-
Review

-
Hydrological applications of polarimetric SAR: Current progress, knowledge gaps, and future directions
편극 SAR의 수문학적 활용: 현황, 개선점 및 향후 방향
-
Hyunsu Park, SeokHwan Hwang, Jungsoo Yoon, Narae Kang,, Seokhyeon Kim
박현수, 황석환, 윤정수, 강나래, 김석현
- Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar (PolSAR) provides unparalleled capability to disentangle surface, volume, and double-bounce scattering, enabling physically grounded observation of hydrological processes …
편파 합성개구레이다(PolSAR)는 표면·체적·이중 반사 성분을 분리해낼 수 있는 독보적 능력을 바탕으로, 광학이나 단일 편파 SAR으로는 관측이 어려운 수문 과정을 물리적으로 정합성 있게 …
- Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar (PolSAR) provides unparalleled capability to disentangle surface, volume, and double-bounce scattering, enabling physically grounded observation of hydrological processes that cannot be captured by optical or single-pol SAR systems. Leveraging this strength, recent studies have demonstrated PolSAR’s expanding value in quantifying soil moisture, detecting flooded vegetation, characterizing wetland hydro-ecological dynamics, and monitoring cryospheric states including snow, ice, and permafrost. This review consolidates these advances by linking the underlying polarimetric scattering principles with the hydrological variables they enable, and critically evaluates their performance across diverse land-surface and vegetation conditions. Despite notable progress, major challenges remain—including persistent quantitative uncertainties, complex mixed scattering in heterogeneous terrain, and limited operational readiness of current, computation-heavy algorithms. We highlight emerging pathways that can fundamentally reshape PolSAR’s role in hydrology, particularly through machine learning, multi-sensor fusion with optical, InSAR, and radiometric missions, and the transformative observational capabilities offered by next-generation L-/P-band satellites such as NISAR and BIOMASS. These developments position PolSAR as a central component of future operational and predictive hydrology.
- COLLAPSE
편파 합성개구레이다(PolSAR)는 표면·체적·이중 반사 성분을 분리해낼 수 있는 독보적 능력을 바탕으로, 광학이나 단일 편파 SAR으로는 관측이 어려운 수문 과정을 물리적으로 정합성 있게 포착할 수 있다. 이러한 강점을 기반으로 최근 연구들은 토양 수분의 정량화, 침수 식생 탐지, 습지 수문–생태 동역학 분석, 적설·빙하·영구동토층을 포함한 빙권 모니터링 등 다양한 분야에서 PolSAR의 활용 가치를 입증해 왔다. 본 총설은 이러한 발전을 체계적으로 정리하고, 편파 산란 원리와 분해 기법이 각 수문 변수 도출과 어떻게 연결되는지를 종합적으로 검토한다. 아울러 다양한 지표·식생·대기 조건에서 PolSAR 기반 기법이 보여주는 성능을 평가하고, 여전히 남아 있는 정량적 불확실성, 복합 지형에서의 혼합·방향성 산란, 높은 계산 비용으로 인한 낮은 운용성 등의 한계를 비판적으로 논의한다. 마지막으로 기계학습, 광학·InSAR·마이크로파 복사계와의 다중 센서 융합, NISAR·BIOMASS 등 차세대 L-/P-밴드 위성의 등장과 같은 최근 흐름이 향후 PolSAR의 실시간·예측 수문학적 활용을 어떻게 확장할 수 있는지를 제시한다.
-
Hydrological applications of polarimetric SAR: Current progress, knowledge gaps, and future directions
-
Research Article
-
Prediction of domestic water demand in the Chungcheong region according to climate change scenarios using machine learning models
머신러닝 모형을 이용한 기후변화에 따른 충청권역 생활용수 수요량 예측
-
Seo-Young Kang, Min Ji Kim, Jiyoung Kim, Tae-Woong Kim
강서영, 김민지, 김지영, 김태웅
- growth and climate change. In Korea, the National Water Management Master Plan (NWMMP) predicted domestic water demand in every five years from …
지속적인 사회발달로 인한 용수 사용량의 증가와 기후변화로 인한 기후변동성의 증가에 따라 안정적인 수자원 관리를 위한 용수 수요량 예측의 중요성이 커지고 있다. 제1차 …
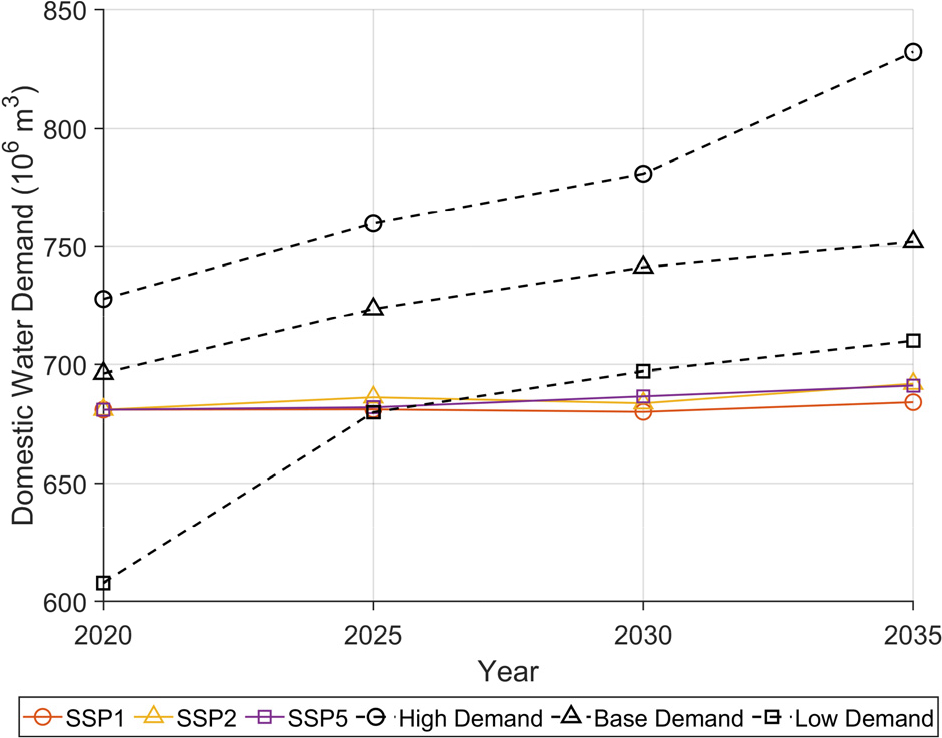
- growth and climate change. In Korea, the National Water Management Master Plan (NWMMP) predicted domestic water demand in every five years from 2020 to 2030. However, social, economic, and meteorological factors were not considered in the NWMMP. In this study, using XGBoost, DNN, and LSTM, we predicted domestic water demand considering social, economic, and meteorological influencing factors provided in climate change scenarios. The LSTM model outperformed other models, achieving an average R2 of 0.98 in the training phase and 0.94 in the validation phase. Accordingly, LSTM was selected to achieve high accuracy and to avoid low risk of overfitting. Three distinct patterns of predicted domestic water demand emerged: decreasing, stabilizing, and increasing. and these patterns were evident in the representative regions of Gyerong, Asan, and Jeungpyeong, respectively. Compared to the domestic water demands derived solely from the planned water supply population in the NWMMP, the increasing trend was similar. The LSTM predicted increases of 0.44%(SSP1), 0.87%(SSP2), and 1.32% (SSP5) by 2035 relative to 2020, while the NWMMP predicted increases of 14.33%(high demand), 8.00%(reference demand), and 16.81%(low demand). These results are expected to support the development of regionally customized water policies.
- COLLAPSE
지속적인 사회발달로 인한 용수 사용량의 증가와 기후변화로 인한 기후변동성의 증가에 따라 안정적인 수자원 관리를 위한 용수 수요량 예측의 중요성이 커지고 있다. 제1차 국가물관리기본계획에서는 2020년부터 2030년까지 5년 단위로 생활용수 수요량을 예측했지만, 사회, 경제, 기상과 같은 변동요인이 고려되지 않았다. 본 연구에서는 기후변화 시나리오에서 제공하는 사회, 경제, 기상 영향인자를 고려하여 생활용수 수요량을 예측했으며, 이를 위해 XGBoost, DNN, LSTM 기법을 활용하였다. LSTM의 평균 R2는 학습과 검증 단계에서 각각 0.98, 0.94로 나타났으며, 다른 모델보다 성능 저하가 가장 낮고 RMSE와 MAE에서 오차 증가가 가장 작았다. 이에 따라 예측 정확도를 높이고 과적합 위험을 피하기 위해 LSTM을 예측모형으로 선정했다. LSTM 분석 결과 각각의 지자체는 미래 수요량이 감소, 안정, 증가하는 것으로 나타났으며, 이러한 경향은 대표지역인 계룡시, 아산시, 증평군에서 뚜렷하게 나타났다. 제1차 국가물관리기본계획이 제시한 계획 급수인구만으로 도출한 생활용수 수요량 값과 비교한 결과 증가 추세가 동일했다. LSTM에 의한 예측 수요량은 2020년 대비 2035년에 0.44%(SSP1), 0.87%(SSP2), 1.32%(SSP5) 증가했고, 국가물관리기본계획은 14.33%(고수요), 8.00%(기준수요), 16.81%(저수요) 증가하였다. 이러한 예측결과는 지역 맞춤형 수자원 정책에 활용될 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
Prediction of domestic water demand in the Chungcheong region according to climate change scenarios using machine learning models
-
Research Article

-
Run of river hydropower potential assessment at Kaldan Weir at Seosicheon, Gurye-gun, Jeollanam-do, Korea
구례군 서시천 깔단보의 하천 흐름을 활용한 초소수력 잠재발전수자원량의 평가
-
Moo-Kyeong Lee, Ji-Min Hwang, Kuk-Hyun Ahn, Dongwon Na, Hyosang Lee
이무경, 황지민, 안국현, 나동원, 이효상
- Hydropower, a conventional renewable energy source, is gaining renewed attention as a practical pathway toward deep decarbonization. This study assesses the feasibility …
수력은 전통적인 재생에너지원으로서 탈탄소 기후위기 대응에서 그 중요성이 재조명되고 있다. 본 연구는 전라남도 구례군 서시천 깔단보를 대상으로 별도의 댐 및 보 설치 …
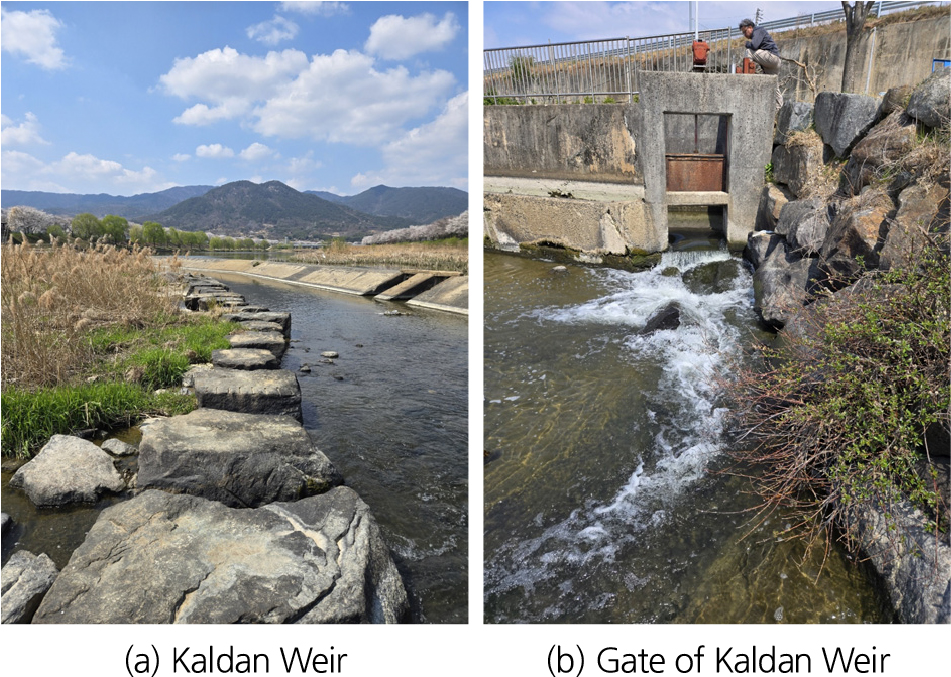
- Hydropower, a conventional renewable energy source, is gaining renewed attention as a practical pathway toward deep decarbonization. This study assesses the feasibility of a small run-of-river (RoR) scheme at the Kaldan Weir on the Seosicheon Stream, Gurye-gun, Jeollanam-do (effective head = 1 m; overall efficiency = 85 %). We first characterize the present river environment and then estimate exploitable hydropower potential without constructing additional dams or barrages. Three independent approaches are applied: (1) the basin-average runoff method, (2) a flow-duration-curve (FDC) approach, and (3) direct use of an observed stage–discharge hydrograph. Annual energy yields are 274,062 kWh/year (method 1), 104,322 kWh/year (method 2, Q185~Q355), and 95,882 kWh/year (method 3, Average, Q185~Q355). Corresponding reductions in greenhouse-gas and particulate emissions are estimated at 125.907 tCO2/ year – 2.095 kg/year (method 1), 47.926 tCO2/year - 0.798kg/year (method 2, Q185~Q355), and 44.049 tCO2/year – 0.733 kg/year (method 3, Average, Q185~Q355), respectively. Results confirm that even low-head reaches in small Korean rivers can deliver meaningful climate- and air-quality co-benefits when developed as RoR hydropower, supporting wider deployment of micro-scale installations in similar settings.
- COLLAPSE
수력은 전통적인 재생에너지원으로서 탈탄소 기후위기 대응에서 그 중요성이 재조명되고 있다. 본 연구는 전라남도 구례군 서시천 깔단보를 대상으로 별도의 댐 및 보 설치 없이 현재의 하천환경, 자연하천 유하량(Run of River, RoR)을 활용한 개발 가능한 발전 수자원량을 산정하고, 이에 대한 탄소발생 및 미세먼지 저감 효과를 평가하여 소규모 수력발전 사업의 가능성을 평가하였다. 발전 수자원량 평가는 1) 유역 평균 유출량 방법, 2) 유황곡선 방법, 3) 실 관측 수문곡선 방법을 적용하며, 발전량을 산정하고, 이에 따른 연간 탄소발생 및 미세먼지 저감 효과를 산정한다. 서시천 깔단보(유효낙차 1 m, 발전 효율 85%)의 발전 수자원량 평가는 각각의 방법에 따라 1) 274,062 kWh/year, 2) 104,322 kWh/year (Q185~Q355), 3) 95,882 kWh/year (평균, Q185~Q355), 이며, 탄소발생-미세먼지(PM2.5) 저감효과는 각각 1) 125.907 tCO2 – 2.095 kg, 2) 47.926 tCO2 – 0.798 kg (Q185~Q355), 3) 44.049 tCO2 – 0.733 kg (평균, Q185~Q355) 이다. 본 연구를 통하여 소규모 하천의 RoR 발전 가능성을 확인하였다.
-
Run of river hydropower potential assessment at Kaldan Weir at Seosicheon, Gurye-gun, Jeollanam-do, Korea
-
Research Article / 우수학생논문상
-
Evaluating the applicability of Multi-satellite based soil moisture products in Korea
국내에서 다중 위성 기반 토양수분 산출물의 적용성 평가
-
Sungjin Han, Kijin Park, Jongmin Park, Byungkyu Kim
한성진, 박기진, 박종민, 김병규
- This study quantitatively evaluated surface soil moisture from the advanced scatterometer (ASCAT) (C-band) and soil moisture active passive (SMAP) Level-4 (L-band) against …
본 연구는 국내 7개 관측소를 대상으로 C-band Advanced scatterometer (ASCAT)와 L-band Soil moisture active passive (SMAP) 표층 토양수분을 지상관측과 비교하여 계절성과 수문상태(건조/습윤)에 …
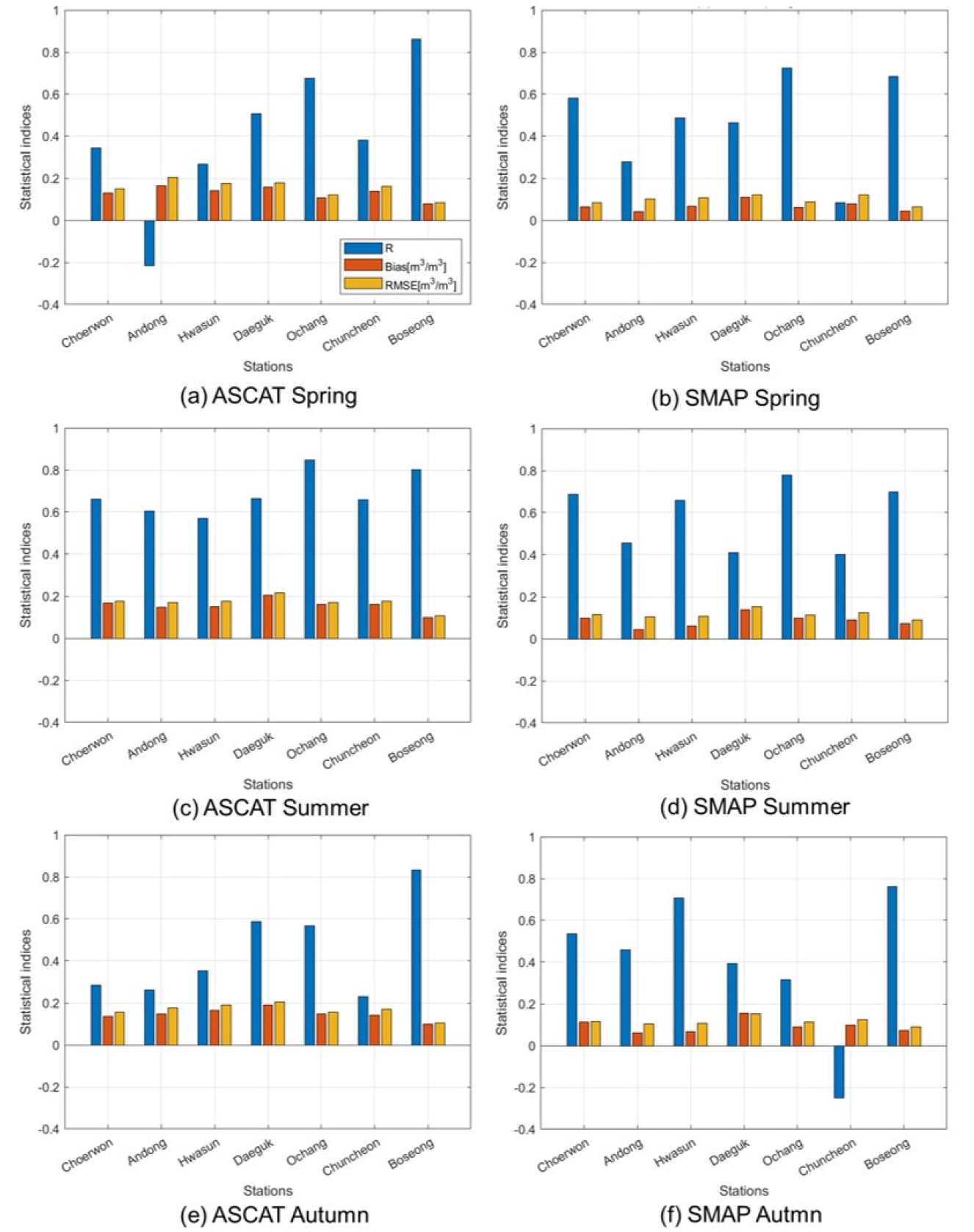
- This study quantitatively evaluated surface soil moisture from the advanced scatterometer (ASCAT) (C-band) and soil moisture active passive (SMAP) Level-4 (L-band) against in-situ observations at seven sites across Korea, focusing on seasonal behavior and hydrologic state (dry/wet). Excluding winter season, we assessed correlation coefficient (R), Bias, and root mean square error (RMSE) for spring, summer, and autumn, and classified years as dry or wet based on the normal mean precipitation. Overall, SMAP soil moisture exhibited lower Bias and RMSE than ASCAT (RMSE: 0.08~0.15 vs. 0.10~0.20 m3 m-3), which is resulted from the higher vegetation penetration of L-band and improved temporal representativeness of the 3-hourly assimilation output. Seasonally, both sensors showed higher R in summer as variability increased due to the monsoon and convective rainfall (ASCAT: 0.57~0.80; SMAP: 0.40~0.78). However, at sites adjacent to airports and military airfields, potential radio-frequency interference in the SMAP L-band, and at sites near rivers and reservoirs, mixed land–water surfaces within the same pixel, amplified errors. In orchards and irrigated areas, canopy structure and irrigation limited SMAP’s ability to capture seasonal variability. During wet periods, many sites exhibited increases in R along with rises in Bias and RMSE, likely due to the nonlinearity of satellite-based products near saturation, post-rainfall surface heterogeneity, and increased vegetation water content.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 국내 7개 관측소를 대상으로 C-band Advanced scatterometer (ASCAT)와 L-band Soil moisture active passive (SMAP) 표층 토양수분을 지상관측과 비교하여 계절성과 수문상태(건조/습윤)에 따른 성능 차이를 정량 평가하였다. 겨울을 제외한 봄·여름·가을 자료에 대해 correlation coefficient (R), Bias, root mean square error (RMSE) 지표를 사용하고, 지점별 정상 연평균 강수량을 기준으로 각각의 연도를 건조/습윤으로 구분하였다. 그 결과 SMAP 토양수분은 전반적으로 Bias와 RMSE가 낮게 나타났으며(RMSE:0.08~0.15 vs. 0.10~0.20 m3 m-3), 이는 L-band의 높은 식생 투과성과 3시간 간격 동화 산출의 시간 대표성 개선 효과에 기인한 것으로 해석된다. 계절적 성능은 두 센서 모두 여름철 장마·대류성 강우로 인해 변동폭이 증가함에 따라 R이 상승(ASCAT 0.57~0.80, SMAP: 0.40~0.78)했다. 단, 일부 공항·군공항 인접 지점에서 SMAP L-band의 전파간섭 가능성, 하천·저수지 인접 지점에서는 동일 픽셀 내 지표-수체 혼재로 오차가 확대되었고, 과수원·관개지에서는 캐노피 구조와 관개의 영향으로 SMAP의 계절 변동성 모의가 제한되었다. 습윤기에는 다수 지점에서 R이 증가하는 동시에 Bias 및 RMSE도 증가하였으며, 이는 포화 근접 시 위성 기반 산출물의 비선형성, 강우 직후 지표 이질성, 식생 수분함량 증가가 주요 원인으로 판단된다.
-
Evaluating the applicability of Multi-satellite based soil moisture products in Korea
-
Research Article
-
An experimental study on gas behavior and effective flow area for liquid in horizontal two-phase flow
수평 이상류 내 기체 거동 및 액체 유효흐름단면에 대한 실험 연구
-
Chaebin Song, Seongeun Kim, Museop Kim, Siwan Lyu
송채빈, 김성은, 김무섭, 류시완
- A series of experiments has been conducted to analyze the void fraction and effective flow area of two-phase flow in a horizontal …
정하였다. 실험은 내경 100 mm 수평관에서 플러그 및 슬러그 흐름 조건을 대상으로 수행되었으며 PIV 기법을 이용한 유속구조 실험과 영상분석기법을 적용한 기포거동 실험을 …
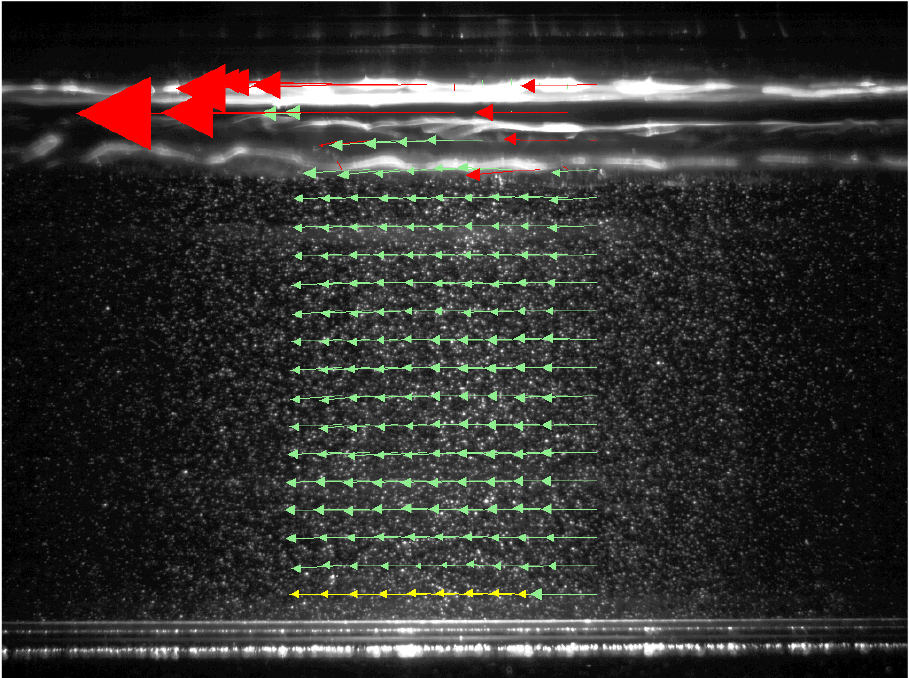
- A series of experiments has been conducted to analyze the void fraction and effective flow area of two-phase flow in a horizontal pipe. Experiments were performed in a 100 mm diameter horizontal pipe under plug and slug flow conditions. The velocity field was measured using Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) and bubble behavior was analyzed using an image processing technique. The in-pipe distribution curve of void fraction was governed by the flow regime rather than the flowrate. For plug flow, a sharp change in the cross-sectional distribution curve of void fraction can be observed due to the accumulation of air in the upper part of a pipe. While the more even distribution of air across a relatively wider area, in slug flow, results in a gradual shape for void fraction distribution profile. The upper part, which shows high void fraction and low PIV valid vector ratio, coincides with the boundary where the difference between the time-averaged and instantaneous velocity fields appears. This boundary can be defined as the edge of the region occupied by gas, this implies that the change of effective flow area contributing to actual liquid conveyance depends on the flow pattern. The effective flow area differed by up to 20 % between plug and slug flows, showing a decrease in the effective liquid flow area depending on the flow pattern. These results suggest that air entrainment should be considered in the design and operation of large-diameter conduit systems to ensure stable hydraulic performance.
- COLLAPSE
정하였다. 실험은 내경 100 mm 수평관에서 플러그 및 슬러그 흐름 조건을 대상으로 수행되었으며 PIV 기법을 이용한 유속구조 실험과 영상분석기법을 적용한 기포거동 실험을 각각 수행하였다. 실험결과를 통해 흐름 내 기체점유율 분포는 유량 조건보다 흐름양상 특성에 지배되는 것을 확인하였다. 플러그 흐름에서는 기체가 관 상부에 집중되어 관 내 기체점유율 분포에서 급격한 변화를 보였으며 슬러그 흐름에서는 기체가 단면 전반으로 확산되며 상대적으로 완만한 분포를 관찰할 수 있었다. 기체점유율이 높은 상부 영역에서는 PIV 유효 벡터비가 감소하였으며 해당 구간이 시간평균 유속장과 순간 유속장 간 차이가 발생하는 경계로 작용함을 확인하였다. 이에 따라 해당 구간을 기체 점유 영역의 경계로 정의하여 흐름양상별 유효흐름단면을 산정하였다. 그 결과 플러그 흐름과 슬러그 흐름 간 유효흐름단면에는 최대 20 % 차이를 확인하였으며 이는 흐름양상에 따라 실제 액체수송에 기여하는 유효단면적의 변화가 발생할 수 있음을 의미한다. 이러한 결과는 이상류가 발생하는 대심도 터널과 같은 대구경 관로에서 흐름양상에 따라 실제 배수능력이 설계 성능에 미치지 못할 수 있음을 의미한다. 따라서 관로시스템 설계 및 운영 시 공기 혼입에 따른 유효흐름단면 감소와 그에 따른 통수능 변화를 고려할 필요가 있다.
-
An experimental study on gas behavior and effective flow area for liquid in horizontal two-phase flow
-
Research Article
-
Deriving factors affecting water quality using multivariate statistical analysis in the Jamsil reach of the Han River
다변량 통계분석을 이용한 한강 잠실수역의 수질영향 요인 도출
-
Sunhwa Choi, Seojin Kang
최선화, 강서진
- This study applied ANOVA, PCA, and factor analysis to identify the water quality characteristics and influencing factors in the Jamsil reach of …
본 연구는 한강 잠실수역의 수질특성과 수질영향 요인을 규명하기 위해 일원분산분석(ANOVA), 주성분분석, 요인분석을 실시하였다. PD와 JS 지점의 평균 수질은 하천 수질환경기준 Ia~Ib 등급에 …
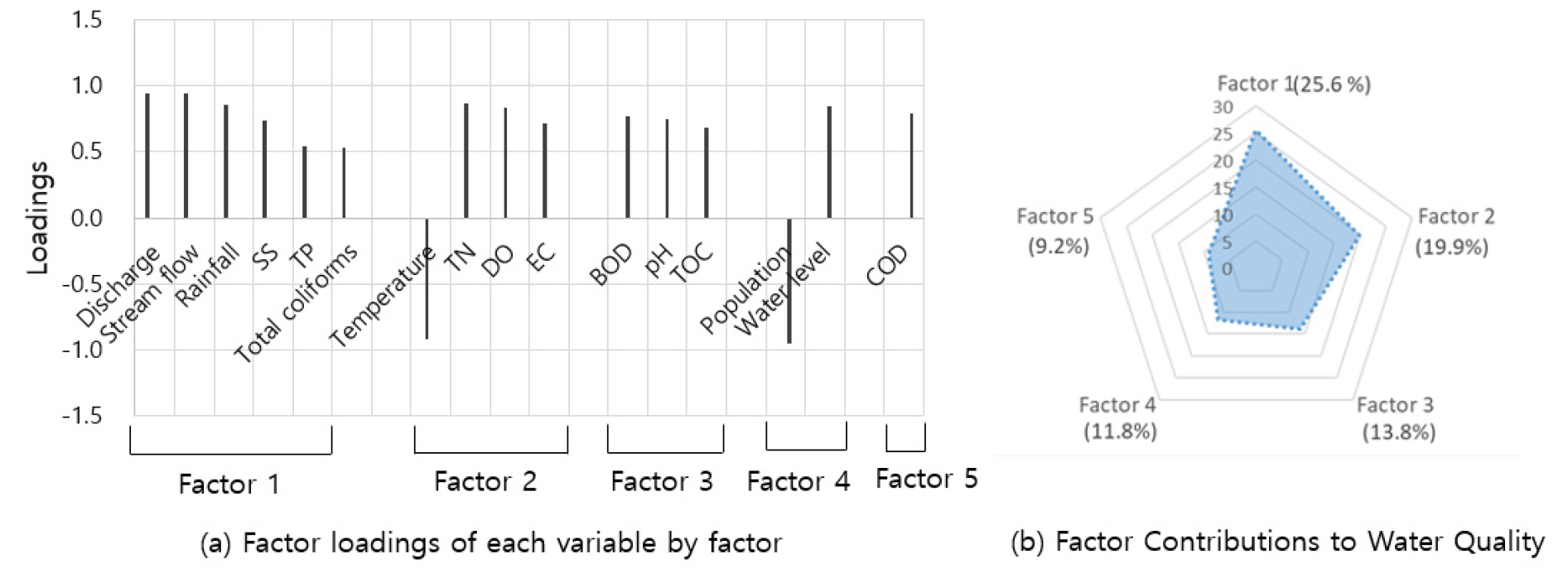
- This study applied ANOVA, PCA, and factor analysis to identify the water quality characteristics and influencing factors in the Jamsil reach of the Han River. The PD and JS sites exhibited average water quality within Class Ia~Ib of the river water quality standards, while the NRJ site fell into Class II. At the JS and NRJ sites, total coliforms contamination increased significantly during the rainy season, necessitating management measures. Five principal components were extracted through PCA. The contribution rates to water quality were 25.6% for Factor 1, 19.9% for Factor 2, 13.8% for Factor 3, 11.8% for Factor 4, and 9.2% for Factor 5, with a cumulative contribution of 80.3%. Factor 1 was strongly associated with dam discharge, streamflow, rainfall, SS, TP, and total coliform. Factor 2 was correlated with water temperature, TN, DO, and EC. Factor 3 was related to BOD, pH, and TOC. Factor 4 was linked to population and water level, while Factor 5 was correlated with COD. For effective water quality management in the lower Han River, it is necessary to block the inflow of non-point source pollutants and refractory substances, strengthen the management of effluents from sewage treatment plants, and increase dam discharge to maintain adequate flow during dry seasons.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 한강 잠실수역의 수질특성과 수질영향 요인을 규명하기 위해 일원분산분석(ANOVA), 주성분분석, 요인분석을 실시하였다. PD와 JS 지점의 평균 수질은 하천 수질환경기준 Ia~Ib 등급에 해당하였으며, NRJ 지점은 II등급으로 나타났다. 우기에는 JS과 NRJ 지점에서 총대장균군 오염도가 크게 증가하여 이에 대한 관리대책이 필요하였다. PCA 결과 5개의 주성분이 도출되었으며, 각 요인의 기여율은 요인 1이 25.6%, 요인 2가 19.9%, 요인 3이 13.8%, 요인 4가 11.8%, 요인 5가 9.2%로 나타났고, 누적기여율은 80.3%였다. 요인 1은 댐 방류량, 유량, 강수량, SS, TP, 총대장균군과 높은 관련성을 보였으며, 요인 2는 수온, TN, DO, EC. 요인 3은 BOD, pH, TOC, 요인 4는 인구수와 수위, 요인 5는 COD와 연관성이 높았다. 한강 하류의 수질관리를 위해서는 유역의 비점오염물질 및 난분해성 오염물질 유입 차단, 하수처리장 방류수 관리 강화, 건기에 적정 수량 확보를 위한 댐 방류량 조절 및 확대가 필요하다.
-
Deriving factors affecting water quality using multivariate statistical analysis in the Jamsil reach of the Han River
-
Research Article
-
Development of urban inundation measurement data based inundation prediction model using LSTM
을 이용한 계측데이터기반 침수 예측모델 개발
-
Jaewoong Cho, Hoseon Kang, Hyejin Moon, Hanseung Lee
조재웅, 강호선, 문혜진, 이한승
- Due to the recurring urban flood damage occurring annually, the National Disaster Management Research Institute (NDMI) has installed and operated such sensors …
최근 도시침수 피해가 매년 반복적으로 발생함에 따라 국립재난안전연구원은 2018년부터 울산, 부산, 인천, 천안, 창원 등에 침수센서를 설치하여 운영하고 있다. 본 연구에서는 다년간 …
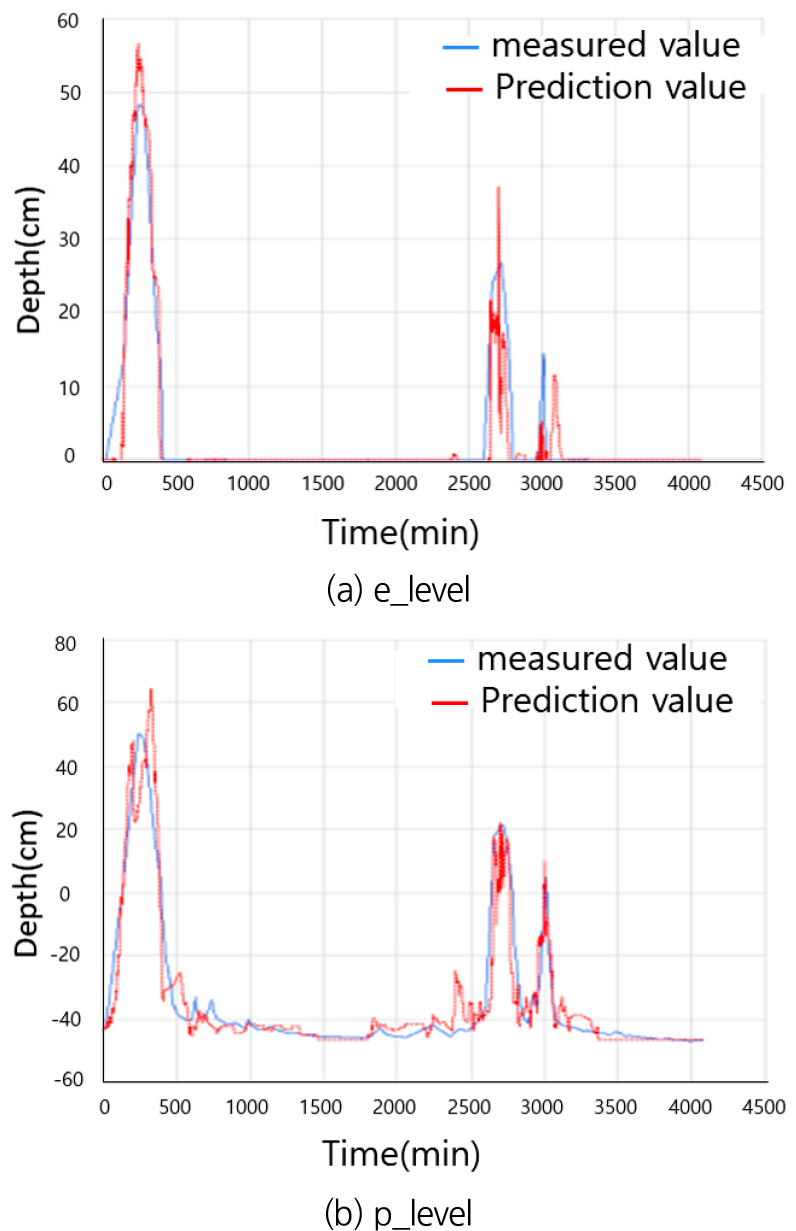
- Due to the recurring urban flood damage occurring annually, the National Disaster Management Research Institute (NDMI) has installed and operated such sensors in cities including Ulsan, Busan, Incheon, Cheonan, and Changwon Since 2018. These sensors are used for both real-time monitoring and validating threshold rainfall levels that cause urban flooding. This study aims to utilize the urban flood measurement data collected over multiple years to predict inundation levels using a time-series prediction model. Specifically, we adopted the Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) model, which excels in learning long-term dependencies. The performance analysis of the model showed that it accurately predicted the onset and end time of flooding, as well as the maximum flood depth, using the both ground surface and rain water inlet sensor data. The model achieved a Mean Absolute Error (MAE) of 1.211 and Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) of 3.166 for ground surface flood depth predictions, and an MAE of 4.136 and RMSE of 7.157 for rain water inlet flood depth predictions. Notably, all correlation coefficients exceeded 0.94, indicating high prediction accuracy. The inundation prediction model developed in this study is expected to contribute to the establishment of real-time flood forecasting and response system in urban areas.
- COLLAPSE
최근 도시침수 피해가 매년 반복적으로 발생함에 따라 국립재난안전연구원은 2018년부터 울산, 부산, 인천, 천안, 창원 등에 침수센서를 설치하여 운영하고 있다. 본 연구에서는 다년간 수집된 도시 침수 계측데이터를 활용하여 침수 예측에 활용하기 위해 시계열 예측모델 중에서 장기 의존성 학습에 강점이 있는 LSTM을 이용하여 계측데이터 기반의 침수심 예측모델을 설계하였다. 모델의 성능분석 결과 지표 및 빗물받이 계측 데이터를 활용하여 침수 시점, 종료 시점, 최대 침수심을 정밀하게 예측하였으며, 지표 침수심의 예측 성능은 MAE 1.211, RMSE 3.166, 빗물받이 침수심의 예측 성능은 MAE 4.136, RMSE 7.157로 분석되었으며, 특히 상관계수는 0.94 이상의 높은 성능을 갖는 것으로 분석되었다. 본 연구에서 개발한 계측데이터 기반의 침수 예측모델은 향후 도시 내 실시간 침수 예측 및 대응 체계에 기여할 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
Development of urban inundation measurement data based inundation prediction model using LSTM
-
Research Article
-
Development and application of a technique to generate seepage fragility curves for river embankments using SEEP/W
SEEP/W를 이용한 하천 제방의 누수 취약도 곡선 작성 기법 개발 및 적용
-
Heeseong Park, Du Han Lee
박희성, 이두한
- This study developed an automated analysis technique based on SEEP/W to probabilistically evaluate the seepage stability of river levees and applied it …
본 연구는 하천 제방의 침투 안정성을 확률론적으로 평가하기 위해 SEEP/W 기반의 자동화 해석 기법을 개발하고, 이를 실제 제방 단면에 적용하여 침투 취약도 …
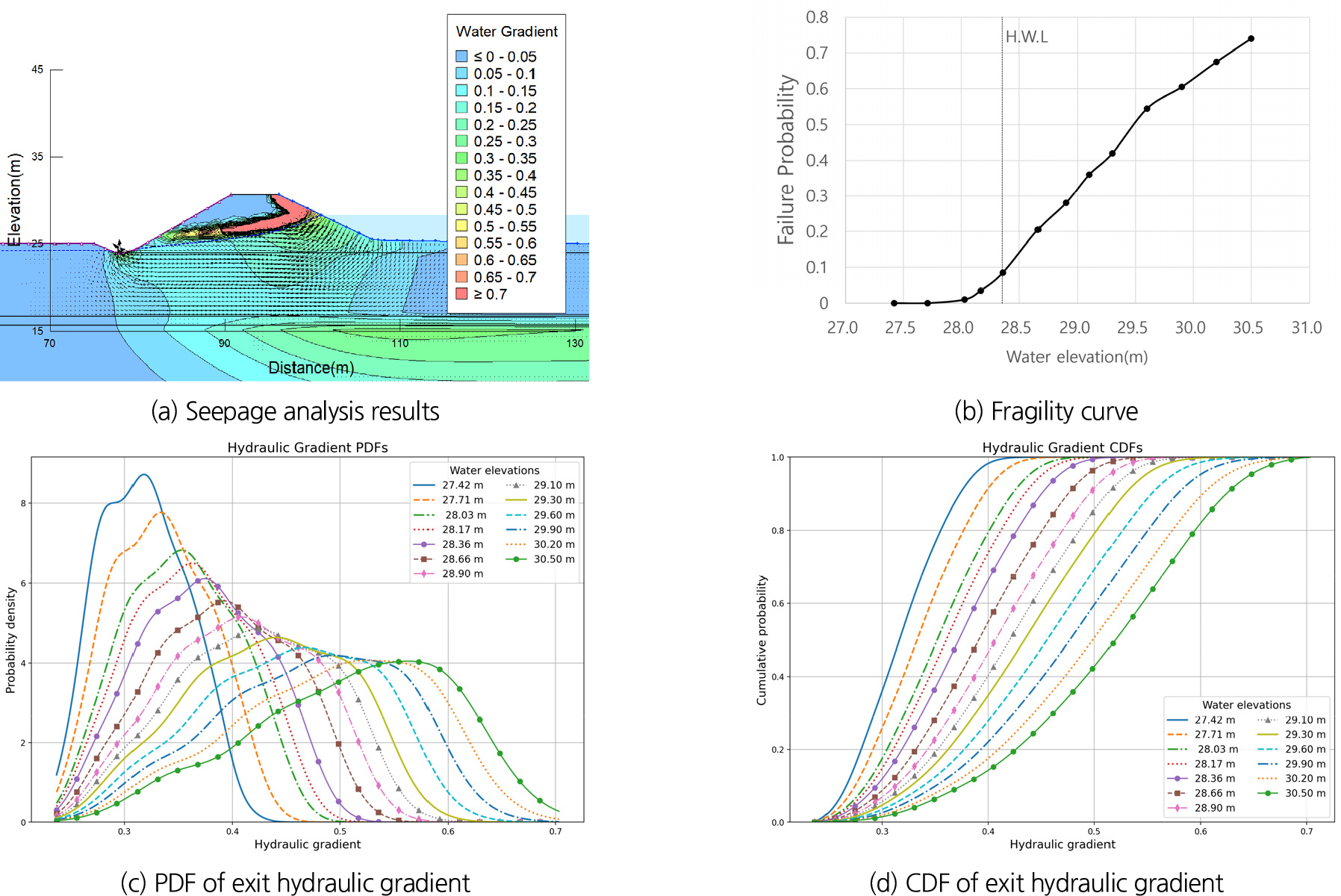
- This study developed an automated analysis technique based on SEEP/W to probabilistically evaluate the seepage stability of river levees and applied it to an actual levee cross-section to derive seepage fragility curves. To account for the uncertainty of levee materials—particularly the variability of saturated hydraulic conductivity—Monte Carlo simulation and Latin Hypercube Sampling were employed. A Python-based automation program was implemented to handle input data generation, iterative simulations, result storage, and visualization in an integrated manner. When applied to a real levee cross-section, the method identified the hydraulic conductivities of the embankment and foundation soil, the length and head of the phreatic line, and the levee geometry as the main factors influencing the probability of failure. Probability density function (PDF) analysis showed that as the water level rises, the distribution of exit hydraulic gradients becomes flatter and the mode shifts to the right. These findings are consistent with previous studies, demonstrating the validity of the proposed methodology. The presented approach can be practically applied to setting priorities for levee reinforcement and inspection, managing flood risk, and formulating investment plans.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 하천 제방의 침투 안정성을 확률론적으로 평가하기 위해 SEEP/W 기반의 자동화 해석 기법을 개발하고, 이를 실제 제방 단면에 적용하여 침투 취약도 곡선을 산정하였다. 제방 재료의 불확실성, 특히 포화 투수계수의 변동성을 반영하기 위해 몬테카를로 시뮬레이션과 라틴 하이퍼큐프 샘플링 기법을 적용하였으며, Python 기반 자동화 프로그램을 통해 입력 자료 생성, 반복 해석 수행, 결과 저장 및 시각화를 일괄적으로 수행할 수 있도록 하였다. 개발된 기법을 실제 제방 단면에 적용하였다. 적용 결과에 의하면 제체와 하부 지반의 투수계수, 침윤선 길이와 수두, 제방 형상 등이 파괴 확률의 주요 인자로 나타났다. PDF 분석에서는 수위 상승 시 유출 동수경사 분포가 평탄화되며 최빈값이 우측으로 이동하는 특성이 나타났다. 이러한 결과는 기존 연구와 일치하며 본 연구에서 제시한 방법론이 적합함을 나타낸다. 제시된 방법론은 제방의 보강·점검 우선순위 설정, 홍수 위험도 관리 및 투자계획 수립 등에 실무적으로 적용될 수 있다.
-
Development and application of a technique to generate seepage fragility curves for river embankments using SEEP/W
-
Research Article
-
Water body detection during drought and flood seasons using a Swin-Transformer with CAS500-1 satellite imagery
국토위성(CAS500-1) 영상을 활용한 Swin-Transformer 기반 갈수기홍수기 수체 탐지
-
Shinhyeon Cho, Wanyub Kim, Doseob Ahn, Seungchul Kim, Sangil Kim, Yangwon Lee, Minha Choi
조신현, 김완엽, 안도섭, 김승철, 김상일, 이양원, 최민하
- In recent years, the frequency of water-related disasters, such as droughts and floods, has increased. This phenomenon underscores the imperative for the …
최근, 가뭄 및 홍수와 같은 수재해가 빈번하게 발생함에 따라, 이를 효율적으로 관리하기 위해 고해상도 위성 자료 기반의 수체 모니터링의 필요성이 증대되고 있다. …
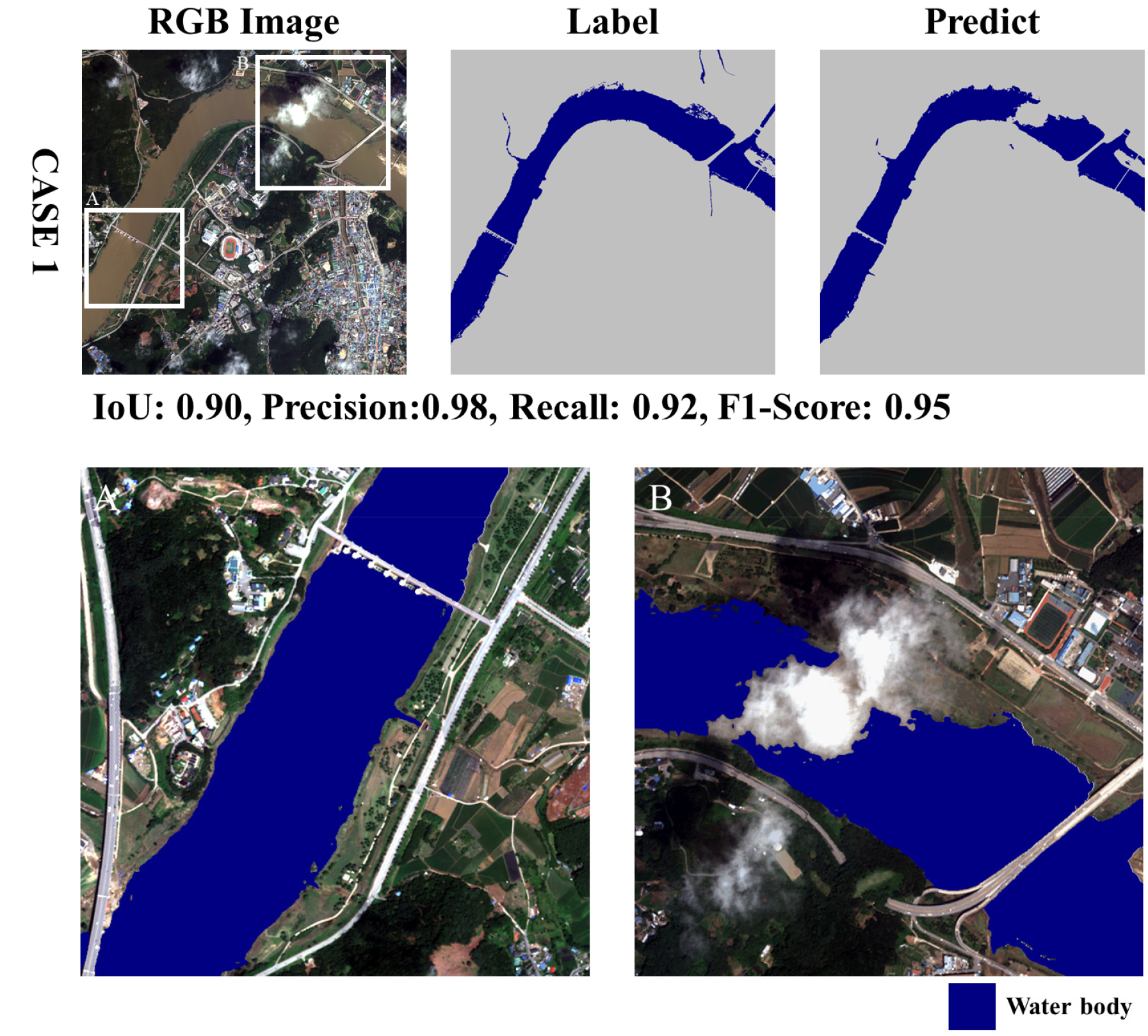
- In recent years, the frequency of water-related disasters, such as droughts and floods, has increased. This phenomenon underscores the imperative for the development of methodologies for the monitoring of water bodies using high-resolution satellite data. High-resolution satellite imagery facilitates the precise monitoring of both large-scale water bodies and smaller reservoirs and river channels, offering substantial advantages for disaster response. These include the rapid identification of inundation areas during floods and the tracking of reservoir storage decline under drought conditions. The Compact Advanced Satellite 500-1 (CAS500-1), also referred to as the Korean National Satellite, offers 2-meter spatial resolution, facilitating more precise water body detection in comparison to conventional medium- and low-resolution satellite data. In this study, the Swin-Transformer model was applied to CAS500-1 imagery for quantitative assessment of the performance of water body detection. Additionally, the study investigated the applicability of the model under real hydrological conditions, utilizing case studies of drought and flood events. Preliminary findings based on confusion matrix indicators demonstrate that the Swin-Transformer model has a high degree of accuracy, with IoU values ranging from 0.94 to 0.97 and F1-scores ranging from 0.97 to 0.98, across a range of reservoir scales. Case studies revealed that low water levels and narrow tributary conditions in the Seomjin River and Imha Reservoir during drought affected Precision and Recall variations, while flood-season imagery of the Geum River (Gongju Weir) showed limited boundary detection due to cloud cover, water level rise, and turbid water. These findings demonstrate that combining CAS500-1 imagery with Transformer-based models enables robust water body detection. However, they also indicate the need for further enhancements under extreme hydrological events. This study corroborates the applicability of CAS500-1 data and is expected to contribute to the advancement of satellite-based monitoring systems for water resource management and disaster response to droughts and floods in Korea.
- COLLAPSE
최근, 가뭄 및 홍수와 같은 수재해가 빈번하게 발생함에 따라, 이를 효율적으로 관리하기 위해 고해상도 위성 자료 기반의 수체 모니터링의 필요성이 증대되고 있다. 특히, 고해상도 위성 영상은 대규모 수계뿐만 아니라 소규모 저수지와 하천까지도 정밀하게 모니터링할 수 있어, 홍수 시 범람 지역의 신속한 파악이나 가뭄에 따른 저수량 감소 관측 등 재해 대응 측면에서도 큰 이점을 제공한다. 국토위성으로 불리는 차세대중형위성 1호(CAS500-1)는 2 m급 공간해상도를 제공하여 기존 중·저해상도 위성 자료보다 정밀한 수체 탐지가 가능하다. 본 연구에서는 CAS500-1 영상을 대상으로 Swin-Transformer 모델을 적용하여 수체 탐지 성능을 정량적으로 평가하고, 갈수기와 홍수기 사례를 통해 실제 수문학적 조건에서의 적용 가능성을 검토하였다. 혼동행렬 지표 기반 성능 분석 결과, Swin-Transformer는 다양한 규모의 저수지에서 IoU= 0.94-0.97, F1-score= 0.97-0.98을 기록하며 높은 정확도를 보였다. 사례 분석에서는 갈수기 섬진강과 임하호에서 수위 저하와 협소한 지류 조건이 Precision과 Recall 변동에 영향을 주었으며, 홍수기 금강 공주보에서는 구름 피복, 수위 상승, 탁수로 인해 경계부 탐지가 제한되는 현상이 나타났다. 이러한 결과는 CAS500-1 영상과 Transformer 기반 모델이 결합될 경우 안정적인 수체 탐지가 가능함을 보여주며, 동시에 극한 수문학적 상황에서는 추가적인 보완이 필요함을 드러낸다. 본 연구는 국토위성 자료의 활용 가능성을 확인하였으며, 향후 국내 수자원 관리와 가뭄·홍수 재해 대응을 위한 위성 기반 모니터링 체계 고도화에 기여할 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
Water body detection during drought and flood seasons using a Swin-Transformer with CAS500-1 satellite imagery
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of Korea Water Resources Association
Journal of Korea Water Resources Association
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of Korea Water Resources Association
Journal of Korea Water Resources Association