여 대기운동벡터(AMV)를 산출하는 기법을 제시하고 라디오존데 관측값과 검증하였다. GAN 모델 학습을 위해 …
- In this study, a method for deriving atmospheric motion vectors (AMVs) by combining generative AI–based satellite image frame prediction with a cross-correlation technique is proposed and validated using radiosonde observations. For training the generative adversarial network (GAN) model, infrared satellite images of 68 typhoons observed by the COMS geostationary satellite were used to predict satellite images up to 1 hour ahead. The predicted frames exhibited high pixel-wise correlation coefficients with the corresponding ground truth images (approximately 0.97–0.98), confirming reliable reconstruction of cloud structures. AMVs derived from the predicted consecutive frames showed overall reductions in mean vector difference (MVD) and root mean square error (RMSE) compared to numerical weather prediction (NWP) based wind vectors when validated against radiosonde observations. However, for typhoon cases characterized by low cloud brightness contrast, it was found that a training iteration number of at least approximately 700,000 was required to maintain a certain level of prediction accuracy.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 생성형 AI 기반 위성영상 프레임 예측과 상호연관 기법을 결합하여 대기운동벡터(AMV)를 산출하는 기법을 제시하고 라디오존데 관측값과 검증하였다. GAN 모델 학습을 위해 천리안 1호 태풍 위성영상(68개 태풍)을 학습해 최대 1시간 이후 영상을 예측하였다. AI 모델의 평가 사례들에서 예측된 프레임은 실제 촬영된 프레임과 높은 픽셀 상관(약 0.97~0.98)을 보여 구름 구조 재현성을 확인하였다. 예측된 연속 프레임들을 이용해 산출한 AMV는 라디오존데 관측과 비교했을 때 NWP 기반 벡터보다 MVD 및 RMSE가 전반적으로 감소하였다. 다만 구름 명암 변화가 낮은 사례에서는 정확도 유지를 위해 학습 반복횟수를 약 70만 회 이상 수행할 필요가 있음을 확인하였다.
-
Atmospheric motion vector derivation technique using generative AI–based satellite image prediction
-
Special Issue: 지능형 도시홍수 예측
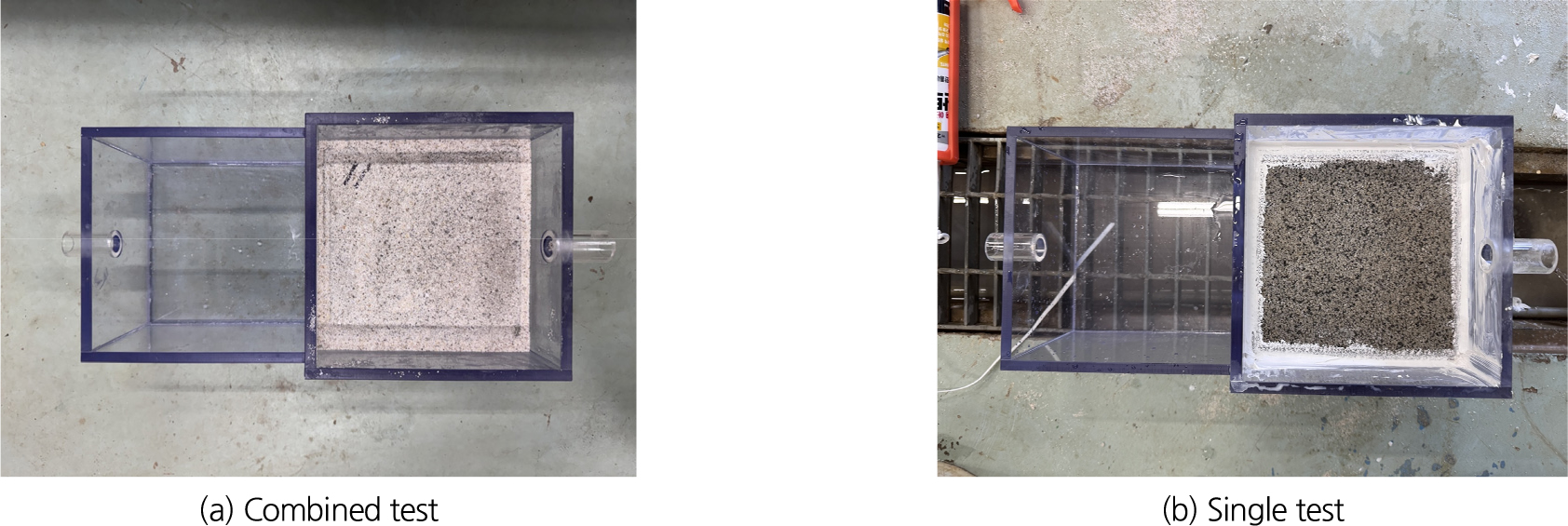
-
Experimental study on the hydraulic performance of permeable block systems with joints
지속가능한 배수시스템 포장의 줄눈 여부에 따른 배출성능에 대한 실험적 검증
-
Seongil Yeom, Jungkyu Ahn, Jeongmin Lee
염성일, 안정규, 이정민
- The expansion of impervious surfaces caused by urbanization has intensified urban flooding, revealing the hydraulic limitations of conventional urban drainage systems (CUDs). …
도시화로 인한 불투수면적의 확장은 도시 홍수를 가중시키며, 이에 따라 기존 전통적 배수시스템(Conventional Urban Drainage Systems, CUDs)의 수리적 한계가 지적되고 있다. 이러한 문제를 …
- The expansion of impervious surfaces caused by urbanization has intensified urban flooding, revealing the hydraulic limitations of conventional urban drainage systems (CUDs). As an alternative, sustainable urban drainage systems (SUDs) have been introduced, among which infiltration-type drainage systems (IRDs) are regarded as an effective solution for flood mitigation and hydrological restoration. This study experimentally investigated the hydraulic role of joints in permeable block systems by comparing the discharge and permeability under two configurations: Combined (with joints) and Single (without joints). Constant-head tests were conducted using five samples. The average discharge under the Combined condition was 2.82×10-5 m3/s, approximately 9 % higher than that under the Single condition (2.59×10-5 m3/s). The standard deviation and variance decreased by 38 % and about threefold, respectively, indicating improved discharge stability and reproducibility. The mean hydraulic conductivities were similar between conditions (6.39 × 10-4 m/s and 6.47 ×10-4 m/s). However, samples 2 and 5 in the Single case exhibited greater variability, suggesting localized clogging when joints were absent. These findings demonstrate that joints function not only as drainage paths but also as key structural elements that ensure hydraulic stability within IRDs. Furthermore, the results provide quantitative evidence of the role of joints in promoting flow uniformity and can serve as fundamental data for the design optimization and long-term performance evaluation of infiltration-type drainage systems.
- COLLAPSE
도시화로 인한 불투수면적의 확장은 도시 홍수를 가중시키며, 이에 따라 기존 전통적 배수시스템(Conventional Urban Drainage Systems, CUDs)의 수리적 한계가 지적되고 있다. 이러한 문제를 해결하기 위한 대안으로 지속가능한 도시배수시스템(Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems, SUDs)이 도입되고 있으며, 그중 침투형 배수시스템(Infiltration-type Drainage Systems, IRDs)은 도시 물순환 회복과 홍수 저감에 효과적인 기술로 평가된다. 본 연구는 IRDs의 핵심 구성 요소인 투수블록과 줄눈(joint)의 수리학적 기능을 규명하기 위해, 줄눈 유무에 따른 유출 특성과 투수 성능을 실내 정수두 실험을 통해 정량적으로 비교·분석하였다. 실험은 총 5개의 시료를 Combined(줄눈 포함) 및 Single(줄눈 제외) 조건으로 구분하여 수행하였다. 그 결과, Combined 조건의 평균 유출량은 2.82×10-5 m3/s로 Single 조건(2.59×10-5 m3/s) 대비 약 9 % 높게 나타났으며, 표준편차와 분산은 각각 38 % 및 약 3 배 감소하여 유출 안정성과 재현성이 향상되었다. 평균 투수계수는 Combined 6.39×10-4 m/s, Single 6.47×10-4 m/s로 유사하였으나, Single 조건에서는 Sample 2와 5에서 변동성이 뚜렷이 증가하여 줄눈 차단에 따른 국부적 막힘(clogging) 현상이 확인되었다. 이러한 결과는 줄눈이 단순한 배수 통로를 넘어 유출 안정성(hydraulic stability)과 유동 균질성(flow uniformity)을 유지하는 핵심 구조요소임을 실험적으로 입증한 것이다. 본 연구의 결과는 향후 IRD 설계 및 장기 성능평가를 위한 기초 자료로 활용될 수 있으며, 향후 인공강우 실험과 3차원 수치해석을 통해 줄눈 구조 최적화와 막힘 저항성 향상을 규명할 필요가 있다.
-
Experimental study on the hydraulic performance of permeable block systems with joints
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of Korea Water Resources Association
Journal of Korea Water Resources Association
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of Korea Water Resources Association
Journal of Korea Water Resources Association